Electrocardiogram (EKG, ECG) - Dr. Ray Winstead`s Front Page
... As the heart undergoes depolarization and repolarization, the electrical currents that are generated spread not only within the heart, but also throughout the body. This electrical activity generated by the heart can be measured by an array of electrodes placed on the body surface. The recorded trac ...
... As the heart undergoes depolarization and repolarization, the electrical currents that are generated spread not only within the heart, but also throughout the body. This electrical activity generated by the heart can be measured by an array of electrodes placed on the body surface. The recorded trac ...
Abstract_InaHRS2016_Ervan_Zuhri(1)
... Brugada syndrome (BS) is reported to be responsible for about 4% of all sudden deaths and about 20% of all sudden deaths in people without structural heart disease. BS is characterized by a coved-type ST-segment elevation ≥2 mm in the right precordial leads (BS type I) and a tendency to develop mali ...
... Brugada syndrome (BS) is reported to be responsible for about 4% of all sudden deaths and about 20% of all sudden deaths in people without structural heart disease. BS is characterized by a coved-type ST-segment elevation ≥2 mm in the right precordial leads (BS type I) and a tendency to develop mali ...
ECG Dysrhythmias
... ECG is used to represent the conduction of electrical impulses from the atria to the ventricles ECG is used to characterize rhythms and conduction abnormalities of the heart ...
... ECG is used to represent the conduction of electrical impulses from the atria to the ventricles ECG is used to characterize rhythms and conduction abnormalities of the heart ...
Treatment - Digoxin Immune Fab
... stage, associated with decreased AP duration. The QRS begins to widen and P wave amplitude decreases. PR interval prolongation can occur followed by second/third degree AV block. Complete loss of P waves can occur too. Moderate to severe hyperkalaemia occasionally induces ST elevations in the righ p ...
... stage, associated with decreased AP duration. The QRS begins to widen and P wave amplitude decreases. PR interval prolongation can occur followed by second/third degree AV block. Complete loss of P waves can occur too. Moderate to severe hyperkalaemia occasionally induces ST elevations in the righ p ...
CMA Practice Test Cardiopulmonary procedures
... ____ 25. Which of the following may cause an alternating current artifact? a. Patient movement b. Lead wires not following body contour c. A broken patient cable d. Parkinson’s disease ____ 26. Which of the following represents an ERROR in technique when running an electrocardiogram? a. Positioning ...
... ____ 25. Which of the following may cause an alternating current artifact? a. Patient movement b. Lead wires not following body contour c. A broken patient cable d. Parkinson’s disease ____ 26. Which of the following represents an ERROR in technique when running an electrocardiogram? a. Positioning ...
Introduction
... loop can exist when two or more electrical monitoring devices are connected to the patient. Another problem caused by the ground currents is related to the fact that, because the ground lead of the electrocardiograph usually runs alongside the signal leads, magnetic fields caused by the current in t ...
... loop can exist when two or more electrical monitoring devices are connected to the patient. Another problem caused by the ground currents is related to the fact that, because the ground lead of the electrocardiograph usually runs alongside the signal leads, magnetic fields caused by the current in t ...
Determining Axis and Axis Deviation on an ECG - e
... The average direction of electrical flow detected by a lead at any point in time is the lead's orientation angle. It can be represented by an arrow, or vector. The electrical axis is the average direction, or the mean vector, of all the waves of depolarization in the heart at a given point in time. ...
... The average direction of electrical flow detected by a lead at any point in time is the lead's orientation angle. It can be represented by an arrow, or vector. The electrical axis is the average direction, or the mean vector, of all the waves of depolarization in the heart at a given point in time. ...
Blood
... E. What causes the tracing or pattern on an ECG? F. What are the four diagnostic information can you get from an ECG? G. What is the normal pattern for an ECG? H. Systole is the __________ of the heart. I. Diastole is the __________ of the heart. J. What is the device on a blood pressure cuff used ...
... E. What causes the tracing or pattern on an ECG? F. What are the four diagnostic information can you get from an ECG? G. What is the normal pattern for an ECG? H. Systole is the __________ of the heart. I. Diastole is the __________ of the heart. J. What is the device on a blood pressure cuff used ...
Ch 14: Cardiovascular Physiology, Part 2
... Reflects electrical activity of whole heart not of single cell! EC fluid = “salt solution” (NaCl) good conductor of electricity to skin surface Signal very weak by time it gets to skin ...
... Reflects electrical activity of whole heart not of single cell! EC fluid = “salt solution” (NaCl) good conductor of electricity to skin surface Signal very weak by time it gets to skin ...
Intermittent Complete Right Bundle Branch Block
... II and III show no BBB at rates of 58-60/rain., while aVR again shows CRBBB at rate 65. The intermittency is also well seen in lead V2. Intermittent CRBB that is rate-related is an unimportant finding and usually carries no rating. On the other hand, the appearance of fixed (i.e., non-rate-related) ...
... II and III show no BBB at rates of 58-60/rain., while aVR again shows CRBBB at rate 65. The intermittency is also well seen in lead V2. Intermittent CRBB that is rate-related is an unimportant finding and usually carries no rating. On the other hand, the appearance of fixed (i.e., non-rate-related) ...
The Electrocardiogram (ECG)
... record of the electrical activity of the heart as measured externally from skin-contact electrodes placed on the body. • The ECG is considered a very powerful diagnostic tool by Cardiologists (medical doctors specializing in the human heart). • It identifies a time sequence of the contractions of th ...
... record of the electrical activity of the heart as measured externally from skin-contact electrodes placed on the body. • The ECG is considered a very powerful diagnostic tool by Cardiologists (medical doctors specializing in the human heart). • It identifies a time sequence of the contractions of th ...
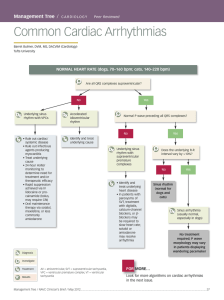
Common Cardiac Arrhythmias
... FOR MORE… Look for more algorithms on cardiac arrhythmias in the next issue. ...
... FOR MORE… Look for more algorithms on cardiac arrhythmias in the next issue. ...
Ablation
... • Complete 180° twist of QRS complexes in 10-12 beats is present. • Usually, a prolonged QT interval and pathological U waves are present, reflecting abnormal ventricular repolarization. The most consistent indicator of QT prolongation is a QT of 0.60 s or longer or a QTc (corrected for heart rate) ...
... • Complete 180° twist of QRS complexes in 10-12 beats is present. • Usually, a prolonged QT interval and pathological U waves are present, reflecting abnormal ventricular repolarization. The most consistent indicator of QT prolongation is a QT of 0.60 s or longer or a QTc (corrected for heart rate) ...
Mechanic work of the heart.
... The electrical currents generate lines of force similar to those produced by a magnet and are conducted through the salty water-like body fluids to the surface of the body and can be received, amplified and recorded by electrodes of an instrument – an electrocardiograph. The record obtained is an el ...
... The electrical currents generate lines of force similar to those produced by a magnet and are conducted through the salty water-like body fluids to the surface of the body and can be received, amplified and recorded by electrodes of an instrument – an electrocardiograph. The record obtained is an el ...
Title : Clinical aspects of cardiovascular physiology
... a. The electrical currents generated in the heart can be detected by recording electrodes on the skin. An electrocardiograph amplifies these signals and produces an electrocardiogram. It consists of deflections, segments and intervals. To the most important deflections belong b. The P wave- correspo ...
... a. The electrical currents generated in the heart can be detected by recording electrodes on the skin. An electrocardiograph amplifies these signals and produces an electrocardiogram. It consists of deflections, segments and intervals. To the most important deflections belong b. The P wave- correspo ...
Applied cardiology. Clinical aspects
... a. The electrical currents generated in the heart can be detected by recording electrodes on the skin. An electrocardiograph amplifies these signals and produces an electrocardiogram. It consists of deflections, segments and intervals. To the most important deflections belong b. The P wave- correspo ...
... a. The electrical currents generated in the heart can be detected by recording electrodes on the skin. An electrocardiograph amplifies these signals and produces an electrocardiogram. It consists of deflections, segments and intervals. To the most important deflections belong b. The P wave- correspo ...
BASIC CONCEPT OF ECG
... ECG Leads To measure the heart’s electrical activity a routine ECG normally employs 12 leads. The 12 conventional leads may be divided electrophysiologically into two groups, one being orientated in the frontal plane of the body, and the other in the horizontal plane. Bipolar standard leads I, II an ...
... ECG Leads To measure the heart’s electrical activity a routine ECG normally employs 12 leads. The 12 conventional leads may be divided electrophysiologically into two groups, one being orientated in the frontal plane of the body, and the other in the horizontal plane. Bipolar standard leads I, II an ...
ECG NOTES
... No P wave in front of abnormally wide QRS complexes (they will be greater than 0.1 second). It may be difficult to identify parts as being QRST. There will be more QRS complexes than P waves in the strip. ...
... No P wave in front of abnormally wide QRS complexes (they will be greater than 0.1 second). It may be difficult to identify parts as being QRST. There will be more QRS complexes than P waves in the strip. ...
Electrocardiography abd Pulmonary Function Testing
... 52-1 Describe the anatomy and physiology of the heart. 52-2 Explain the conduction system of the heart. 52-3 Describe the basic patterns of an electrocardiogram (ECG.) 52-4 Identify the components of an electrocardiograph and what each does. 52-5 Explain how to position the limb and precordial ...
... 52-1 Describe the anatomy and physiology of the heart. 52-2 Explain the conduction system of the heart. 52-3 Describe the basic patterns of an electrocardiogram (ECG.) 52-4 Identify the components of an electrocardiograph and what each does. 52-5 Explain how to position the limb and precordial ...
Chapter 20 I am - Mrs Smith`s Biology
... I am the three distinct waves that make up the normal ECG pattern Diastole ...
... I am the three distinct waves that make up the normal ECG pattern Diastole ...
Electrocardiography
Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG*) is the process of recording the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time using electrodes placed on a patient's body. These electrodes detect the tiny electrical changes on the skin that arise from the heart muscle depolarizing during each heartbeat.In a conventional 12 lead ECG, ten electrodes are placed on the patient's limbs and on the surface of the chest. The overall magnitude of the heart's electrical potential is then measured from twelve different angles (""leads"") and is recorded over a period of time (usually 10 seconds). In this way, the overall magnitude and direction of the heart's electrical depolarization is captured at each moment throughout the cardiac cycle. The graph of voltage versus time produced by this noninvasive medical procedure is referred to as an electrocardiogram (abbreviated ECG or EKG).During each heartbeat, a healthy heart will have an orderly progression of depolarization that starts with pacemaker cells in the sinoatrial node, spreads out through the atrium, passes through the atrioventricular node down into the bundle of His and into the Purkinje fibers spreading down and to the left throughout the ventricles. This orderly pattern of depolarization gives rise to the characteristic ECG tracing. To the trained clinician, an ECG conveys a large amount of information about the structure of the heart and the function of its electrical conduction system. Among other things, an ECG can be used to measure the rate and rhythm of heartbeats, the size and position of the heart chambers, the presence of any damage to the heart's muscle cells or conduction system, the effects of cardiac drugs, and the function of implanted pacemakers.