Final Exam Review 2010 UbD
... What is the most reactive metal? __________ Why? _______________________________________ What is the most reactive non-metal? ______ Why? _______________________________________ ...
... What is the most reactive metal? __________ Why? _______________________________________ What is the most reactive non-metal? ______ Why? _______________________________________ ...
Quantitative chemistry 1
... Chemistry was a late developer as a physical science. Newton was working on the laws of physics more than a century before the work of the French chemist Antoine Lavoisier (1743–1794) brought chemistry into the modern age. Chemical reactions involve changes in smell, colour and texture and these are ...
... Chemistry was a late developer as a physical science. Newton was working on the laws of physics more than a century before the work of the French chemist Antoine Lavoisier (1743–1794) brought chemistry into the modern age. Chemical reactions involve changes in smell, colour and texture and these are ...
Reaction Rate Graphs C12-3
... and the fractions of those collisions that are effective. Reaction Rate is measured as a decrease in the concentration of reactants per unit time or an increase in the concentration of products per unit time. Units are: mol/L/s, however other units are possible if properties other than concentration ...
... and the fractions of those collisions that are effective. Reaction Rate is measured as a decrease in the concentration of reactants per unit time or an increase in the concentration of products per unit time. Units are: mol/L/s, however other units are possible if properties other than concentration ...
11-4 Infrared Spectroscopy
... Absorption of infrared light causes molecular vibrations. The infrared region is range of the electromagnetic spectrum just below visible light. Absorption of light of this wavelength causes vibrational excitation of the bonds in a molecule. Middle infrared light (λ~2.5-16.7 μm, or 600-4000 cm-1) ha ...
... Absorption of infrared light causes molecular vibrations. The infrared region is range of the electromagnetic spectrum just below visible light. Absorption of light of this wavelength causes vibrational excitation of the bonds in a molecule. Middle infrared light (λ~2.5-16.7 μm, or 600-4000 cm-1) ha ...
Lab 3. Chemical Reactions
... gained. All of the atoms used as reactants are converted into products. Every atom of every element must be accounted for since they are not destroyed or created, just rearranged and recombined into new things. The numbers (coefficients) before each formula in a chemical equation indicate how many u ...
... gained. All of the atoms used as reactants are converted into products. Every atom of every element must be accounted for since they are not destroyed or created, just rearranged and recombined into new things. The numbers (coefficients) before each formula in a chemical equation indicate how many u ...
n - TU Chemnitz
... α-Azido alcohols derived from aldehydes are not known in literature but postulated to be unstable intermediates in solvolysis reactions. The synthesis starting from α-azidoalkyl trimethylsilyl ethers,[1] geminal diazides[2] or α-azido ethers[3] only led to the corresponding aldehydes but not to α-az ...
... α-Azido alcohols derived from aldehydes are not known in literature but postulated to be unstable intermediates in solvolysis reactions. The synthesis starting from α-azidoalkyl trimethylsilyl ethers,[1] geminal diazides[2] or α-azido ethers[3] only led to the corresponding aldehydes but not to α-az ...
printable version
... stopped, in fact the products are still being made and used up-but at the same speed (rate). • Equilibrium is symbolized by the use of a double arrow ( ) or an equals sign (=) ...
... stopped, in fact the products are still being made and used up-but at the same speed (rate). • Equilibrium is symbolized by the use of a double arrow ( ) or an equals sign (=) ...
Equilibrium Electrochemistry
... themselves have different conc, either because they are gas electrodes operating at different pressures or because they are amalgams (sol in mercury) with ...
... themselves have different conc, either because they are gas electrodes operating at different pressures or because they are amalgams (sol in mercury) with ...
Chapter 6 - Chemistry
... Enthalpy of Reaction enthalpy of reaction - the change in enthalpy for a reaction at a given temperature and pressure - obtained by subtracting the enthalpy of the reactants from the enthalpy of the products H = Hfinal Hinitial - since you start from reactants and end with products, enthalpy of reac ...
... Enthalpy of Reaction enthalpy of reaction - the change in enthalpy for a reaction at a given temperature and pressure - obtained by subtracting the enthalpy of the reactants from the enthalpy of the products H = Hfinal Hinitial - since you start from reactants and end with products, enthalpy of reac ...
8. Molecular Geometry
... Bonds are polar when one atom is positive and the other negative. Molecules with many atoms have polarity, with one end positive, the other negatively charged. You can predict the polarity of the molecule by looking at the ends of the molecule to see if it has a positive end and a negative end. Lone ...
... Bonds are polar when one atom is positive and the other negative. Molecules with many atoms have polarity, with one end positive, the other negatively charged. You can predict the polarity of the molecule by looking at the ends of the molecule to see if it has a positive end and a negative end. Lone ...
5.4.2 Organic nitrogen compounds: amines, amides, amino acids
... Add about 2 mg of the sample to 1 mL of a solution of 0.2 g of ninhydrin (1,2,3indanetrione monohydrate) in 50 mL of water. The test mixture is heated to boiling for 15-20 sec; This reaction is important not only because it is a qualitative test, but also because it is the source of the absorbing ma ...
... Add about 2 mg of the sample to 1 mL of a solution of 0.2 g of ninhydrin (1,2,3indanetrione monohydrate) in 50 mL of water. The test mixture is heated to boiling for 15-20 sec; This reaction is important not only because it is a qualitative test, but also because it is the source of the absorbing ma ...
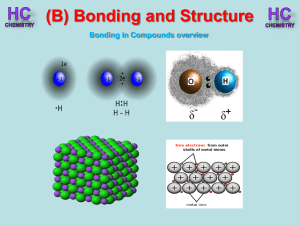
Lesson 1 - Bonding in compounds overview
... m.p.’s increase because the strength of the London dispersion forces increase with the increasing size of the molecule. So more Energy is needed to separate molecules. ...
... m.p.’s increase because the strength of the London dispersion forces increase with the increasing size of the molecule. So more Energy is needed to separate molecules. ...
Export To Word
... A. A working definition of matter is that it takes up space, has mass, and has measurable properties. Matter is comprised of atomic, subatomic, and elementary particles. B. Electrons are key to defining chemical and some physical properties, reactivity, and molecular structures. Repeating (periodic) ...
... A. A working definition of matter is that it takes up space, has mass, and has measurable properties. Matter is comprised of atomic, subatomic, and elementary particles. B. Electrons are key to defining chemical and some physical properties, reactivity, and molecular structures. Repeating (periodic) ...
CBS Reduction
... Recent paper 2016 • Sanderson and coworkers developed flow process for CBS asymmetric reduction of ketones , using chip-microreactors. • They used BH3 , (85% 2-MeTHF, 15% THF) and oxazaborolidine for reduction. • Under such reaction conditions, the reaction was complete in 10 minutes and alcohol wa ...
... Recent paper 2016 • Sanderson and coworkers developed flow process for CBS asymmetric reduction of ketones , using chip-microreactors. • They used BH3 , (85% 2-MeTHF, 15% THF) and oxazaborolidine for reduction. • Under such reaction conditions, the reaction was complete in 10 minutes and alcohol wa ...
Chapter Nine Organic Chemistry Hydrocarbon 1
... the compound is belonging to (alkanes chain) , The prefix of the name indicates the number of carbon atoms in the molecule . For example the prefix Meth = 1 , Eth = 2 , Prop = 3 , But = 4 , Pent =5 and so on . Alkanes form a homologous series. 19-Homologous series: It is a group of compounds that ha ...
... the compound is belonging to (alkanes chain) , The prefix of the name indicates the number of carbon atoms in the molecule . For example the prefix Meth = 1 , Eth = 2 , Prop = 3 , But = 4 , Pent =5 and so on . Alkanes form a homologous series. 19-Homologous series: It is a group of compounds that ha ...