H + H–H H∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙ H∙∙∙∙∙∙H H∙∙∙∙∙∙H∙∙∙∙∙∙H
... This process can be generalized as: A + B-C [ABC] A-B + C Activated complex Transition state ...
... This process can be generalized as: A + B-C [ABC] A-B + C Activated complex Transition state ...
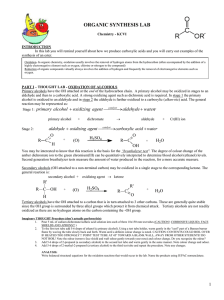
Secondary alcohols
... Polyethers solvate metal ions: crown ethers and ionophores. Crown ethers can render salts soluble in organic solvents by chelating the metal cations. This allows reagents such as KMnO4 to act as an oxidizing agent in the organic solvents. ...
... Polyethers solvate metal ions: crown ethers and ionophores. Crown ethers can render salts soluble in organic solvents by chelating the metal cations. This allows reagents such as KMnO4 to act as an oxidizing agent in the organic solvents. ...
21:3 Classifying Chemical Reactions
... to humans. Yeast is necessary to make leavened bread, beer, and cheese. It is rich in B vitamins; a form of yeast called brewer's yeast is used as a diet supplement. Yeasts are found in the soil, in water, on the surface of plants, and on the skin of humans and other animals. Like other fungi, yeast ...
... to humans. Yeast is necessary to make leavened bread, beer, and cheese. It is rich in B vitamins; a form of yeast called brewer's yeast is used as a diet supplement. Yeasts are found in the soil, in water, on the surface of plants, and on the skin of humans and other animals. Like other fungi, yeast ...
WRL0437.tmp
... Alkyl halides are most commonly synthesized from alcohols by replacing the hydroxyl group with a halide substituent. This is an example of nucleophilic aliphatic substitution, which is part of a very important group of reactions. The overall reaction is the same, but the mechanism varies depending o ...
... Alkyl halides are most commonly synthesized from alcohols by replacing the hydroxyl group with a halide substituent. This is an example of nucleophilic aliphatic substitution, which is part of a very important group of reactions. The overall reaction is the same, but the mechanism varies depending o ...
Ch. 2 Chemistry
... (b) An electron can move from one level to another only if the energy it gains or loses is exactly equal to the difference in energy between the two levels. Arrows indicate some of the step-wise changes in potential energy that are possible. Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Ben ...
... (b) An electron can move from one level to another only if the energy it gains or loses is exactly equal to the difference in energy between the two levels. Arrows indicate some of the step-wise changes in potential energy that are possible. Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Ben ...
Chapter 9
... • Follow the rules below: 1. Draw a skeleton structure joining atoms by single bond. 2. Count the number of valence electrons, including the charge. 3. Deduct 2 electrons for each bond from step 1. 4. Distribute remaining electrons to give all atoms an octet of electrons (Octet rule) ...
... • Follow the rules below: 1. Draw a skeleton structure joining atoms by single bond. 2. Count the number of valence electrons, including the charge. 3. Deduct 2 electrons for each bond from step 1. 4. Distribute remaining electrons to give all atoms an octet of electrons (Octet rule) ...
AP Chemistry
... When energy required to break bonds is greater than the energy released to form new bonds, then products are at a higher energy state than reactants (making the product bonds weaker than the reactant bonds) and energy of the system increases (+H), which is described as endothermic because the surro ...
... When energy required to break bonds is greater than the energy released to form new bonds, then products are at a higher energy state than reactants (making the product bonds weaker than the reactant bonds) and energy of the system increases (+H), which is described as endothermic because the surro ...
CP - Fundamentals
... materials and not only came up with the law of multiple proportions, but also a relative ratio of weights of the different elements. For example, they found that by assigning hydrogen, the lightest element, an atomic mass unit of one, the following approximate relative ratios of other elements were: ...
... materials and not only came up with the law of multiple proportions, but also a relative ratio of weights of the different elements. For example, they found that by assigning hydrogen, the lightest element, an atomic mass unit of one, the following approximate relative ratios of other elements were: ...
Exp 4_Properties of Alcohols
... Solubility- Alcohols with a small organic part such as methanol or ethanol are much like water , thus miscible with water. Alcohols with a larger organic radical are more like alkanes and less like water. Alcohols with more than two –OH groups are more water soluble than similar alcohols with only o ...
... Solubility- Alcohols with a small organic part such as methanol or ethanol are much like water , thus miscible with water. Alcohols with a larger organic radical are more like alkanes and less like water. Alcohols with more than two –OH groups are more water soluble than similar alcohols with only o ...
Chapter 3
... • Methionine, an amino acid used by organisms to make proteins, is represented below. Write the formula for methionine and calculate its molar mass. (red = O; gray = C; blue = N; yellow = S; ivory = H) ...
... • Methionine, an amino acid used by organisms to make proteins, is represented below. Write the formula for methionine and calculate its molar mass. (red = O; gray = C; blue = N; yellow = S; ivory = H) ...
Chemical Reaction and Matter Review
... information that it provides will vary slightly. Before we go about learning how to write chemical formulas, it is important that you clearly understand the difference between covalent (molecular) compounds and ionic compounds. Ionic compounds are composed of charged ions that are held together by e ...
... information that it provides will vary slightly. Before we go about learning how to write chemical formulas, it is important that you clearly understand the difference between covalent (molecular) compounds and ionic compounds. Ionic compounds are composed of charged ions that are held together by e ...
The Periodic Table HL Page 1 of 3 G. Galvin Name: Periodic Table
... • He switched some pairs of elements in his table so they would fit in the with the properties expected in that group • Transition metals did not have a separate block 4. Mosely: Arranged elements in order of increasing atomic number. Defn: The atomic number of an atom is the number of protons in th ...
... • He switched some pairs of elements in his table so they would fit in the with the properties expected in that group • Transition metals did not have a separate block 4. Mosely: Arranged elements in order of increasing atomic number. Defn: The atomic number of an atom is the number of protons in th ...
specimen
... 3 Chemists have developed models for bonding and structure. These models are used to explain different properties of metals and non-metals. (a) (i) Draw a labelled diagram to show the currently accepted model for metallic bonding. ...
... 3 Chemists have developed models for bonding and structure. These models are used to explain different properties of metals and non-metals. (a) (i) Draw a labelled diagram to show the currently accepted model for metallic bonding. ...
X012/13/02
... (i) When the reactants have been heated gently for about 15 to 20 minutes, the mixture is allowed to cool. Separation of the product is carried out by adding saturated sodium chloride solution to the reaction mixture and vigorously shaking them together for about a minute and allowing them to settl ...
... (i) When the reactants have been heated gently for about 15 to 20 minutes, the mixture is allowed to cool. Separation of the product is carried out by adding saturated sodium chloride solution to the reaction mixture and vigorously shaking them together for about a minute and allowing them to settl ...