MULTIPLY CHOICE QUESTIONS ON MEDICAL CHEMISTRY
... 1.9. Thermodynamic systems may be divided into following types according to the way of their interaction with the surroundings: А. physical and chemical B. one-, two- and threecomponents C. homogeneous and heterogeneous D. isolated, closed, open E. equilibrium and nonequilibrium 1.10. Chemical therm ...
... 1.9. Thermodynamic systems may be divided into following types according to the way of their interaction with the surroundings: А. physical and chemical B. one-, two- and threecomponents C. homogeneous and heterogeneous D. isolated, closed, open E. equilibrium and nonequilibrium 1.10. Chemical therm ...
Section 1.3 - The Student Room
... The formation of a compound from its elements may be an exothermic reaction (DHf negative) or an endothermic reaction (DHf positive). However, energy is liberated whenever a substance burns, so combustion reactions are always exothermic (DHc negative). ...
... The formation of a compound from its elements may be an exothermic reaction (DHf negative) or an endothermic reaction (DHf positive). However, energy is liberated whenever a substance burns, so combustion reactions are always exothermic (DHc negative). ...
AS Chemistry 1
... We now know that atoms can be split and that there are particles smaller than atoms, subatomic particles, electrons, protons and neutrons. You will need to know about these particles, which make up the different kinds of atoms. However, you must understand that chemistry is all about rearrangements ...
... We now know that atoms can be split and that there are particles smaller than atoms, subatomic particles, electrons, protons and neutrons. You will need to know about these particles, which make up the different kinds of atoms. However, you must understand that chemistry is all about rearrangements ...
Chemical Equilibrium - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
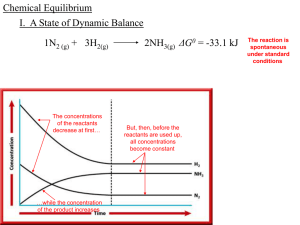
... I. A State of Dynamic Balance -when a ________ reaction results in the almost ________ complete conversion of ________ reactants to ________, products the 1N2 (g) + 3H2(g) 2NH3(g) ________ reaction is said to go to completion but _____ most _________ reactions __________, 1N2 (g) + 3H2(g) 2NH3(g) __ ...
... I. A State of Dynamic Balance -when a ________ reaction results in the almost ________ complete conversion of ________ reactants to ________, products the 1N2 (g) + 3H2(g) 2NH3(g) ________ reaction is said to go to completion but _____ most _________ reactions __________, 1N2 (g) + 3H2(g) 2NH3(g) __ ...
3.1 Life`s molecular diversity is based on the properties of carbon
... Skeletons may be unbranched or branched. H H H H C C C C H H H H H H ...
... Skeletons may be unbranched or branched. H H H H C C C C H H H H H H ...
Modulated 2:1 layer silicates: Review, systematics, and
... Presumably, tetrahedral in-plane rotation can readily compensatefor this type of sheetmisfit. Tak6uchi( 1965) discussedthe parameterin dioctahedralmicas,but of more interest for the discussion here is the case where D is positive and the octahedral sheet is larger than the tetrahedral sheet. The con ...
... Presumably, tetrahedral in-plane rotation can readily compensatefor this type of sheetmisfit. Tak6uchi( 1965) discussedthe parameterin dioctahedralmicas,but of more interest for the discussion here is the case where D is positive and the octahedral sheet is larger than the tetrahedral sheet. The con ...
Chapter 17 Amines
... the decomposition of aryl diazonium Chlorides to chloroarenes in the presence of copper (I) chloride in 1884. He also worked on the triphenylmethane dyes and the synthesis of isatin. Many years before, he had suggested Traugott Sandmeyer to Victor Meyer an impurity in commerical benzene was responsi ...
... the decomposition of aryl diazonium Chlorides to chloroarenes in the presence of copper (I) chloride in 1884. He also worked on the triphenylmethane dyes and the synthesis of isatin. Many years before, he had suggested Traugott Sandmeyer to Victor Meyer an impurity in commerical benzene was responsi ...
study guide spring 2012
... b. calculations. d. estimation. The actual yield of a chemical reaction is a. less than the theoretical yield. c. equal to the percentage yield. b. greater than the theoretical yield. d. greater than the percentage yield. For the reaction SO3 + H2O H2SO4, calculate the percentage yield if 500. g o ...
... b. calculations. d. estimation. The actual yield of a chemical reaction is a. less than the theoretical yield. c. equal to the percentage yield. b. greater than the theoretical yield. d. greater than the percentage yield. For the reaction SO3 + H2O H2SO4, calculate the percentage yield if 500. g o ...
Kinetic Modeling Of Methanol Synthesis From Carbon Monoxide
... using supports and promoters [2, 3]. Major kinetic studies for methanol synthesis were done as early as 1977, and, even recently, authors are trying to model the process kinetics [2]. Although reaction mechanisms for this process have been studied for decades now, there has been no agreement on one ...
... using supports and promoters [2, 3]. Major kinetic studies for methanol synthesis were done as early as 1977, and, even recently, authors are trying to model the process kinetics [2]. Although reaction mechanisms for this process have been studied for decades now, there has been no agreement on one ...
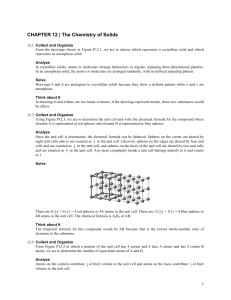
CHAPTER 12 | The Chemistry of Solids
... Because the melting point and boiling point of NaCl are higher than those of Na, ionic bonds are stronger than metallic bonds. ...
... Because the melting point and boiling point of NaCl are higher than those of Na, ionic bonds are stronger than metallic bonds. ...
Chapter 4 Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions
... • dilute solutions have a small amount of solute compared to solvent • concentrated solutions have a large amount of solute compared to solvent • quantitatively, the relative amount of solute in the solution is called the concentration Burns 4/e Chap 4 ...
... • dilute solutions have a small amount of solute compared to solvent • concentrated solutions have a large amount of solute compared to solvent • quantitatively, the relative amount of solute in the solution is called the concentration Burns 4/e Chap 4 ...
The story of V
... do not have left reactive groups in the matrix: no reactive end groups (-OH, -COOH), no unreacted carboncarbon double bonds (= unsaturated, (vinyl group = ethenyl group = unsaturated end-group)). Vinyl-Ester (VE) systems, like most resin systems, shrink during the curing (polymerisation). The volume ...
... do not have left reactive groups in the matrix: no reactive end groups (-OH, -COOH), no unreacted carboncarbon double bonds (= unsaturated, (vinyl group = ethenyl group = unsaturated end-group)). Vinyl-Ester (VE) systems, like most resin systems, shrink during the curing (polymerisation). The volume ...
Lab Manual (Eng. Medium)
... top (zero) calibration mark and then drained into a separate container until the calibration mark for the desired volume is reached. The remaining liquid is either discarded or returned to its original container. The maximum indicated capacity of some graduated pipettes is delivered by draining to a ...
... top (zero) calibration mark and then drained into a separate container until the calibration mark for the desired volume is reached. The remaining liquid is either discarded or returned to its original container. The maximum indicated capacity of some graduated pipettes is delivered by draining to a ...
Chapter 03 - KFUPM Faculty List
... from O2 and thus we must have 3 O2, so the balanced equation is C2H5OH + 3 O2 2 CO2 + 3 H2O: 2C + 6H + 7O both on the left and on the right, so it is ok. (NH4)2Cr2O7 Cr2O3 + H2O + N2 left: 7O + 2Cr + 8H + 2N; right: 4O + 2Cr + 2H + 2N, so 3O and 6H are missing on the right and correspond to 3 H2 ...
... from O2 and thus we must have 3 O2, so the balanced equation is C2H5OH + 3 O2 2 CO2 + 3 H2O: 2C + 6H + 7O both on the left and on the right, so it is ok. (NH4)2Cr2O7 Cr2O3 + H2O + N2 left: 7O + 2Cr + 8H + 2N; right: 4O + 2Cr + 2H + 2N, so 3O and 6H are missing on the right and correspond to 3 H2 ...