Cardiovascular System – self test
... What is the normal range of CVP and what does it tell us? What are the main differences between veins and arteries? How would you define i) tachycardia? ii) bradycardia? What are some possible causes of tachycardia? Define the term “shock.” What is asystole? What is VT?, VF? What does capillary refi ...
... What is the normal range of CVP and what does it tell us? What are the main differences between veins and arteries? How would you define i) tachycardia? ii) bradycardia? What are some possible causes of tachycardia? Define the term “shock.” What is asystole? What is VT?, VF? What does capillary refi ...
ECG Recording and Interpretation
... Direction of vector is in positive direction So recording on ECG is also positive and it represent atrial depolarization It is known as P wave ...
... Direction of vector is in positive direction So recording on ECG is also positive and it represent atrial depolarization It is known as P wave ...
leads - WordPress.com
... • List the criteria for identification of right or left bundle branch blocks. • List the anatomically congruent leads associated with an inferior, lateral and anterior wall MI • Describe morphology of Q wave presence ...
... • List the criteria for identification of right or left bundle branch blocks. • List the anatomically congruent leads associated with an inferior, lateral and anterior wall MI • Describe morphology of Q wave presence ...
المحاضرة 02 كيفية رسم وقراءة التغيرات الكهربية للقلب 1
... The leads of the ECG machine detect the movement of the cardiac depolarisation and repolarisation waves as they spread through the atria and ventricles. Leads capable of detecting electrical signal are placed on the patient’s body and the different lead positions record the flow of current through t ...
... The leads of the ECG machine detect the movement of the cardiac depolarisation and repolarisation waves as they spread through the atria and ventricles. Leads capable of detecting electrical signal are placed on the patient’s body and the different lead positions record the flow of current through t ...
chifs-card-arrhythmia - Children`s Health Queensland
... The pumping action of the heart is powered by an electrical pathway that runs through the nerves in the walls of the heart. With each heartbeat, an electrical signal is generated and travels from the top of the heart to the bottom. The signal begins in a group of cells in the right atrium (the upper ...
... The pumping action of the heart is powered by an electrical pathway that runs through the nerves in the walls of the heart. With each heartbeat, an electrical signal is generated and travels from the top of the heart to the bottom. The signal begins in a group of cells in the right atrium (the upper ...
CJO~@§l13@j @YJ? ffOO@ OO§t6l.KtfT
... tricular myocardium. Prolongation of this interval beyond .20 seconds may reflect an AV conduction biock. The QRS complex reflects depolarization of the ventricular myocardium. This complex of deflections immediately precedes venlricular contraction. wherein blood is forced into the pulmonary trunk ...
... tricular myocardium. Prolongation of this interval beyond .20 seconds may reflect an AV conduction biock. The QRS complex reflects depolarization of the ventricular myocardium. This complex of deflections immediately precedes venlricular contraction. wherein blood is forced into the pulmonary trunk ...
Heart Study Aid 1) Pericardium Fibrous ______ Parietal layer
... 4) Blood flow through the heart: right atrium (via vena cava) ...
... 4) Blood flow through the heart: right atrium (via vena cava) ...
HSM-300 Heart Sounds Monitor
... heart valves opening and closing, into voltages which can be recorded and displayed. A piezo-electric sensor, mounted on the side of the HSM-300 picks up the vibrations that are created by the heart sounds. The piezo crystals on the sensor convert the changes in pressure created by the vibrations in ...
... heart valves opening and closing, into voltages which can be recorded and displayed. A piezo-electric sensor, mounted on the side of the HSM-300 picks up the vibrations that are created by the heart sounds. The piezo crystals on the sensor convert the changes in pressure created by the vibrations in ...
Atrial fibrillation
... impairment of AV-conduction in which NOT ALL impulses are being conducted to ventricles. 2nd degree AV-block type Mobitz-I (Wenckebach block) : progressive prolongation of PQ(R) in consecutive cycles with non-conducted subsequent P and no QRS. (Wenckebach periods). ...
... impairment of AV-conduction in which NOT ALL impulses are being conducted to ventricles. 2nd degree AV-block type Mobitz-I (Wenckebach block) : progressive prolongation of PQ(R) in consecutive cycles with non-conducted subsequent P and no QRS. (Wenckebach periods). ...
Final Poster - Research
... • Our system allows the users significantly more control over the simulation than their current system permits, enabling the system to be used to simulate multiple different situations. ...
... • Our system allows the users significantly more control over the simulation than their current system permits, enabling the system to be used to simulate multiple different situations. ...
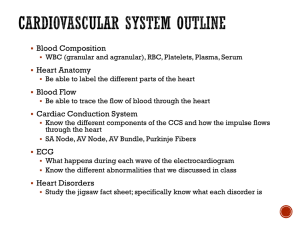
Cardiovascular System Outline 2014
... Trace the flow of electricity through the heart to conduct one ...
... Trace the flow of electricity through the heart to conduct one ...
1. ECG - Ping Pong - Karolinska Institutet
... electrode. The most common reference electrode is called Wilson’s electrode made by coupling the three limb leads together (Fig 3) designated by the abbreviation V. Bipolar recordings are made by recording the potential difference between any two electrodes. If these electrodes sit at the same dista ...
... electrode. The most common reference electrode is called Wilson’s electrode made by coupling the three limb leads together (Fig 3) designated by the abbreviation V. Bipolar recordings are made by recording the potential difference between any two electrodes. If these electrodes sit at the same dista ...
slide_3
... The P wave immediately precedes atrial contraction. The QRS complex immediately precedes ventricular contraction. The ventricles remain contracted until a few milliseconds after the end of the T repolarization wave. The atria remain contracted until the atria are repolarized, but an atrial repolariz ...
... The P wave immediately precedes atrial contraction. The QRS complex immediately precedes ventricular contraction. The ventricles remain contracted until a few milliseconds after the end of the T repolarization wave. The atria remain contracted until the atria are repolarized, but an atrial repolariz ...
Ventricular Ectopic Beats: How Many is Too Much?
... myocardial changes induced by physical training from those associated with an early stage of cardiomyopathy Such considerations appear of particular relevance in the presence of frequent and complex VA ...
... myocardial changes induced by physical training from those associated with an early stage of cardiomyopathy Such considerations appear of particular relevance in the presence of frequent and complex VA ...
MAC 400 brochure english
... standards. Through its collaboration with world-leading cardiologists, GE continues to develop ECG products to the highest standards of quality. With over 40 years‘ heritage in highly reliable ECG analysis and interpretation, you can trust the Marquette® 12SLTM program to support your clinical decis ...
... standards. Through its collaboration with world-leading cardiologists, GE continues to develop ECG products to the highest standards of quality. With over 40 years‘ heritage in highly reliable ECG analysis and interpretation, you can trust the Marquette® 12SLTM program to support your clinical decis ...
pseudo ecg myocardial infarction in young man with severe chornic
... acute coronary syndrome disease and on the risk of its major cardiac events. That assessment is based on the triplet: 1. Clinical setting, 2. ECG findings, 3. Biomarkers of myocardial lesion. Machado et al1, report the case of a 58-year-old male chagasic chronic cardiomyopathy (CCC) patient admitted ...
... acute coronary syndrome disease and on the risk of its major cardiac events. That assessment is based on the triplet: 1. Clinical setting, 2. ECG findings, 3. Biomarkers of myocardial lesion. Machado et al1, report the case of a 58-year-old male chagasic chronic cardiomyopathy (CCC) patient admitted ...
Ecg And Heart Blocks By Dr Amna Tahir
... Adams-Stokes (A-S) syndrome, is usually due to venticular standstill secondary to failure of the idioventricular pacemaker in advanced or complete heart block.1 Occasionally the A-S syndrome is due to extreme sinus bradycardia without heart block, e.g., rates below 20 per minute, with consequent ...
... Adams-Stokes (A-S) syndrome, is usually due to venticular standstill secondary to failure of the idioventricular pacemaker in advanced or complete heart block.1 Occasionally the A-S syndrome is due to extreme sinus bradycardia without heart block, e.g., rates below 20 per minute, with consequent ...
Underwriting Puzzler Answer (2/15/14, Vol. 5, #1)
... Yes, RVH strain pattern with ST depression/T wave inversion in the right precordial leads (V1-3) ...
... Yes, RVH strain pattern with ST depression/T wave inversion in the right precordial leads (V1-3) ...
Slide ()
... Electroanatomic voltage map of the left ventricle in a patient with sustained monomorphic ventricular tachycardia (VT) caused by an old anterior wall myocardial infarction. Right anterior oblique (RAO) and left anterior oblique (LAO) projections are shown. In contrast to the maps shown in Figs. 44-5 ...
... Electroanatomic voltage map of the left ventricle in a patient with sustained monomorphic ventricular tachycardia (VT) caused by an old anterior wall myocardial infarction. Right anterior oblique (RAO) and left anterior oblique (LAO) projections are shown. In contrast to the maps shown in Figs. 44-5 ...
FX-8222 - Fukuda
... The best-selling electrocardiograph with 145 mm wide paper has been developed from Fukuda Denshi’s long history over 70 years. The FX-8222 comes with a smarter design and easier operation. For more efficiency and agreeable ECG examination, functions and performance have been enriched and also the oper ...
... The best-selling electrocardiograph with 145 mm wide paper has been developed from Fukuda Denshi’s long history over 70 years. The FX-8222 comes with a smarter design and easier operation. For more efficiency and agreeable ECG examination, functions and performance have been enriched and also the oper ...
Folie 1
... Treatment of ACS on Board • Acute myocardial infarction is certainly the most feared event among CVDs. There is a chance of sudden death and long-term disability. • The prognosis of an AMI depends on the ability to manage acute complications such as life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias and, in the ...
... Treatment of ACS on Board • Acute myocardial infarction is certainly the most feared event among CVDs. There is a chance of sudden death and long-term disability. • The prognosis of an AMI depends on the ability to manage acute complications such as life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias and, in the ...
Electrocardiography
Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG*) is the process of recording the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time using electrodes placed on a patient's body. These electrodes detect the tiny electrical changes on the skin that arise from the heart muscle depolarizing during each heartbeat.In a conventional 12 lead ECG, ten electrodes are placed on the patient's limbs and on the surface of the chest. The overall magnitude of the heart's electrical potential is then measured from twelve different angles (""leads"") and is recorded over a period of time (usually 10 seconds). In this way, the overall magnitude and direction of the heart's electrical depolarization is captured at each moment throughout the cardiac cycle. The graph of voltage versus time produced by this noninvasive medical procedure is referred to as an electrocardiogram (abbreviated ECG or EKG).During each heartbeat, a healthy heart will have an orderly progression of depolarization that starts with pacemaker cells in the sinoatrial node, spreads out through the atrium, passes through the atrioventricular node down into the bundle of His and into the Purkinje fibers spreading down and to the left throughout the ventricles. This orderly pattern of depolarization gives rise to the characteristic ECG tracing. To the trained clinician, an ECG conveys a large amount of information about the structure of the heart and the function of its electrical conduction system. Among other things, an ECG can be used to measure the rate and rhythm of heartbeats, the size and position of the heart chambers, the presence of any damage to the heart's muscle cells or conduction system, the effects of cardiac drugs, and the function of implanted pacemakers.