V3ch02a2 - SchultzMedic
... Transfer of pacemaker sites from the sinus node to other latent pacemaker sites in the atria and AV junction A variant of sinus dysrhythmia, a normal phenomenon in the very young or the aged, Ischemic heart disease, atrial dilation ...
... Transfer of pacemaker sites from the sinus node to other latent pacemaker sites in the atria and AV junction A variant of sinus dysrhythmia, a normal phenomenon in the very young or the aged, Ischemic heart disease, atrial dilation ...
The Human Heart
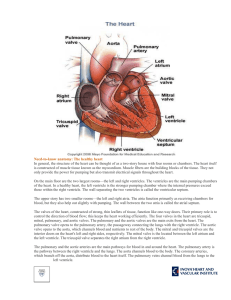
... In general, the structure of the heart can be thought of as a two-story house with four rooms or chambers. The heart itself is constructed of muscle tissue known as the myocardium. Muscle fibers are the building blocks of the tissue. They not only provide the power for pumping but also transmit elec ...
... In general, the structure of the heart can be thought of as a two-story house with four rooms or chambers. The heart itself is constructed of muscle tissue known as the myocardium. Muscle fibers are the building blocks of the tissue. They not only provide the power for pumping but also transmit elec ...
To Article
... as ST-deviation) occur in the frequency range below 100 Hz. However, smaller, high-frequency changes that are superimposed on the more prominent waveforms of the QRS complex provide additional information about the electrical conduction of the heart [5,6]. These changes can be studied by recording a ...
... as ST-deviation) occur in the frequency range below 100 Hz. However, smaller, high-frequency changes that are superimposed on the more prominent waveforms of the QRS complex provide additional information about the electrical conduction of the heart [5,6]. These changes can be studied by recording a ...
Pulmonary Embolism Mimicking Anteroseptal Acute Myocardial Infarction
... As stated previously, ST-segment elevation associated with PE is rare, and the direct relationship remains unclear. Anteroseptal ST-segment elevation was noted in one case2 involving a 42year-old woman with echocardiographic evidence of right ventricular pressure overload, which resolved after admin ...
... As stated previously, ST-segment elevation associated with PE is rare, and the direct relationship remains unclear. Anteroseptal ST-segment elevation was noted in one case2 involving a 42year-old woman with echocardiographic evidence of right ventricular pressure overload, which resolved after admin ...
The Measurement and Prediction of Maximum Heart Rate
... during the final stages of ventricle repolarization. The interval between two R points of the QRS complex is what is measured to determine one heart beat. HR is the number of heartbeats per minute. ...
... during the final stages of ventricle repolarization. The interval between two R points of the QRS complex is what is measured to determine one heart beat. HR is the number of heartbeats per minute. ...
(cardiac) output
... Cardiac electrical activity can be monitored by using ECG; a resting, ambulatory (Holter monitoring), continuous cardiac monitoring, or by telemetry Cardiac dysrhythmias are heartbeat disturbances (beat formation, beat conduction, myocardial response to beat). Dysrhythmias are classified by th ...
... Cardiac electrical activity can be monitored by using ECG; a resting, ambulatory (Holter monitoring), continuous cardiac monitoring, or by telemetry Cardiac dysrhythmias are heartbeat disturbances (beat formation, beat conduction, myocardial response to beat). Dysrhythmias are classified by th ...
Atrial Fibrillation - Weber State University
... The signals don’t travel normally and may spread throughout the atria in a rapid, disorganized way. Abnormal signals flood AV node with electrical impulses and as a result, the ventricles also begin to beat very fast, however, the AV node can’t conduct the signals to the ventricles as fast as they ...
... The signals don’t travel normally and may spread throughout the atria in a rapid, disorganized way. Abnormal signals flood AV node with electrical impulses and as a result, the ventricles also begin to beat very fast, however, the AV node can’t conduct the signals to the ventricles as fast as they ...
Frog Heart Physiology
... The frog heart, like other vertebrate hearts, is inherently rhythmic so that it continues to beat as long as the circulation is intact. The electrical signal which initiates the heart beat arises in pacemaker cells in the tissue of all the major chambers of the heart. The membrane potential of ...
... The frog heart, like other vertebrate hearts, is inherently rhythmic so that it continues to beat as long as the circulation is intact. The electrical signal which initiates the heart beat arises in pacemaker cells in the tissue of all the major chambers of the heart. The membrane potential of ...
Practical - ISpatula
... -This all happen at the cellular level, but in clinic practice, how do we measure this? ...
... -This all happen at the cellular level, but in clinic practice, how do we measure this? ...
UNIT –2 - E
... resonance and friction. Many writers are constructed so that the pen arm moves in an arc. This introduces both amplitude and timing errors which increase in nonlinear manner with the deflection and cause some distortion of he wave shape. 4. Explain the origin of electrocardiography Electrocardiograp ...
... resonance and friction. Many writers are constructed so that the pen arm moves in an arc. This introduces both amplitude and timing errors which increase in nonlinear manner with the deflection and cause some distortion of he wave shape. 4. Explain the origin of electrocardiography Electrocardiograp ...
Transient electrocardiographic abnormalities following blunt chest
... from cardiac causes is mandatory and requires prompt therapy. Patients with abnormal ECG findings and suspected BCI should be admitted and monitored, as they are at risk for developing complications. In general, it is suggested that monitoring of cardiac rhythm should be continued for up to 72 hours ...
... from cardiac causes is mandatory and requires prompt therapy. Patients with abnormal ECG findings and suspected BCI should be admitted and monitored, as they are at risk for developing complications. In general, it is suggested that monitoring of cardiac rhythm should be continued for up to 72 hours ...
Electrophysiology: Pacemakers, ICDs, and Ablation
... (ICDs) are small devices that can be implanted in the body to send electrical impulses to the heart muscle to maintain a suitable heart rate and rhythm. They are implanted during a minor surgical procedure. ...
... (ICDs) are small devices that can be implanted in the body to send electrical impulses to the heart muscle to maintain a suitable heart rate and rhythm. They are implanted during a minor surgical procedure. ...
Relationship between anthropometric measures and early
... http://www.biomedcentral.com/1756-0500/7/931 ...
... http://www.biomedcentral.com/1756-0500/7/931 ...
Week 10: Cardiovascular system
... Discuss what is meant by the cardiac cycle. What is blood pressure and what do measurements such as 120 / 80 mean in terms of physiology? Discuss the logic underlying blood pressure assessment. ...
... Discuss what is meant by the cardiac cycle. What is blood pressure and what do measurements such as 120 / 80 mean in terms of physiology? Discuss the logic underlying blood pressure assessment. ...
Some clinical indicators of heart disease during Pregnancy
... peripartum period 3) a decline in systemic vascular resistance, reaching a nadir in the 2nd trimester, and then rising to 20% below normal by late pregnancy 4) hyprcoagulability of special importance in women requiring anticoagulation in the non pregnant state ...
... peripartum period 3) a decline in systemic vascular resistance, reaching a nadir in the 2nd trimester, and then rising to 20% below normal by late pregnancy 4) hyprcoagulability of special importance in women requiring anticoagulation in the non pregnant state ...
Slide ()
... A. Prevalence of hypertension, defined as systolic blood pressure ≥140 mm Hg or diastolic blood pressure ≥90 mm Hg or current use of medication for purposes of treating high blood pressure. Data are based on National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) III (1988-1991). B. Incidence of a ...
... A. Prevalence of hypertension, defined as systolic blood pressure ≥140 mm Hg or diastolic blood pressure ≥90 mm Hg or current use of medication for purposes of treating high blood pressure. Data are based on National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) III (1988-1991). B. Incidence of a ...
Slide ()
... A. Prevalence of hypertension, defined as systolic blood pressure ≥140 mm Hg or diastolic blood pressure ≥90 mm Hg or current use of medication for purposes of treating high blood pressure. Data are based on National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) III (1988-1991). B. Incidence of a ...
... A. Prevalence of hypertension, defined as systolic blood pressure ≥140 mm Hg or diastolic blood pressure ≥90 mm Hg or current use of medication for purposes of treating high blood pressure. Data are based on National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) III (1988-1991). B. Incidence of a ...
Tako-tsubo cardiomyopathy
... inverted T-waves and a markedly prolonged QTinterval in both precordial and limb leads. The QTinterval prolongation often normalizes within two days, but the T-wave abnormalities can take weeks or even months to normalize [6,11]. ...
... inverted T-waves and a markedly prolonged QTinterval in both precordial and limb leads. The QTinterval prolongation often normalizes within two days, but the T-wave abnormalities can take weeks or even months to normalize [6,11]. ...
Atrial Fibrillation in Dogs
... Atrial fibrillation is a malfunction of the heart's electrical system. Instead of the electrical impulse originating from the SA node, the impulse originates from many different areas of the right atrium in an unorganized manner. This causes the atrial tissue to fibrillate (quiver). With the atrium ...
... Atrial fibrillation is a malfunction of the heart's electrical system. Instead of the electrical impulse originating from the SA node, the impulse originates from many different areas of the right atrium in an unorganized manner. This causes the atrial tissue to fibrillate (quiver). With the atrium ...
Contemporary Reviews in Cardiovascular Medicine
... adulthood. In patients who have not undergone surgery, ECG findings more directly relate to hemodynamic consequences than to specific location.26 Newly diagnosed congenital VSDs in adulthood are most often small and restrictive or large and unrestrictive with Eisenmenger’s complex (ie, flow reversal ...
... adulthood. In patients who have not undergone surgery, ECG findings more directly relate to hemodynamic consequences than to specific location.26 Newly diagnosed congenital VSDs in adulthood are most often small and restrictive or large and unrestrictive with Eisenmenger’s complex (ie, flow reversal ...
Electrocardiography
Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG*) is the process of recording the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time using electrodes placed on a patient's body. These electrodes detect the tiny electrical changes on the skin that arise from the heart muscle depolarizing during each heartbeat.In a conventional 12 lead ECG, ten electrodes are placed on the patient's limbs and on the surface of the chest. The overall magnitude of the heart's electrical potential is then measured from twelve different angles (""leads"") and is recorded over a period of time (usually 10 seconds). In this way, the overall magnitude and direction of the heart's electrical depolarization is captured at each moment throughout the cardiac cycle. The graph of voltage versus time produced by this noninvasive medical procedure is referred to as an electrocardiogram (abbreviated ECG or EKG).During each heartbeat, a healthy heart will have an orderly progression of depolarization that starts with pacemaker cells in the sinoatrial node, spreads out through the atrium, passes through the atrioventricular node down into the bundle of His and into the Purkinje fibers spreading down and to the left throughout the ventricles. This orderly pattern of depolarization gives rise to the characteristic ECG tracing. To the trained clinician, an ECG conveys a large amount of information about the structure of the heart and the function of its electrical conduction system. Among other things, an ECG can be used to measure the rate and rhythm of heartbeats, the size and position of the heart chambers, the presence of any damage to the heart's muscle cells or conduction system, the effects of cardiac drugs, and the function of implanted pacemakers.