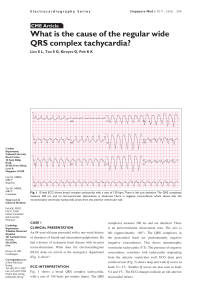
What is the cause of the regular wide QRS
... In general, the prognosis for VT is best predicted ...
... In general, the prognosis for VT is best predicted ...
Document
... based heart rate meter system is discussed in this project. The design considerations for this project are mostly influenced by the proposed users of the system. These users are medical practitioners in developing countries, who have very limited medical infrastructure. Hence, low cost, low power, p ...
... based heart rate meter system is discussed in this project. The design considerations for this project are mostly influenced by the proposed users of the system. These users are medical practitioners in developing countries, who have very limited medical infrastructure. Hence, low cost, low power, p ...
Atrial Fibrillation - Northwestern Medicine
... Moves along a standard path within the ventricles ...
... Moves along a standard path within the ventricles ...
Sudden Cardiac Death - LeadER Animal Specialty Hospital
... high-velocity jet of mitral regurgitation within the heart strikes the inside lining of the left atrium, very small tears in the muscle may occur over time. This can eventually lead to a small hole in the wall of the atrium, and bleeding may occur suddenly within the pericardial sac. If too much blo ...
... high-velocity jet of mitral regurgitation within the heart strikes the inside lining of the left atrium, very small tears in the muscle may occur over time. This can eventually lead to a small hole in the wall of the atrium, and bleeding may occur suddenly within the pericardial sac. If too much blo ...
CARDIOLOGY PATIENT PAGE Atrial Fibrillation
... AF. This can cause the patient to worry that they will have a heart attack or that their heart will stop. This rarely occurs, but urgent medical advice should be sought for any new cardiac symptom so that a precise diagnosis can be made. Those with persistent or permanent AF tend to notice palpitati ...
... AF. This can cause the patient to worry that they will have a heart attack or that their heart will stop. This rarely occurs, but urgent medical advice should be sought for any new cardiac symptom so that a precise diagnosis can be made. Those with persistent or permanent AF tend to notice palpitati ...
File - Joanna Weremijewicz
... charge and is measured using an ammeter. Solid conductive metals contain large population of free electrons, which are bound to the metal lattice and move around randomly due to thermal energy. When two terminals of a voltage source (battery) are connected via a metal wire, the free electrons of the ...
... charge and is measured using an ammeter. Solid conductive metals contain large population of free electrons, which are bound to the metal lattice and move around randomly due to thermal energy. When two terminals of a voltage source (battery) are connected via a metal wire, the free electrons of the ...
ECG tutorial
... your mouse. You will see that the depolarization time of the selected node is changed to the value where you set the knob. Also, the depolarization times within in the range of ...
... your mouse. You will see that the depolarization time of the selected node is changed to the value where you set the knob. Also, the depolarization times within in the range of ...
Pulmonary Vein Isolation - Bristol Sexual Health Centre
... may not be reversible. Less than 1 in 100 risk of needing a permanent pacemaker due to unintentional damage to the normal conduction system in your heart. 1-5 in 100 risk of bruising or swelling (false aneurysm) where the wires have been removed from the vein after the procedure. 40-50 in 100 risk o ...
... may not be reversible. Less than 1 in 100 risk of needing a permanent pacemaker due to unintentional damage to the normal conduction system in your heart. 1-5 in 100 risk of bruising or swelling (false aneurysm) where the wires have been removed from the vein after the procedure. 40-50 in 100 risk o ...
Heart Anatomy and Cardiac Muscle Cell Structure
... Fig 12.10: Pacemaker Cell Ion channels in pacemaker cells: see page 381 ...
... Fig 12.10: Pacemaker Cell Ion channels in pacemaker cells: see page 381 ...
Common ECG Lead Placement Errors. Part I: Limb lead Reversals
... mnemonic is one such tool that outlines the most frequent abnormal findings on ECG (Table 1).7 Of note to our cases, three common limb lead reversals are identified in the mnemonic; (1) reversal of the left arm and right arm electrodes, (2) reversal of the right leg electrode with either of the arms ...
... mnemonic is one such tool that outlines the most frequent abnormal findings on ECG (Table 1).7 Of note to our cases, three common limb lead reversals are identified in the mnemonic; (1) reversal of the left arm and right arm electrodes, (2) reversal of the right leg electrode with either of the arms ...
12 Lead EKG Interpretation
... is is in in fact fact actually actually rhythm rhythm strip strip interpretation. interpretation. ...
... is is in in fact fact actually actually rhythm rhythm strip strip interpretation. interpretation. ...
The Evolution of the Electrocardiogram in the Developing Head
... recently become known and therefore the classical rotational concept may have to be reviewed. Precordial Leads. Right sided predominance in the ventricles at birth and its subsidence later on is demonstrated by the developmental changes that occur in the precordial leads of the electrocardiogram. Th ...
... recently become known and therefore the classical rotational concept may have to be reviewed. Precordial Leads. Right sided predominance in the ventricles at birth and its subsidence later on is demonstrated by the developmental changes that occur in the precordial leads of the electrocardiogram. Th ...
The Evolution of ICD Therapy:
... – Transvenous lead is introduced into a vein and advanced into the heart Epicardial/Myocardial lead ...
... – Transvenous lead is introduced into a vein and advanced into the heart Epicardial/Myocardial lead ...
Sudden Death In the Structurally Normal Heart
... • ECG pattern only = Brugada pattern ECG but not Brugada Syndrome • Exclude other heart conditions ...
... • ECG pattern only = Brugada pattern ECG but not Brugada Syndrome • Exclude other heart conditions ...
sick sinus syndrome
... The heart of the dog or cat is composed of four chambers; the top two chambers are the right and left atria and the bottom two chambers are the right and left ventricles; heart valves are located between the right atrium and the right ventricle (tricuspid valve); between the left atrium and the le ...
... The heart of the dog or cat is composed of four chambers; the top two chambers are the right and left atria and the bottom two chambers are the right and left ventricles; heart valves are located between the right atrium and the right ventricle (tricuspid valve); between the left atrium and the le ...
Heart Physiology
... 1. A.k.a. the Bundle of His 2. Inferior part of the interatrial septum 3. The only electrical connection between the atria and ventricles a. No gap junctions between cells iv. Bundle branches 1. Right & left 2. Run along the interventricular septum v. Purkinje fibers 1. Complete the pathway through ...
... 1. A.k.a. the Bundle of His 2. Inferior part of the interatrial septum 3. The only electrical connection between the atria and ventricles a. No gap junctions between cells iv. Bundle branches 1. Right & left 2. Run along the interventricular septum v. Purkinje fibers 1. Complete the pathway through ...
Document
... • Large negative precordial T waves • Left axis deviation • No ECG finding is predictive of future events • Tall R and deep S waves weakly corelated with magnitude of LV hypertrophy ...
... • Large negative precordial T waves • Left axis deviation • No ECG finding is predictive of future events • Tall R and deep S waves weakly corelated with magnitude of LV hypertrophy ...
Training Effects
... This is where the heart gets bigger and stronger as there is an increase of ventricle size which allows them to fill with more blood during the diastolic phase of the cardiac cycle. This will result in bradycardia (decrease in resting heart rate) and an increase in stroke volume). Maximum Cardiac ...
... This is where the heart gets bigger and stronger as there is an increase of ventricle size which allows them to fill with more blood during the diastolic phase of the cardiac cycle. This will result in bradycardia (decrease in resting heart rate) and an increase in stroke volume). Maximum Cardiac ...
Cardiology for Psychiatrists Dr. Patrick Gladding, FRACP
... • Echo – Rheumatic valvular disease, moderate MR, LVEF 45-50% (old/new?) • N=1 trial with Global longitudinal strain ...
... • Echo – Rheumatic valvular disease, moderate MR, LVEF 45-50% (old/new?) • N=1 trial with Global longitudinal strain ...
Basics in ECG Interpretation (Part 1) – By Dr. Anidu Pathirana
... Electrodes are paired (one positive and other negative)to sense the change in voltage between them. Such a pair is ...
... Electrodes are paired (one positive and other negative)to sense the change in voltage between them. Such a pair is ...
DDD Pacemaker Implantation in A Patient with Congenitally
... which it was found that he had no inferior vena cava (IVC) draining into the right atrium (RA). Venogram showed venous drainage into the superior vena cava (SVC) from a dilated azygos vein (Fig A). Accordingly, the electrode was positioned in the right-sided ventricle via the azygos vein and SVC. Ec ...
... which it was found that he had no inferior vena cava (IVC) draining into the right atrium (RA). Venogram showed venous drainage into the superior vena cava (SVC) from a dilated azygos vein (Fig A). Accordingly, the electrode was positioned in the right-sided ventricle via the azygos vein and SVC. Ec ...
35 jmscr
... CCTGA, is a rare (less than 1% of all CHD) and complex heart defect [5]. It is characterized by AV and ventriculoatrial discordance. The aorta is located closer to the anterior and more to the left than the pulmonary artery. The AV valves follow their respective ventricles. Because of the displaceme ...
... CCTGA, is a rare (less than 1% of all CHD) and complex heart defect [5]. It is characterized by AV and ventriculoatrial discordance. The aorta is located closer to the anterior and more to the left than the pulmonary artery. The AV valves follow their respective ventricles. Because of the displaceme ...
Electrocardiography
Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG*) is the process of recording the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time using electrodes placed on a patient's body. These electrodes detect the tiny electrical changes on the skin that arise from the heart muscle depolarizing during each heartbeat.In a conventional 12 lead ECG, ten electrodes are placed on the patient's limbs and on the surface of the chest. The overall magnitude of the heart's electrical potential is then measured from twelve different angles (""leads"") and is recorded over a period of time (usually 10 seconds). In this way, the overall magnitude and direction of the heart's electrical depolarization is captured at each moment throughout the cardiac cycle. The graph of voltage versus time produced by this noninvasive medical procedure is referred to as an electrocardiogram (abbreviated ECG or EKG).During each heartbeat, a healthy heart will have an orderly progression of depolarization that starts with pacemaker cells in the sinoatrial node, spreads out through the atrium, passes through the atrioventricular node down into the bundle of His and into the Purkinje fibers spreading down and to the left throughout the ventricles. This orderly pattern of depolarization gives rise to the characteristic ECG tracing. To the trained clinician, an ECG conveys a large amount of information about the structure of the heart and the function of its electrical conduction system. Among other things, an ECG can be used to measure the rate and rhythm of heartbeats, the size and position of the heart chambers, the presence of any damage to the heart's muscle cells or conduction system, the effects of cardiac drugs, and the function of implanted pacemakers.























