JF Physical Chemistry 2010-2011. JF CH 1101: Introduction to
... a. What is the internal energy U and the enthalpy H of a system? Write down an expression for the First Law of Thermodynamics which relates the change in internal energy of a system to the work done on the system and the heat absorbed by the system. Hence derive a relationship between the change in ...
... a. What is the internal energy U and the enthalpy H of a system? Write down an expression for the First Law of Thermodynamics which relates the change in internal energy of a system to the work done on the system and the heat absorbed by the system. Hence derive a relationship between the change in ...
Chapter 1.1 –Chemistry is a Physical Science Chemistry is one of
... • Ice melting, water freezing, water evaporating, and steam condensing are all examples of a state change. • These are physical changes, not chemical. • Diluting a solution is a physical change, even if the color becomes fainter. ...
... • Ice melting, water freezing, water evaporating, and steam condensing are all examples of a state change. • These are physical changes, not chemical. • Diluting a solution is a physical change, even if the color becomes fainter. ...
Chemistry - Plymouth Public Schools
... Central Concept: Atoms bond with each other by transferring or sharing valence electrons to form compounds. MA CHM 4.1 Explain how atoms combine to form compounds through both ionic and covalent bonding. Predict chemical formulas based on the number of valence electrons. MA CHM 4.2 Draw Lewis dot st ...
... Central Concept: Atoms bond with each other by transferring or sharing valence electrons to form compounds. MA CHM 4.1 Explain how atoms combine to form compounds through both ionic and covalent bonding. Predict chemical formulas based on the number of valence electrons. MA CHM 4.2 Draw Lewis dot st ...
answers_ch03
... However, it would be wrong to conclude that all amino acids with hydrophobic side chains are located in transmembrane regions and all amino acids with polar side chains are located intracellularly or extracellularly. H2N ...
... However, it would be wrong to conclude that all amino acids with hydrophobic side chains are located in transmembrane regions and all amino acids with polar side chains are located intracellularly or extracellularly. H2N ...
Unit 8 Test Review
... the equation. Tip: Start by balancing an element that appears in only one reactant and product. Once one element is balanced, proceed to balance another, and another, until all elements are balanced. Balance chemical formulas by placing coefficients in front of them. Do not add subscripts, because t ...
... the equation. Tip: Start by balancing an element that appears in only one reactant and product. Once one element is balanced, proceed to balance another, and another, until all elements are balanced. Balance chemical formulas by placing coefficients in front of them. Do not add subscripts, because t ...
Infrared Spectroscopy and Mass Spectroscopy
... Take the Weight of ion, divide by 13 This answer is N, for (CH)N and any numerical remainder is added as H e.g.; 92 92/13 = 7 with remainder = 1; C7H8 weighs 92. This is our candidate formula Can evaluate other alternative candidate formulas possessing heteroatoms. For each member of the list below, ...
... Take the Weight of ion, divide by 13 This answer is N, for (CH)N and any numerical remainder is added as H e.g.; 92 92/13 = 7 with remainder = 1; C7H8 weighs 92. This is our candidate formula Can evaluate other alternative candidate formulas possessing heteroatoms. For each member of the list below, ...
Unit 4, Lesson #3 - Patterson Science
... The value of Keq is determined experimentally. Chemists allow reactions to occur at stated temperatures, until the system no longer changes. At this point, they measure the amounts of both the reactants and products. Just as chemists monitor changes in pH, colour, gas pressure or conductivity of sol ...
... The value of Keq is determined experimentally. Chemists allow reactions to occur at stated temperatures, until the system no longer changes. At this point, they measure the amounts of both the reactants and products. Just as chemists monitor changes in pH, colour, gas pressure or conductivity of sol ...
CHEM1102 Worksheet 7: Reactions of Carbonyls and Acid
... contains the hydride ion, H, and CH3CH2MgBr reacts as it contains the carbanion, CH3CH2) ...
... contains the hydride ion, H, and CH3CH2MgBr reacts as it contains the carbanion, CH3CH2) ...
Essentials of Coordination Chemistry Brochure
... centers, before discussing the variety of isomerism exhibited by coordination compounds, such as structural, geometrical and optical isomerism. As thermodynamics and kinetics provide a gateway to synthesis and reactivity of coordination compounds, the book then describes the determination of stabili ...
... centers, before discussing the variety of isomerism exhibited by coordination compounds, such as structural, geometrical and optical isomerism. As thermodynamics and kinetics provide a gateway to synthesis and reactivity of coordination compounds, the book then describes the determination of stabili ...
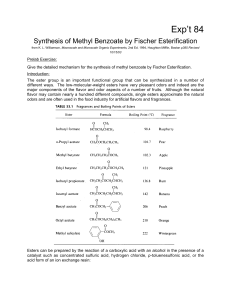
Synthesis of Methyl Benzoate by Fisher Esterification
... equilibrium. To upset the equilibrium we can, by Le Chatelier's principle, increase the concentration of either the alcohol or acid, as noted above. If either one is doubled, the theoretical yield increases to 85%. When one is tripled, it goes to 90%. But note that in the example cited the boiling p ...
... equilibrium. To upset the equilibrium we can, by Le Chatelier's principle, increase the concentration of either the alcohol or acid, as noted above. If either one is doubled, the theoretical yield increases to 85%. When one is tripled, it goes to 90%. But note that in the example cited the boiling p ...
無投影片標題
... • Identify the longest continuous carbon chain – It must contain any double or triple bond if present – Number from end nearest any substituent (alkyl or halogen) – If any multiple bonds are present, number from end closest to these. – The halogens are written as prefixes: fluoro- (F), chloro(Cl), b ...
... • Identify the longest continuous carbon chain – It must contain any double or triple bond if present – Number from end nearest any substituent (alkyl or halogen) – If any multiple bonds are present, number from end closest to these. – The halogens are written as prefixes: fluoro- (F), chloro(Cl), b ...
SCHLOSS RINGBERG
... We study in detail a recently developed first-principles approach, which employs an Independent Electron Surface Hopping (IESH) algorithm to model the nonadiabatic dynamics on a NewnsAnderson Hamiltonian derived from density functional theory. This approach has been successful when compared to previ ...
... We study in detail a recently developed first-principles approach, which employs an Independent Electron Surface Hopping (IESH) algorithm to model the nonadiabatic dynamics on a NewnsAnderson Hamiltonian derived from density functional theory. This approach has been successful when compared to previ ...
Thursday, January 22
... 2000 cm2 (1 significant figure) 2100 cm2 (2 significant figures) 2060 cm2 (3 significant figures) 2.10 x 103 cm2 (3 significant figures) 2060. cm2 (4 significant figures) ...
... 2000 cm2 (1 significant figure) 2100 cm2 (2 significant figures) 2060 cm2 (3 significant figures) 2.10 x 103 cm2 (3 significant figures) 2060. cm2 (4 significant figures) ...
Unit 1: Basic Chemistry for Biology QUIZ STUDY GUIDE Things to
... -You will see 12 of them on the quiz tomorrow. ...
... -You will see 12 of them on the quiz tomorrow. ...
The Equilibrium Constant
... Number of molecules on the left side: __________. Number of molecules on the right side: __________. The pressure of the system would decrease if it shifted to the ________________. Why? ...
... Number of molecules on the left side: __________. Number of molecules on the right side: __________. The pressure of the system would decrease if it shifted to the ________________. Why? ...
Organic_chemistry
... Homologous series • The ability of carbon atoms to form chains leads to the existence of a series of compounds that have the • same functional group (and hence similar chemical properties) and • only differ from each other by the presence of an additional carbon atom and its two associated hydroge ...
... Homologous series • The ability of carbon atoms to form chains leads to the existence of a series of compounds that have the • same functional group (and hence similar chemical properties) and • only differ from each other by the presence of an additional carbon atom and its two associated hydroge ...