Cardiac output and Venous Return
... Remember: sinus tachycardia is a response to physical or psychological stress, not a primary arrhythmia. ...
... Remember: sinus tachycardia is a response to physical or psychological stress, not a primary arrhythmia. ...
Electrocardiogram
... - receives an impulse from the SA Node - electrical signal continues down the specialized conducting system - Depolarizes: 15 – 20 x/ min - When the SA node is diseased, the AV node takes over - If a person had a heart rate of only 40 bpm, they either were a high aerobic athlete or they need a pace ...
... - receives an impulse from the SA Node - electrical signal continues down the specialized conducting system - Depolarizes: 15 – 20 x/ min - When the SA node is diseased, the AV node takes over - If a person had a heart rate of only 40 bpm, they either were a high aerobic athlete or they need a pace ...
Figure 1 - Grupo Akros
... Electrical interference: baseline with oscillations. Cause: poor ground connection; inappropriate cleaning of the skin; baseline oscillations; limbs movement: sudden irregularities of the baseline: children or neurological patients with involuntary movements, Parkinson’s tremor. It may resemble VT ( ...
... Electrical interference: baseline with oscillations. Cause: poor ground connection; inappropriate cleaning of the skin; baseline oscillations; limbs movement: sudden irregularities of the baseline: children or neurological patients with involuntary movements, Parkinson’s tremor. It may resemble VT ( ...
Sinus_Tachycardia
... Sinus tachycardia occurs when the sinus rhythm is faster than 100 beats per minute. The rhythm is similar to normal sinus rhythm with the exception that the RR interval is shorter, less than 0.6 seconds. P waves are present and regular and each P-wave is followed by a QRS complex in a ratio of 1:1. ...
... Sinus tachycardia occurs when the sinus rhythm is faster than 100 beats per minute. The rhythm is similar to normal sinus rhythm with the exception that the RR interval is shorter, less than 0.6 seconds. P waves are present and regular and each P-wave is followed by a QRS complex in a ratio of 1:1. ...
ECG quiz - Ipswich-Year2-Med-PBL-Gp-2
... V4 (but also V2 and V5) Inferior: changes in lead III and aVF Lateral infarction: changes in leads I, aVL, V5-6. ...
... V4 (but also V2 and V5) Inferior: changes in lead III and aVF Lateral infarction: changes in leads I, aVL, V5-6. ...
juicy j xanax - Romanian Ski Days
... CMV is good when specimens are properly stored. When positive urine specimens are stored at 4 C for 7 days, the rate of isolation decreases to only 93; it decreases to only 50 after 1 juicy j xanax of storage. ...
... CMV is good when specimens are properly stored. When positive urine specimens are stored at 4 C for 7 days, the rate of isolation decreases to only 93; it decreases to only 50 after 1 juicy j xanax of storage. ...
Progress Preentation
... It is also useful in the fact that the patient can conduct their normal activities while wearing the device. ...
... It is also useful in the fact that the patient can conduct their normal activities while wearing the device. ...
EKG Final Exam TEST A - 50 questions
... B. Normal sinus rhythm @60 bpm, left axis C. Normal sinus rhythm@ 75 bpm, normal axis D. Normal sinus rhythm @60 bpm, normal axis 36. Which of the following best describes the QRS morphology? A. Wide complex QRS with R-R’in V1 B. Narrow complex QRS with R-R’in V6 C. Wide complex QRS with R-R’ in V6 ...
... B. Normal sinus rhythm @60 bpm, left axis C. Normal sinus rhythm@ 75 bpm, normal axis D. Normal sinus rhythm @60 bpm, normal axis 36. Which of the following best describes the QRS morphology? A. Wide complex QRS with R-R’in V1 B. Narrow complex QRS with R-R’in V6 C. Wide complex QRS with R-R’ in V6 ...
Slide () - AccessAnesthesiology
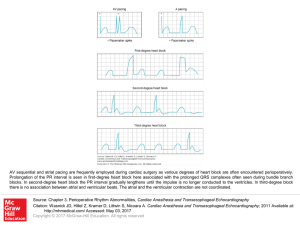
... AV sequential and atrial pacing are frequently employed during cardiac surgery as various degrees of heart block are often encountered perioperatively. Prolongation of the PR interval is seen in first-degree heart block here associated with the prolonged QRS complexes often seen during bundle branch ...
... AV sequential and atrial pacing are frequently employed during cardiac surgery as various degrees of heart block are often encountered perioperatively. Prolongation of the PR interval is seen in first-degree heart block here associated with the prolonged QRS complexes often seen during bundle branch ...
rhytmcen
... unlikely to have side effects. However, the underlying condition leading to AF is unchanged. The heart may go right back into the rhythm Chemical conversion is slower, but leads to conditions more likely to allow permanent conversion. However the drugs used (class 1a and 3) can all cause major dys ...
... unlikely to have side effects. However, the underlying condition leading to AF is unchanged. The heart may go right back into the rhythm Chemical conversion is slower, but leads to conditions more likely to allow permanent conversion. However the drugs used (class 1a and 3) can all cause major dys ...
Factsheet - Flecainide-Page 1
... the ventricles from too frequent conduction from an atrial rhythm to the ventricles. Flecainide usually produces very few side effects but has the potential to cause other abnormal heart rhythms, and can occasionally produce other transient symptoms such as visual disturbances, light headedness or ga ...
... the ventricles from too frequent conduction from an atrial rhythm to the ventricles. Flecainide usually produces very few side effects but has the potential to cause other abnormal heart rhythms, and can occasionally produce other transient symptoms such as visual disturbances, light headedness or ga ...
I. Atrial tachy
... activity modify impaired conduction that leads to arrhythmias. Conduction velocity depens on the size of the inward current during upstroke of the ...
... activity modify impaired conduction that leads to arrhythmias. Conduction velocity depens on the size of the inward current during upstroke of the ...
THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM, PRINCIPLES AND RECORDING
... - right arm (R): red - left arm (L): yellow - left foot (F): green - right foot: black – the grounding electrode The limb electrodes can be far down on the limbs avoiding bony prominences or close to the hips/shoulders, but they must be symmetrical. ...
... - right arm (R): red - left arm (L): yellow - left foot (F): green - right foot: black – the grounding electrode The limb electrodes can be far down on the limbs avoiding bony prominences or close to the hips/shoulders, but they must be symmetrical. ...
12-Lead EKG Chapter 5 Worksheet
... ____1. Leads V 3 and V 4 ____2. Where the end of the QRS complex makes a sudden sharp change in direction ____3. Significant EKG wave changes seen in 2 anatomically contiguous leads (see the same area of the heart. ____4. ST segment elevation curved upward; “frowny face.” ____5. Wave form that now a ...
... ____1. Leads V 3 and V 4 ____2. Where the end of the QRS complex makes a sudden sharp change in direction ____3. Significant EKG wave changes seen in 2 anatomically contiguous leads (see the same area of the heart. ____4. ST segment elevation curved upward; “frowny face.” ____5. Wave form that now a ...
ischemic changes in ecg and myocardial infarction learning objectives
... The branches of coronary arteries arising from the aortic root are distributed on the epicardial surface of the heart. These in turn provide intramural branches that supply the cardiac muscle. Myocardial ischemia (IHD) generally appears first and is more extensive in the sub-endocardial region since ...
... The branches of coronary arteries arising from the aortic root are distributed on the epicardial surface of the heart. These in turn provide intramural branches that supply the cardiac muscle. Myocardial ischemia (IHD) generally appears first and is more extensive in the sub-endocardial region since ...
2 Guided notes slides 31-end - Liberty Union High School District
... Electrical impulses from the SA node spread throughout both __________________and stimulate them to Contract. (pushing blood into the ventricles) Atrial ______________. The AV (Atrioventricular) node is located on the other side of right atrium near the atrioventricular valve, and serves as the gate ...
... Electrical impulses from the SA node spread throughout both __________________and stimulate them to Contract. (pushing blood into the ventricles) Atrial ______________. The AV (Atrioventricular) node is located on the other side of right atrium near the atrioventricular valve, and serves as the gate ...
Technosphere QT Study
... A centralized, independent ECG reading lab was used to read the ECGs with interpretation by a high-resolution manual on-screen caliper method with annotations to minimize inter-reader variability. The central ECG laboratory was blinded to subjects and their treatment. All treatments included a singl ...
... A centralized, independent ECG reading lab was used to read the ECGs with interpretation by a high-resolution manual on-screen caliper method with annotations to minimize inter-reader variability. The central ECG laboratory was blinded to subjects and their treatment. All treatments included a singl ...
20-1: The Heart - Jordan High School
... • Purpose of coronary circulation • Coronary arteries vs. coronary veins (functions, not names) • Read Spotlight Figure 20-10 (pg 682 – 683) on heart disease & heart attacks ...
... • Purpose of coronary circulation • Coronary arteries vs. coronary veins (functions, not names) • Read Spotlight Figure 20-10 (pg 682 – 683) on heart disease & heart attacks ...
ECG How to’s - CecchiniCuore
... •Lead I: causes right forelimb to become a negative pole and the left forelimb to become a positive pole. •Lead II: causes right forelimb to become negative and left rear limb to become positive •Lead III: the left hind limb becomes a positive pole and the left forelimb becomes a negative pole. •Wha ...
... •Lead I: causes right forelimb to become a negative pole and the left forelimb to become a positive pole. •Lead II: causes right forelimb to become negative and left rear limb to become positive •Lead III: the left hind limb becomes a positive pole and the left forelimb becomes a negative pole. •Wha ...
ECG Assignment
... Due by 8am Monday Feb 15th, hand it in on Friday in lecture if you can (completing this will also help for lab exam). Identify these ECG parts and their clinical significance on the sample ECG below: A) Wave Amplitude: mVolts or mm paper deflection (boxes) from ECG baseline to farthest part of the w ...
... Due by 8am Monday Feb 15th, hand it in on Friday in lecture if you can (completing this will also help for lab exam). Identify these ECG parts and their clinical significance on the sample ECG below: A) Wave Amplitude: mVolts or mm paper deflection (boxes) from ECG baseline to farthest part of the w ...
ECG Assignment
... Due by 5pm Friday Feb 10th, hand it in on Friday in lecture if you can (completing this will also help for lab exam). Identify these ECG parts and their clinical significance on the sample ECG below: A) Wave Amplitude: mVolts or mm paper deflection (boxes) from ECG baseline to farthest part of the w ...
... Due by 5pm Friday Feb 10th, hand it in on Friday in lecture if you can (completing this will also help for lab exam). Identify these ECG parts and their clinical significance on the sample ECG below: A) Wave Amplitude: mVolts or mm paper deflection (boxes) from ECG baseline to farthest part of the w ...
Electrocardiography
Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG*) is the process of recording the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time using electrodes placed on a patient's body. These electrodes detect the tiny electrical changes on the skin that arise from the heart muscle depolarizing during each heartbeat.In a conventional 12 lead ECG, ten electrodes are placed on the patient's limbs and on the surface of the chest. The overall magnitude of the heart's electrical potential is then measured from twelve different angles (""leads"") and is recorded over a period of time (usually 10 seconds). In this way, the overall magnitude and direction of the heart's electrical depolarization is captured at each moment throughout the cardiac cycle. The graph of voltage versus time produced by this noninvasive medical procedure is referred to as an electrocardiogram (abbreviated ECG or EKG).During each heartbeat, a healthy heart will have an orderly progression of depolarization that starts with pacemaker cells in the sinoatrial node, spreads out through the atrium, passes through the atrioventricular node down into the bundle of His and into the Purkinje fibers spreading down and to the left throughout the ventricles. This orderly pattern of depolarization gives rise to the characteristic ECG tracing. To the trained clinician, an ECG conveys a large amount of information about the structure of the heart and the function of its electrical conduction system. Among other things, an ECG can be used to measure the rate and rhythm of heartbeats, the size and position of the heart chambers, the presence of any damage to the heart's muscle cells or conduction system, the effects of cardiac drugs, and the function of implanted pacemakers.