Flecainide Considerations for Use
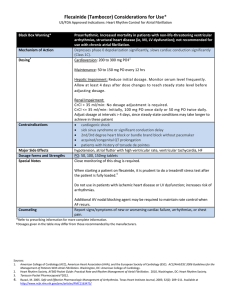
... hypotension, atrial flutter with high ventricular rate, ventricular tachycardia, HF PO: 50, 100, 150mg tablets Close monitoring of this drug is required. When starting a patient on flecainide, it is prudent to do a treadmill stress test after the patient is fully loaded.4 Do not use in patients with ...
... hypotension, atrial flutter with high ventricular rate, ventricular tachycardia, HF PO: 50, 100, 150mg tablets Close monitoring of this drug is required. When starting a patient on flecainide, it is prudent to do a treadmill stress test after the patient is fully loaded.4 Do not use in patients with ...
WPW Syndrome – ECG Manifestations
... The preexcitation in cases of right free wall AP is marked since the atrial end of the AP is close to the sinus node and so the atrial impulse reaches quickly from the sinus node to the AP as in the present case. In contrast, in left free wall pathways, the AP lies in the lateral mitral annular regi ...
... The preexcitation in cases of right free wall AP is marked since the atrial end of the AP is close to the sinus node and so the atrial impulse reaches quickly from the sinus node to the AP as in the present case. In contrast, in left free wall pathways, the AP lies in the lateral mitral annular regi ...
Cardio81-ECGPt2
... thus direction of axis is upward and toward right arm augmented limb lead L (+) electrode placed on left arm (-) input to ECG is the electrical sum of the left leg and right arm thus, direction of axis is upward and toward left arm augmented limb lead F (+) electrode placed on left leg ( ...
... thus direction of axis is upward and toward right arm augmented limb lead L (+) electrode placed on left arm (-) input to ECG is the electrical sum of the left leg and right arm thus, direction of axis is upward and toward left arm augmented limb lead F (+) electrode placed on left leg ( ...
Chapter04_Detailed_Answers
... True: Determining the heart rate helps you identify abnormal ECG rhythms. For this reason it is an important step in assessing the ECG. Begin by quickly checking the ECG monitor or tracing to see if the rate is slow, normal, or fast. Extremely slow or fast heart rates are a cause for ...
... True: Determining the heart rate helps you identify abnormal ECG rhythms. For this reason it is an important step in assessing the ECG. Begin by quickly checking the ECG monitor or tracing to see if the rate is slow, normal, or fast. Extremely slow or fast heart rates are a cause for ...
Analysis of normal electrocardiograms of Jamunapari goats
... and different species is reported especially for QRS complex [1,11]. Qs pattern of QRS complex predominated in I, II, aVL leads, R pattern in lead III and Qr in aVR and aVF among the goats studied (data not shown). The variability in the wave (form and amplitude) of the ECG may be attributed to dete ...
... and different species is reported especially for QRS complex [1,11]. Qs pattern of QRS complex predominated in I, II, aVL leads, R pattern in lead III and Qr in aVR and aVF among the goats studied (data not shown). The variability in the wave (form and amplitude) of the ECG may be attributed to dete ...
3Rd degree block
... Arrhythmia—telemetry strip—regular how fast—not diagnostic Leads: Lead II expect upward deflection of P wave, baseline MCL-I modified chest lead P upright and QRS is downward. EKG—1 mm tiny box—0.04 sec. 5 mm Big box—0.2 sec. ...
... Arrhythmia—telemetry strip—regular how fast—not diagnostic Leads: Lead II expect upward deflection of P wave, baseline MCL-I modified chest lead P upright and QRS is downward. EKG—1 mm tiny box—0.04 sec. 5 mm Big box—0.2 sec. ...
Heart Physiology Cardiac Conduction System Electrical System
... · recording of the electrical changes in the myocardium · P wave - atrial depolarization ...
... · recording of the electrical changes in the myocardium · P wave - atrial depolarization ...
Chapter 20- Transport Mechanisms- Revision
... 6. When the SL valves close after blood has left the ventricles what characteristic heart sound is heard through a stethoscope? 7. What causes abnormal heart sounds to be produced? 8. What is the other name for the pacemaker? 9. Where is the pacemaker located? 10. When the pacemaker sends an electri ...
... 6. When the SL valves close after blood has left the ventricles what characteristic heart sound is heard through a stethoscope? 7. What causes abnormal heart sounds to be produced? 8. What is the other name for the pacemaker? 9. Where is the pacemaker located? 10. When the pacemaker sends an electri ...
12 Lead ECG Interpretation
... • Views the surfaces of the left ventricle from 12 different angles ...
... • Views the surfaces of the left ventricle from 12 different angles ...
12 Lead ECG Interpretation - Learning
... • Views the surfaces of the left ventricle from 12 different angles ...
... • Views the surfaces of the left ventricle from 12 different angles ...
Schedule
... on the surface of the body, usually on two limbs. Different pairs of electrodes are used to record signals described as "Lead I", "Lead II" and "Lead III". For example, Lead I records the voltage at the Left Arm minus the voltage at the Right Arm. The 3 patterns are shown on the diagram. There is a ...
... on the surface of the body, usually on two limbs. Different pairs of electrodes are used to record signals described as "Lead I", "Lead II" and "Lead III". For example, Lead I records the voltage at the Left Arm minus the voltage at the Right Arm. The 3 patterns are shown on the diagram. There is a ...
ECG and the Heart*s Internal Conduction System
... contraction & explain why each is important to cardiac function. ...
... contraction & explain why each is important to cardiac function. ...
ECG and the Heart*s Internal Conduction System
... contraction & explain why each is important to cardiac function. ...
... contraction & explain why each is important to cardiac function. ...
ECG and the Heart’s Internal Conduction System
... contraction & explain why each is important to cardiac function. ...
... contraction & explain why each is important to cardiac function. ...
winter 16 - HeartCare Western Australia
... and are not related to ischaemia. Such ST changes are also commonly seen with PVCs, where ventricular depolarization is abnormal. In summary the hallmarks of WPW ECG are: Short PR interval, slurred Delta wave, broad QRS and T wave changes. These ECG features can be subtle if the degree of ventricula ...
... and are not related to ischaemia. Such ST changes are also commonly seen with PVCs, where ventricular depolarization is abnormal. In summary the hallmarks of WPW ECG are: Short PR interval, slurred Delta wave, broad QRS and T wave changes. These ECG features can be subtle if the degree of ventricula ...
EKG Self Study Guide - Phlebotomy Career Training
... -15 large boxes is a three second strip! -30 large boxes represents a six second strip! -For irregularly irregular rhythms, try to calculate rate with a decent time interval, preferably greater than a 3 second strip. ...
... -15 large boxes is a three second strip! -30 large boxes represents a six second strip! -For irregularly irregular rhythms, try to calculate rate with a decent time interval, preferably greater than a 3 second strip. ...
DRUG DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Ajmaline 1 mg/kg over 5
... The test should be monitored with a continuous ECG recording (a speed of 10 mms‐1 can be used throughout the test period, interposed with recordings at 25 or 50 mm‐1) and should be terminated when the diagnostic type 1 Brugada ECG develops, the ST segment in type 2 ECG increases by ≥2 mm, pr ...
... The test should be monitored with a continuous ECG recording (a speed of 10 mms‐1 can be used throughout the test period, interposed with recordings at 25 or 50 mm‐1) and should be terminated when the diagnostic type 1 Brugada ECG develops, the ST segment in type 2 ECG increases by ≥2 mm, pr ...
What tests should GPs be doing and how frequently? E.g. blood
... Tests are needed at three distinct time points in course of the patient journey. At the outset tests will be needed to make the diagnosis and look for an underlying cause. Further tests may be needed to assess the response to drugs or other interventions and beyond that to evaluate the patient’s evo ...
... Tests are needed at three distinct time points in course of the patient journey. At the outset tests will be needed to make the diagnosis and look for an underlying cause. Further tests may be needed to assess the response to drugs or other interventions and beyond that to evaluate the patient’s evo ...
USB Based Data Acquisition System for Heart Rate
... regulatory impulses that affect its rhythm • HRV analysis is an important parameter for assessment of the cardiovascular autonomic nervous system ...
... regulatory impulses that affect its rhythm • HRV analysis is an important parameter for assessment of the cardiovascular autonomic nervous system ...
Electrocardiography
Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG*) is the process of recording the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time using electrodes placed on a patient's body. These electrodes detect the tiny electrical changes on the skin that arise from the heart muscle depolarizing during each heartbeat.In a conventional 12 lead ECG, ten electrodes are placed on the patient's limbs and on the surface of the chest. The overall magnitude of the heart's electrical potential is then measured from twelve different angles (""leads"") and is recorded over a period of time (usually 10 seconds). In this way, the overall magnitude and direction of the heart's electrical depolarization is captured at each moment throughout the cardiac cycle. The graph of voltage versus time produced by this noninvasive medical procedure is referred to as an electrocardiogram (abbreviated ECG or EKG).During each heartbeat, a healthy heart will have an orderly progression of depolarization that starts with pacemaker cells in the sinoatrial node, spreads out through the atrium, passes through the atrioventricular node down into the bundle of His and into the Purkinje fibers spreading down and to the left throughout the ventricles. This orderly pattern of depolarization gives rise to the characteristic ECG tracing. To the trained clinician, an ECG conveys a large amount of information about the structure of the heart and the function of its electrical conduction system. Among other things, an ECG can be used to measure the rate and rhythm of heartbeats, the size and position of the heart chambers, the presence of any damage to the heart's muscle cells or conduction system, the effects of cardiac drugs, and the function of implanted pacemakers.























