* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Normal heart rate - Engineering World Health
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
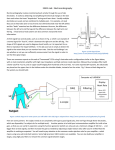
Electrocardiogram (ECG) PhillipN, (2007) Display device of a medical monitor as used in anesthesia [photograph]. Retrieved from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Monitoring_(medicine)#/media/File:Monitor_(medical).jpg Summary • • • • • Clinical Use • Specifications • History Principles of Operation • • Block Diagram Commercial Examples Preventive Maintenance Common Problems Test Procedures Typical Heart Rate Normal heart rate – 60 to 80 beats/min (5 liters/min) During Exercise – 120 to 160 beats/min (15 to 25 liters/min) Tachycardia - heart rate more than 100 beats/min (resting). Bradycardia - heart rate less than 60 beats/min (resting). Maximum Heart Rate = 220 – Age Athletes - Max HR = 160 to 220 Circulation Two separate pumps: Right Side moves deoxygenated blood to the lungs for oxygenation Left Side moves oxygenated blood to the body Which leads to two distinct circulatory systems: Pulmonary vessels to and from the lungs Systemic vessels to and from the rest of the body Vessels that move blood away from the heart are called arteries and vessels that return blood to the heart are called veins. Blausen Medical Communications, Inc. (2013), Cardiovascular System [image]. Retrieved fromhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Talk:Circulatory_system#/medi a/File:Blausen_0168_CardiovascularSystem.png The Nernst Equation EK= -61.5 log (Ki/Ko) Membrane potential depends of ions concentration: Na+, K+, ClIonic Current Animation: http://outreach.mcb.harvard.edu/animations/actionpotential.swf Cell Depolarization Villetakanen (Own work), Nerve Cell Depolarization [CC BY-SA 4.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)], via Wikimedia Commons Cell Depolarization • The cardiac pacemaker cell action potential: Silvia3 (2010), Pacemaker Action Potential [image]. Retrieved fromhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cardiac _action_potential#/media/File:Pacemaker _potential_annotated.gif Heart’s Anatomy Wikipedia. “Heart.” Wikipedia, p. 1-12. Retrieved from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heart Heart’s Anatomy Blood Flow in Heart: Four-chambered muscular vessel: Two Atria (left and right) Two Ventricles (left and right) Atrium: Filling chamber Pushes blood into ventricle Ventricle: Pressurization chamber Ejects blood into circulation Wikipedia. “Heart.” Wikipedia, p. 1-12. Retrieved from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heart Chambers separated by heart valves: One-way flow valves Four in total (tricuspid, pulmonary, mitral, aortic) Circulatory Pressures Yaddah (2006), View from the front [image]. Retrieved from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Circulatory_system#/media/File:Diagram_of_the_human_heart_(cropped).svg Clinical Use • Measures – Rate and regularity of heartbeats – Size and position of the chambers – Presence of any damage to the heart – Effects of drugs Specifications • Input: Voltage (biopotential) • Output : – Electronically (display) – Paper Principles of Operation Einthoven’s triangle Kychot (2009), Einthoven Triangle [image]. Rwtrieved from https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:ECG-Einthoven-triangle.svg ECG Signal ECGpedia.org, “Basics.” Wikipedia. Retrieved from: http://en.ecgpedia.org/wiki/Basics ECG Signal Openstax College. “The Cardiac Cycle, Fig. 40.14.” From the publication: Biology. Rice University: 2013, pgs. 1205 . ECG Signal • P – atrial depolarization • QRS complex – ventricular depolarization • T – ventricular repolarization Anthony Atkelski (2007), Schematic diagram of a normal sinus rhythm [image]. Retrieved from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electrocardiography#/media/File:SinusRhythmLabels.svg Signal of Heart Diseases Atrial Fibrillation Michael Rosengarten BEng, MD.McGill [CC BY-SA 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons Ventricular Fibrillation Jer5150 (Own work) [GFDL (http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html) or CC BY-SA 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons Sensor Electrodes Disposable Ag/AgCl surface electrode Malkin, Robert. Medical Instrumentation in the Developing World. Engineering World Health, 2006. Electrodes TYPES: • Disposable: $.05 to $.11 each • Reusable • Plate electrode Gel is important for a good contact with skin! Diagnostic ECG ECGpedia.org,.“ECG.Reference.Card.”.Wikipedia..Retrieved.from:. http://www.ecgpedia.org/A4/ECGpedia_on_1_A4En.pdf. Cooper, Justin and Alex Dahinten for EWH. “Electrocardiogram (ECG) Preventative Maintenance.” From the publication: Medical Equipment Troubleshooting Flowchart Handbook. Durham, NC: Engineering World Health, 2013. Wave Forms Npatchett (2015), Derivation of the limb leads [image]. Retrieved from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electrocardiography#/media/File:Limb_leads_of_EKG.png Wave Forms Malkin, Robert. Medical Instrumentation in the Developing World. Engineering World Health, 2006. Block Diagram for an analog ECG Amplifier VOUT = (V1 – V2)R2/R1 Amplifies a difference. VOUT = AC(V1 + V2) + AD(V1 – V2) AD:differential (signal) gain, AC:common mode (noise) gain. The ratio AD/AC (Common Mode Rejection Ratio – CMRR) is a very important parameter. Ideally CMRR →∞ Amplifier ECG amplifier (instrumentation amplifier) Input impedance >100 MΩ Range: 0.05–150 Hz Differential amplifiers with high gains (1000) CMMRs: 80 – 120 dB Differential Amplifier Arthur Ogawa (2014), Differential Amplifier with non-ideal on amp [image]. Retrieved from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Differential_amplifier#/media/File:Op-Amp_Differential_Amplifier_input_impedence_and_common_bias.svg Sampling The heartbeat rate itself is typically in the 60 to 200 beats per minute (1 Hz to 3.3 Hz) 4 Hz Range: 0.05–150 Hz 512 Hz sampling (2 ms) 10 samples at the QRS complex 12 bit resolution in analog-to-digital conversion 150 Hz ECGpedia.org,.“ECG.Reference.Card.”.Wikipedia..Retrieved.fro m:. http://www.ecgpedia.org/A4/ECGpedia_on_1_A4En.pdf. Sources of Interference AC interference: Cooper, Justin and Alex Dahinten for EWH. “Electrocardiogram (ECG) Preventative Maintenance.” From the publication: Medical Equipment Troubleshooting Flowchart Handbook. Durham, NC: Engineering World Health, 2013. Muscular interference Commercial Examples PhillipN, (2007) Display device of a medical monitor as used in anesthesia [photograph]. Retrieved from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Monitoring_(medicine)#/media/File:Monitor_ (medical).jpg DiverDave (2010), Bispectral index monitor indicating a nearly isoelectric pattern of electroencephalographic activity [photograph]. Retrieved from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bispectral_index#/media/File:BIS _Monitor-Burst_Suppression.JPG Commercial Examples Pollo (2010), Biphasic defibrillator [photograph]. Retrieved from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Defibrillation#/media/File:Defibrillator_monitor_Lifepak_12.jpg Defibrillators also have a wave II ECG signal Patient’s Safety • Leak currents –Sometimes ECG may be used in direct contact with the heart –Even a small current running through the lead wires can cause death (ventricular fibrillation) Defibrillators display ECG leads I, II & III Preventive Maintenance • Calibration • Clean reusable electrodes with alcohol and cloth • physical checks-lead wires, Welch cups (if used), case damage, connectors, keypad/switches • operation-paper speed, calibration pulse, trace/printout quality, front panel buttons and lights, battery life (if applicable) • cleaning • electrical patient safety Common Problems • Weak or poor signal: – – – – – – User error (may be no manual) User error in position of electrodes Loose wire Dry disposable electrode AC inference Interference from other machines Common Problems • No signal: – No contact at Electrode (fallen off, no gel, broken wire) – Saturated Amp (gain too high) – Problem with cable connection – Damaged amplifier due to defibrillator Common Problems • User error – Manual lack or disregard – Complex user interface – Older models may require to adjust the gain for proper rate reading – Stylus position if applicable Common Problems • User error – Other electrode devices (ESU, bioimpedance) may interfere with each other – Wrong brightness settings – no display trace Common Problems • User error – Wrong electrodes positioning Symptom: Signal is saturated or distorted by power line noise Rules, electrodes should not be placed : 1 - On scar tissue 2 - Over a lot of body hair 3 - Closer than 2 inches from each other may Common Problems • Lead wires and main cord damage • Lead interference Common Problems • AC interference – 50 Hz/60 Hz: Check for a filter switch Common Problems • AC interference Line fluctuation Procedure: Test the machine in another room Connect the equipment to a voltage regulator ligia diniz [CC BY 2.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0)], via Wikimedia Commons Common Problems • Movement Artifact –Check to see if the patient is cold or nervous (muscle tremors interfere) –Patient or nurse touching any metal or wall Common Problems • Lack of disposable electrodes and gel – One can make cheap electrodes with sewing snaps and tape – Gel can be replaced by an ion free solution (Ex: salt water) or hand cream, shampoo, etc… By Grkauls (Own work) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons Common Problems • Paper feed problems • No trace in the printer –Newer devices: clean the print head with alcohol gently with a fine soft clean cloth or Q-tip –Older devices (use alcohol to clean clotting in the ink tube) Test Procedures • Test on yourself • Check the heart rate alarms: – Lower than your own heart rate (upper rate alarm) – Higher than your own heart rate (lower rate alarm). • Check battery (if present) charging circuit Test Procedures • Electrode lead leakage. (connect 1 KΩ resistor from electrode wire to ground, measure voltage (< 50 mV) in resistor and compute current (should be < 50 µA) ECG Lead < 50 mV < 50 µA 1 KΩ David R. (Own work) [CC BY-SA 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0) or GFDL (http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html)], via Wikimedia Commons By Thiagoalmeidasa (Own work) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons PhillipN, (2007) Display device of a medical monitor as used in anesthesia [photograph]. Retrieved from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Monitoring_(medicine)#/media/Fil e:Monitor_(medical).jpg Troubleshooting Cooper, Justin and Alex Dahinten for EWH. “Electrocardiogram (ECG) Troubleshooting Flowchart.” From the publication: Medical Equipment Troubleshooting Flowchart Handbook. Durham, NC: Engineering World Health, 2013.