24 Analysis of ECG
... the amplitude and c) determine the duration. Analysis of segment interval and P -Q segment is measured from the end of P before Q. The interval is measured from the beginning of P to the Q. Analysis of the QRS complex includes: 1. Assessment of wave Q: a) measurement of its amplitude and compare it ...
... the amplitude and c) determine the duration. Analysis of segment interval and P -Q segment is measured from the end of P before Q. The interval is measured from the beginning of P to the Q. Analysis of the QRS complex includes: 1. Assessment of wave Q: a) measurement of its amplitude and compare it ...
Classification of Electrocardiogram (ECG) Waveforms for the
... After the implementing the Bandpass filter & differentiation this suppresses P and T waves. Squaring makes all the results positive and emphasising from large differences arising for the QRS complexes ...
... After the implementing the Bandpass filter & differentiation this suppresses P and T waves. Squaring makes all the results positive and emphasising from large differences arising for the QRS complexes ...
AV node block
... • Limb leads are I, II, III. So called because at one time subjects had to literally place arms and legs in buckets of salt water. • Each of the leads are bipolar; i.e., it requires two sensors on the skin to make a lead. • If one connects a line between two sensors, one has a vector. • There will b ...
... • Limb leads are I, II, III. So called because at one time subjects had to literally place arms and legs in buckets of salt water. • Each of the leads are bipolar; i.e., it requires two sensors on the skin to make a lead. • If one connects a line between two sensors, one has a vector. • There will b ...
Electro Cardio Gram “MCQ”
... b- Deflection record occurs only during complete depolarization or repolarization c- +ve wave occurs when depolarizing current approaches the +ve terminal electrode of the meter. d- -ve wave happens when repolarizing current approaches the +ve terminal electrode. ...
... b- Deflection record occurs only during complete depolarization or repolarization c- +ve wave occurs when depolarizing current approaches the +ve terminal electrode of the meter. d- -ve wave happens when repolarizing current approaches the +ve terminal electrode. ...
Canine electrocardiography
... may indicate heart enlargement (cardiomegaly). The ECG may assist the detection of abnormalities in electrolyte balance and metabolic disturbances and is also used to monitor the efficacy of cardiac drug therapy. It is used in isolation as a diagnostic aid, during anaesthesia as a monitoring tool an ...
... may indicate heart enlargement (cardiomegaly). The ECG may assist the detection of abnormalities in electrolyte balance and metabolic disturbances and is also used to monitor the efficacy of cardiac drug therapy. It is used in isolation as a diagnostic aid, during anaesthesia as a monitoring tool an ...
Cardiac Conduction
... AP’s from the SA node to the ventricles AV bundle: a pathway for the AP’s from the AV node to travel through the septum as it splits into R and L branches toward apex of heart Purkinje fibers: branches of the AV bundle that travel from the apex upward ...
... AP’s from the SA node to the ventricles AV bundle: a pathway for the AP’s from the AV node to travel through the septum as it splits into R and L branches toward apex of heart Purkinje fibers: branches of the AV bundle that travel from the apex upward ...
8 - ER EKG Overview
... method of separated boxes. Find a QRS complex that starts on a thick line. The best is to use the tip of the tallest wave on the QRS complex- R wave. This will be a starting point. As a second step, find the next QRS complex or any other spot- your end point. Then just count the thick lines in betwe ...
... method of separated boxes. Find a QRS complex that starts on a thick line. The best is to use the tip of the tallest wave on the QRS complex- R wave. This will be a starting point. As a second step, find the next QRS complex or any other spot- your end point. Then just count the thick lines in betwe ...
1. Describe the cardiac conduction system and an ECG. Tell how an
... there, the signal travels to the AV node, through the bundle of HIS, down the bundle branches, and through the Purkinje fibers, causing the ventricles to contract. This signal creates an electrical current that can be seen on a graph called an Electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG). Doctors use an ECG to mo ...
... there, the signal travels to the AV node, through the bundle of HIS, down the bundle branches, and through the Purkinje fibers, causing the ventricles to contract. This signal creates an electrical current that can be seen on a graph called an Electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG). Doctors use an ECG to mo ...
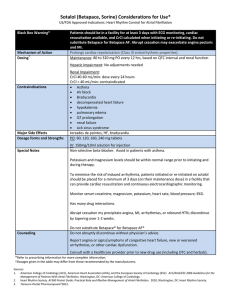
Sotalol Considerations for Use - American College of Cardiology
... Potassium and magnesium levels should be within normal range prior to initiating and during therapy. To minimize the risk of induced arrhythmia, patients initiated or re-initiated on sotalol should be placed for a minimum of 3 days (on their maintenance dose) in a facility that can provide cardiac r ...
... Potassium and magnesium levels should be within normal range prior to initiating and during therapy. To minimize the risk of induced arrhythmia, patients initiated or re-initiated on sotalol should be placed for a minimum of 3 days (on their maintenance dose) in a facility that can provide cardiac r ...
Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia
... increases the amount of blood and oxygen getting to areas that need it. People with CPVT have an abnormal response to adrenaline, which causes the heartbeat to become fast and irregular (ventricular tachycardia [VT]). If this rhythm lasts longer than a few seconds, the brain does not receive enough ...
... increases the amount of blood and oxygen getting to areas that need it. People with CPVT have an abnormal response to adrenaline, which causes the heartbeat to become fast and irregular (ventricular tachycardia [VT]). If this rhythm lasts longer than a few seconds, the brain does not receive enough ...
23 Electrpcardiography evaluation of heart work
... the amplitude and c) determine the duration. Analysis of segment interval and P -Q segment is measured from the end of P before Q. The interval is measured from the beginning of P to the Q. Analysis of the QRS complex includes: 1. Assessment of wave Q: a) measurement of its amplitude and compare it ...
... the amplitude and c) determine the duration. Analysis of segment interval and P -Q segment is measured from the end of P before Q. The interval is measured from the beginning of P to the Q. Analysis of the QRS complex includes: 1. Assessment of wave Q: a) measurement of its amplitude and compare it ...
Electrophysiology Part 2 Worksheet Answers
... 1. SA node- 60-100 Atrial foci- 60-80 AV junction- 40-60 Purkinje fibers- 20-40 (generally referred to as the ventricular rate). Through overdrivesuppression the SA node should be the heart’s pacemaker, causing these other foci to fire at the SA node’s rate (so you only see the SA node firing). 2. W ...
... 1. SA node- 60-100 Atrial foci- 60-80 AV junction- 40-60 Purkinje fibers- 20-40 (generally referred to as the ventricular rate). Through overdrivesuppression the SA node should be the heart’s pacemaker, causing these other foci to fire at the SA node’s rate (so you only see the SA node firing). 2. W ...
learning activity module - selu moodle
... electrical currents that spread throughout the entire body. By applying electrodes to various positions on the body and connecting these electrodes to an electrocardiographic apparatus, the EKG is recorded. Examples of the electrocardiograph include the standard EKG machine, bedside monitors, or tel ...
... electrical currents that spread throughout the entire body. By applying electrodes to various positions on the body and connecting these electrodes to an electrocardiographic apparatus, the EKG is recorded. Examples of the electrocardiograph include the standard EKG machine, bedside monitors, or tel ...
Ventricular Ectopy - Civil Aviation Authority
... a) >2% Ventricular Ectopic Beats (VEBs) recorded in 24hrs b) complex forms seen including non-sustained ventricular tachycardia c) long runs of bigeminy seen d) >20 VEBs per minute seen 2) By a cardiological specialist: 3) Exercise ECG - Bruce protocol and symptom limited. Requirements are at least ...
... a) >2% Ventricular Ectopic Beats (VEBs) recorded in 24hrs b) complex forms seen including non-sustained ventricular tachycardia c) long runs of bigeminy seen d) >20 VEBs per minute seen 2) By a cardiological specialist: 3) Exercise ECG - Bruce protocol and symptom limited. Requirements are at least ...
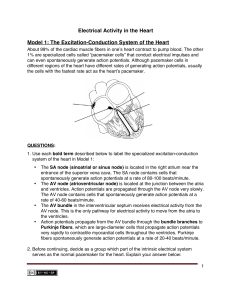
Electrical Activity in the Heart Model 1: The Excitation
... The SA node (sinoatrial or sinus node) is located in the right atrium near the entrance of the superior vena cava. The SA node contains cells that spontaneously generate action potentials at a rate of 80-100 beats/minute. The AV node (atrioventricular node) is located at the junction between the atr ...
... The SA node (sinoatrial or sinus node) is located in the right atrium near the entrance of the superior vena cava. The SA node contains cells that spontaneously generate action potentials at a rate of 80-100 beats/minute. The AV node (atrioventricular node) is located at the junction between the atr ...
Part 2 - BHS Education Resource
... RV strain pattern with RAD and RBBB are the next most common findings. Also look for inverted T-waves, occurring in inferior and anteroseptal simultaneously ...
... RV strain pattern with RAD and RBBB are the next most common findings. Also look for inverted T-waves, occurring in inferior and anteroseptal simultaneously ...
The Heart
... An echocardiogram is an ultrasound of the heart to visualize if the ______________ & _________________ (structures) are working correctly while an electrocardiogram indicates if the _______________________ system is sending the __________________ signal correctly. 2. During ventricular filling, the ...
... An echocardiogram is an ultrasound of the heart to visualize if the ______________ & _________________ (structures) are working correctly while an electrocardiogram indicates if the _______________________ system is sending the __________________ signal correctly. 2. During ventricular filling, the ...
Slide ()
... Positive signal-averaged electrocardiogram in a patient with sustained ventricular tachycardia. All three measured parameters are abnormal. Filtered QRS duration (DUR) is 136 ms, and the root-mean-square (RMS) voltage of the last 40 ms of the QS complex is 4.37 μV. LAS, low-amplitude signal. Reprodu ...
... Positive signal-averaged electrocardiogram in a patient with sustained ventricular tachycardia. All three measured parameters are abnormal. Filtered QRS duration (DUR) is 136 ms, and the root-mean-square (RMS) voltage of the last 40 ms of the QS complex is 4.37 μV. LAS, low-amplitude signal. Reprodu ...
MEDL-408V-001 Rene Maier
... 2. Identify and describe the electrical conduction system of the heart 3. Use cardiac testing procedure and technologies to assist in the assessment of heart function 4. Identify normal and abnormal heart rhythms to determine arrhythmias Course Objective The Electrocardiology component of the Medial ...
... 2. Identify and describe the electrical conduction system of the heart 3. Use cardiac testing procedure and technologies to assist in the assessment of heart function 4. Identify normal and abnormal heart rhythms to determine arrhythmias Course Objective The Electrocardiology component of the Medial ...
Electrocardiography
Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG*) is the process of recording the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time using electrodes placed on a patient's body. These electrodes detect the tiny electrical changes on the skin that arise from the heart muscle depolarizing during each heartbeat.In a conventional 12 lead ECG, ten electrodes are placed on the patient's limbs and on the surface of the chest. The overall magnitude of the heart's electrical potential is then measured from twelve different angles (""leads"") and is recorded over a period of time (usually 10 seconds). In this way, the overall magnitude and direction of the heart's electrical depolarization is captured at each moment throughout the cardiac cycle. The graph of voltage versus time produced by this noninvasive medical procedure is referred to as an electrocardiogram (abbreviated ECG or EKG).During each heartbeat, a healthy heart will have an orderly progression of depolarization that starts with pacemaker cells in the sinoatrial node, spreads out through the atrium, passes through the atrioventricular node down into the bundle of His and into the Purkinje fibers spreading down and to the left throughout the ventricles. This orderly pattern of depolarization gives rise to the characteristic ECG tracing. To the trained clinician, an ECG conveys a large amount of information about the structure of the heart and the function of its electrical conduction system. Among other things, an ECG can be used to measure the rate and rhythm of heartbeats, the size and position of the heart chambers, the presence of any damage to the heart's muscle cells or conduction system, the effects of cardiac drugs, and the function of implanted pacemakers.