Experiments
... Forms H-Bonds with water, but lower solubility than ethanol due to the arene ring. Formerly known as carbolic acid, the pH is only just less than 7 in water. The reason phenols are acidic and alcohols aren’t is because the lone pairs, in their interaction with the delocalised benzene ring, stabilise ...
... Forms H-Bonds with water, but lower solubility than ethanol due to the arene ring. Formerly known as carbolic acid, the pH is only just less than 7 in water. The reason phenols are acidic and alcohols aren’t is because the lone pairs, in their interaction with the delocalised benzene ring, stabilise ...
Today`s literature presentation = 2/5th trivia + 2/5th
... Heavy metals used in most of theses cause problems in removal, must be present <10 ppm levels. Many oxidizing agents are high energy species, giving rise to thermal hazards at scale. ...
... Heavy metals used in most of theses cause problems in removal, must be present <10 ppm levels. Many oxidizing agents are high energy species, giving rise to thermal hazards at scale. ...
Chapter 24 Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
... • Simple: hydrolyze to amino acids only. • Conjugated: bonded to a nonprotein group, such as sugar, nucleic acid, or lipid. • Fibrous: long, stringy filaments, insoluble in water, function as structure. • Globular: folded into spherical shape, function as enzymes, hormones, or transport proteins. ...
... • Simple: hydrolyze to amino acids only. • Conjugated: bonded to a nonprotein group, such as sugar, nucleic acid, or lipid. • Fibrous: long, stringy filaments, insoluble in water, function as structure. • Globular: folded into spherical shape, function as enzymes, hormones, or transport proteins. ...
The CPA EoS, proposed by Kontogeorgis et
... Association equations of state like CPA and SAFT usually model alcohols using the twosite association scheme i.e. the alcohol molecules are assumed to form linear oligomers. More specifically, these theories employ the so-called “2B” scheme (notation following Huang and Radosz10), which implies two ...
... Association equations of state like CPA and SAFT usually model alcohols using the twosite association scheme i.e. the alcohol molecules are assumed to form linear oligomers. More specifically, these theories employ the so-called “2B” scheme (notation following Huang and Radosz10), which implies two ...
Dehydration notes
... Dehydration of alcohols is … Acid catalyzed – creates a good leaving group (i.e. water) Carbocation intermediate formation. First two steps of the mechanism at the same as for SN1. Carbocation will rearrange for increased stability, if possible. 5. Protons can be removed from any adjacent position ...
... Dehydration of alcohols is … Acid catalyzed – creates a good leaving group (i.e. water) Carbocation intermediate formation. First two steps of the mechanism at the same as for SN1. Carbocation will rearrange for increased stability, if possible. 5. Protons can be removed from any adjacent position ...
Microsoft Word - Ethesis@nitr
... RESULT AND DISCUSSION The most important methods for preparing this class of heterocycles are the reaction between hydrazines with β-difunctional compounds25 and 1, 3-dipolar cycloadditions of diazo compounds onto triple bonds26. The former process, considered to be the best method for the preparat ...
... RESULT AND DISCUSSION The most important methods for preparing this class of heterocycles are the reaction between hydrazines with β-difunctional compounds25 and 1, 3-dipolar cycloadditions of diazo compounds onto triple bonds26. The former process, considered to be the best method for the preparat ...
Name - Clydebank High School
... b) Name a liquid which should be present in test tube Y in order to show that carbon dioxide was formed when the fuel burned. Explain what would happen to this liquid when carbon dioxide gas is bubbled though it. ...
... b) Name a liquid which should be present in test tube Y in order to show that carbon dioxide was formed when the fuel burned. Explain what would happen to this liquid when carbon dioxide gas is bubbled though it. ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... 24 What occurs when a magnesium atom becomes a magnesium ion? (1) Electrons are gained and the oxidation number increases. (2) Electrons are gained and the oxidation number decreases. (3) Electrons are lost and the oxidation number increases. (4) Electrons are lost and the oxidation number ...
... 24 What occurs when a magnesium atom becomes a magnesium ion? (1) Electrons are gained and the oxidation number increases. (2) Electrons are gained and the oxidation number decreases. (3) Electrons are lost and the oxidation number increases. (4) Electrons are lost and the oxidation number ...
Oxidation-Reduction Processes in Natural Waters
... negative free energy. (If light energy were included in photosynthesis, it too would of course be favorable as written. Also, hydrogen generation does occur under extremely reducing conditions because the concentrations of the reactants greatly exceed the concentration of products. As written in the ...
... negative free energy. (If light energy were included in photosynthesis, it too would of course be favorable as written. Also, hydrogen generation does occur under extremely reducing conditions because the concentrations of the reactants greatly exceed the concentration of products. As written in the ...
R E V I E W -- P R A C T I C E E X A
... c. decreasing atomic radii, increasing ionization energy, decreasing electronegativity values d. increasing atomic radii, increasing ionization energy and electronegativity values 79. The periodic law states that: a. The physical/chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their at ...
... c. decreasing atomic radii, increasing ionization energy, decreasing electronegativity values d. increasing atomic radii, increasing ionization energy and electronegativity values 79. The periodic law states that: a. The physical/chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their at ...
112 ex iii lec outline f 04
... 1. Lewis bases/ e- donor 2. uni, bi, tri, and polydentates 3. charged and neutral ...
... 1. Lewis bases/ e- donor 2. uni, bi, tri, and polydentates 3. charged and neutral ...
Review Package KCI 2017 Sem 1
... thermochemistry – the study of the energy changes that accompany physical or chemical changes of matter thermal energy – energy available from a substance as a result of the motion of its molecules chemical system – a set of reactants and products under study, usually represented by a chemical equat ...
... thermochemistry – the study of the energy changes that accompany physical or chemical changes of matter thermal energy – energy available from a substance as a result of the motion of its molecules chemical system – a set of reactants and products under study, usually represented by a chemical equat ...
Chemistry Mid-Term Review Sheet
... 41. List the number of orbitals and maximum number of electrons that are in the following sublevels: s, p, d, f, and g. 42. What is the standard electron configuration for zinc? 43. What element has an electron configuration of 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p2? 44. Draw a wave and label the crest, trough, ...
... 41. List the number of orbitals and maximum number of electrons that are in the following sublevels: s, p, d, f, and g. 42. What is the standard electron configuration for zinc? 43. What element has an electron configuration of 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p2? 44. Draw a wave and label the crest, trough, ...
BSC HS CHEMISTRY SEMESTER I to VI CBCEGS
... 1. Structure and Bonding 5 Hrs Hybridization, bond lengths and bond angles, bond energy, localized and delocalized chemical bond, van der Waals interactions, inclusion compounds, clatherates, change transfer complexes, resonance, hyperconjugation, aromaticity, inductive and field effects, hydrogen b ...
... 1. Structure and Bonding 5 Hrs Hybridization, bond lengths and bond angles, bond energy, localized and delocalized chemical bond, van der Waals interactions, inclusion compounds, clatherates, change transfer complexes, resonance, hyperconjugation, aromaticity, inductive and field effects, hydrogen b ...
AP CHEMISTRY – Source: 1999 AP Exam, Also Data Base of MC
... dissolved in water? (A) The solid has a low lattice energy. (B) As the solute dissolves, the temperature of the solution increases. (C) The resulting solution is ideal. (D) The solid is more soluble at higher temperatures. (E) the solid has a high energy of hydration. 14. Which of the following is l ...
... dissolved in water? (A) The solid has a low lattice energy. (B) As the solute dissolves, the temperature of the solution increases. (C) The resulting solution is ideal. (D) The solid is more soluble at higher temperatures. (E) the solid has a high energy of hydration. 14. Which of the following is l ...
AP Chap 2
... chemical bonding between atoms • Atoms with incomplete valence shells can share or transfer valence electrons with certain other atoms • These interactions usually result in atoms staying close together, held by attractions called chemical bonds ...
... chemical bonding between atoms • Atoms with incomplete valence shells can share or transfer valence electrons with certain other atoms • These interactions usually result in atoms staying close together, held by attractions called chemical bonds ...
Chemistry 12 is an intensive course, covering a great deal of
... Assignments will be given daily. Students are responsible for catching up and completing any missed assignments due to absences as soon as possible. Missed tests must be made up the next class present (within a one week period) or be given a mark of zero or omitted at the discretion of the teacher. ...
... Assignments will be given daily. Students are responsible for catching up and completing any missed assignments due to absences as soon as possible. Missed tests must be made up the next class present (within a one week period) or be given a mark of zero or omitted at the discretion of the teacher. ...
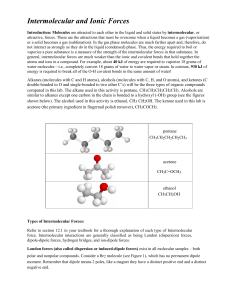
Intermolecular and Ionic Forces
... positively charged Na+ ion and (right) a negatively charged Cl- ion. This experiment focuses on the Intermolecular Forces that are broken when substances undergo phase (or physical) changes. During these processes, the chemical structure of a substance doesn’t change, only its phase changes. For exa ...
... positively charged Na+ ion and (right) a negatively charged Cl- ion. This experiment focuses on the Intermolecular Forces that are broken when substances undergo phase (or physical) changes. During these processes, the chemical structure of a substance doesn’t change, only its phase changes. For exa ...