Today`s Objectives
... Located between the lungs and lower portion of mediastinum Two-thirds of its mass is on the left ...
... Located between the lungs and lower portion of mediastinum Two-thirds of its mass is on the left ...
Evolution of MI and Assessment of Prognosis with ECG Evidences
... AWMI predisposes to both stasis and clot formation. Patient prone to BBB, AVB, SVT, ventricular aneurysm, CHF, pulmonary edema, shock, LV clot and apical akinesis. Ventricular dysrhythmias are seen immediately after MI, and tend to be due to increased automaticity. Anterior MI’s are associated with ...
... AWMI predisposes to both stasis and clot formation. Patient prone to BBB, AVB, SVT, ventricular aneurysm, CHF, pulmonary edema, shock, LV clot and apical akinesis. Ventricular dysrhythmias are seen immediately after MI, and tend to be due to increased automaticity. Anterior MI’s are associated with ...
General Medical Officer (GMO) Manual: Clinical Section
... Holter monitor (24-hour rhythm strip) is helpful in relating symptoms to cardiac rhythm. In patients with less frequent symptoms, an event recorder or loop monitor can be provided and carried by the patient on a month by month basis. The signal-averaged electrocardiogram (ECG) is a new technique dev ...
... Holter monitor (24-hour rhythm strip) is helpful in relating symptoms to cardiac rhythm. In patients with less frequent symptoms, an event recorder or loop monitor can be provided and carried by the patient on a month by month basis. The signal-averaged electrocardiogram (ECG) is a new technique dev ...
Arrhythmias - The Brookside Associates
... Holter monitor (24-hour rhythm strip) is helpful in relating symptoms to cardiac rhythm. In patients with less frequent symptoms, an event recorder or loop monitor can be provided and carried by the patient on a month by month basis. The signal-averaged electrocardiogram (ECG) is a new technique dev ...
... Holter monitor (24-hour rhythm strip) is helpful in relating symptoms to cardiac rhythm. In patients with less frequent symptoms, an event recorder or loop monitor can be provided and carried by the patient on a month by month basis. The signal-averaged electrocardiogram (ECG) is a new technique dev ...
heart beats, blood pressure, heart rate
... WHY DO YOU SHOCK A PERSON TO GET THEIR HEART BEATING AGAIN? The heart generates its own electrical impulse The cardiac electrical signal controls: ...
... WHY DO YOU SHOCK A PERSON TO GET THEIR HEART BEATING AGAIN? The heart generates its own electrical impulse The cardiac electrical signal controls: ...
Slide ()
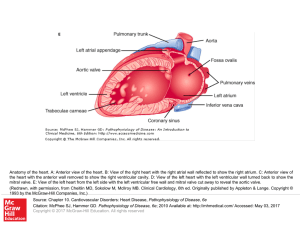
... Anatomy of the heart. A: Anterior view of the heart. B: View of the right heart with the right atrial wall reflected to show the right atrium. C: Anterior view of the heart with the anterior wall removed to show the right ventricular cavity. D: View of the left heart with the left ventricular wall t ...
... Anatomy of the heart. A: Anterior view of the heart. B: View of the right heart with the right atrial wall reflected to show the right atrium. C: Anterior view of the heart with the anterior wall removed to show the right ventricular cavity. D: View of the left heart with the left ventricular wall t ...
Exercise EKG
... stimulated sooner than others. The heart has three important anatomical and physiological properties that can account for this very reproducible event. 1) Automaticity - The cell membranes of most of the myocardial cells, especially pacemaker cells (such as the SA and AV nodes) , have an increased p ...
... stimulated sooner than others. The heart has three important anatomical and physiological properties that can account for this very reproducible event. 1) Automaticity - The cell membranes of most of the myocardial cells, especially pacemaker cells (such as the SA and AV nodes) , have an increased p ...
Sudden Death In the Structurally Normal Heart
... • ECG pattern only = Brugada pattern ECG but not Brugada Syndrome • Exclude other heart conditions ...
... • ECG pattern only = Brugada pattern ECG but not Brugada Syndrome • Exclude other heart conditions ...
Rhythm Recognition.
... Other Features to distinguish VT. Capture beats - normal looking beat. Occurs at exactly right time to be conducted through. VT continues immediately following. Fusion beats combination of sinus and ventricular beat. ...
... Other Features to distinguish VT. Capture beats - normal looking beat. Occurs at exactly right time to be conducted through. VT continues immediately following. Fusion beats combination of sinus and ventricular beat. ...
dysrhythmia cheat sheet
... cause decreased CO/hypertensi on Rapid discharges from SA node. More than 100bpm, regular rhythm, may cause decreased CO, MI From an ectopic atrial foci, usually with normal conduction. Irregular rhythm, impulse may be delayed or nonconducted, varies in rate From an ecotopic focus above the bundle o ...
... cause decreased CO/hypertensi on Rapid discharges from SA node. More than 100bpm, regular rhythm, may cause decreased CO, MI From an ectopic atrial foci, usually with normal conduction. Irregular rhythm, impulse may be delayed or nonconducted, varies in rate From an ecotopic focus above the bundle o ...
presentation source
... D. When the action potential produced by the SA node reaches other myocardial cells, they produce action potentials with a long plateau phase because of the slow, inward diffusion of Ca2+. E. The long action potential and long refractory period of myocardial cells allows the entire mass of cells to ...
... D. When the action potential produced by the SA node reaches other myocardial cells, they produce action potentials with a long plateau phase because of the slow, inward diffusion of Ca2+. E. The long action potential and long refractory period of myocardial cells allows the entire mass of cells to ...
Basic Dysrhythmia Interpretation
... heart-used as a diagnostic tool rather than a monitoring device Electrode-adhesive pad that contains conductive gel and designed to be attached to skin Leads-wires generally color coded. For the EKG to receive a clear picture of electrical impulses, there must be a positive, a negative and a ground. ...
... heart-used as a diagnostic tool rather than a monitoring device Electrode-adhesive pad that contains conductive gel and designed to be attached to skin Leads-wires generally color coded. For the EKG to receive a clear picture of electrical impulses, there must be a positive, a negative and a ground. ...
Arrhythmias - Llusurgery .org
... Arrhythmias Valerie Seabaugh MD Jerry L Pettis Memorial VA Hospital ...
... Arrhythmias Valerie Seabaugh MD Jerry L Pettis Memorial VA Hospital ...
THE HEART
... B. Modifying the basic rhythm 1. sympathetic nervous system increases rate and force of contractions 2. parasympathetic slows heart rate C. Electrocardiography - Graphing the electrical changes during heart activity. Typical ECG shows 3 distinguishable deflection waves (see figure 15.21) 1. P wave r ...
... B. Modifying the basic rhythm 1. sympathetic nervous system increases rate and force of contractions 2. parasympathetic slows heart rate C. Electrocardiography - Graphing the electrical changes during heart activity. Typical ECG shows 3 distinguishable deflection waves (see figure 15.21) 1. P wave r ...
Cardiac Stimulants and Depressants
... The Heart Main pacemakers of heart: Sinoatrial node: 60-100 bpm; primary ...
... The Heart Main pacemakers of heart: Sinoatrial node: 60-100 bpm; primary ...
document
... palpable beats; in many cardiac arrhythmias, the premature or abnormal beats do not produce an effective pumping action and are experienced as "skipped" beats). The simplest specific diagnostic test for assessment of heart rhythm is the electrocardiogram. A Holter monitor is an EKG recorded over a 2 ...
... palpable beats; in many cardiac arrhythmias, the premature or abnormal beats do not produce an effective pumping action and are experienced as "skipped" beats). The simplest specific diagnostic test for assessment of heart rhythm is the electrocardiogram. A Holter monitor is an EKG recorded over a 2 ...
Post-test to accompany acute coronary syndrome
... Post-test to accompany acute coronary syndrome: 1. What is the purpose of aspirin given early on in an acute coronary event? a) To decrease the chest pain b) To protect the lining of the stomach c) To help with headaches d) To decrease platelet aggregation 2. What does the ventricular tachycardia p ...
... Post-test to accompany acute coronary syndrome: 1. What is the purpose of aspirin given early on in an acute coronary event? a) To decrease the chest pain b) To protect the lining of the stomach c) To help with headaches d) To decrease platelet aggregation 2. What does the ventricular tachycardia p ...
Interpreting ECGs with Confidence: Part 2
... pacemaker cells that depolarize more slowly than the sinus node or AV node. Canine patients with third-degree AV block usually present with weakness, exercise intolerance, syncope, congestive heart failure, and/or dyspnea; some have experienced sudden death. Dogs reportedly may also be asymptomatic ...
... pacemaker cells that depolarize more slowly than the sinus node or AV node. Canine patients with third-degree AV block usually present with weakness, exercise intolerance, syncope, congestive heart failure, and/or dyspnea; some have experienced sudden death. Dogs reportedly may also be asymptomatic ...
Anesthesia Assistants Review Course
... We are writing to give you some assistance as you prepare for the upcoming AAOMS Anesthesia Assistant’s Review Course (AARC) which you will be attending on March 4-5, 2017. Over the years it has been our experience that the EKG/Dysrhythmia material is the most difficult for the attendees. Although s ...
... We are writing to give you some assistance as you prepare for the upcoming AAOMS Anesthesia Assistant’s Review Course (AARC) which you will be attending on March 4-5, 2017. Over the years it has been our experience that the EKG/Dysrhythmia material is the most difficult for the attendees. Although s ...
detection and identification of lbbb and rbbb rhythms in ecg waves
... RECTOR, RR Group of Institutions, Bangalore, India. ...
... RECTOR, RR Group of Institutions, Bangalore, India. ...
Life Threatening Arrhythmia and Management
... rhythms have an automatic focus, arising from cells that are spontaneously depolarizing at a rapid rate shock delivery to a heart with a rapid automatic focus may increase the rate of the tachyarrhythmia ...
... rhythms have an automatic focus, arising from cells that are spontaneously depolarizing at a rapid rate shock delivery to a heart with a rapid automatic focus may increase the rate of the tachyarrhythmia ...
Electrocardiography
Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG*) is the process of recording the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time using electrodes placed on a patient's body. These electrodes detect the tiny electrical changes on the skin that arise from the heart muscle depolarizing during each heartbeat.In a conventional 12 lead ECG, ten electrodes are placed on the patient's limbs and on the surface of the chest. The overall magnitude of the heart's electrical potential is then measured from twelve different angles (""leads"") and is recorded over a period of time (usually 10 seconds). In this way, the overall magnitude and direction of the heart's electrical depolarization is captured at each moment throughout the cardiac cycle. The graph of voltage versus time produced by this noninvasive medical procedure is referred to as an electrocardiogram (abbreviated ECG or EKG).During each heartbeat, a healthy heart will have an orderly progression of depolarization that starts with pacemaker cells in the sinoatrial node, spreads out through the atrium, passes through the atrioventricular node down into the bundle of His and into the Purkinje fibers spreading down and to the left throughout the ventricles. This orderly pattern of depolarization gives rise to the characteristic ECG tracing. To the trained clinician, an ECG conveys a large amount of information about the structure of the heart and the function of its electrical conduction system. Among other things, an ECG can be used to measure the rate and rhythm of heartbeats, the size and position of the heart chambers, the presence of any damage to the heart's muscle cells or conduction system, the effects of cardiac drugs, and the function of implanted pacemakers.