Cardiac Conditions in Athletes - American College of Emergency
... Preparticipation Screening ‘Positive EKG’ P wave left atrial enlargement: negative portion of P wave V1 right atrial enlargement: peaked P wave II/III/V1 QRS Complex frontal plane axis deviation R>+120, L -30 to -90 increased voltage: amplitude of R or S wave >2mV in standard lead; S wave >3mV in V1 ...
... Preparticipation Screening ‘Positive EKG’ P wave left atrial enlargement: negative portion of P wave V1 right atrial enlargement: peaked P wave II/III/V1 QRS Complex frontal plane axis deviation R>+120, L -30 to -90 increased voltage: amplitude of R or S wave >2mV in standard lead; S wave >3mV in V1 ...
Echocardiography - Eastern Washington University
... b. lasers c. sound waves d. magnetic fields e. opaque dye Click here for answer(s) ...
... b. lasers c. sound waves d. magnetic fields e. opaque dye Click here for answer(s) ...
The Mammalian Heart
... Control of the Heartbeat a bundle of specialized muscle tissue in the wall of the right atrium stimulates the muscle fibres to contract and relax rhythmically Tissue is called the _______________________________ (S-A node or pacemaker - #1 on diagram) Recording the Heart Rate The S-A node gen ...
... Control of the Heartbeat a bundle of specialized muscle tissue in the wall of the right atrium stimulates the muscle fibres to contract and relax rhythmically Tissue is called the _______________________________ (S-A node or pacemaker - #1 on diagram) Recording the Heart Rate The S-A node gen ...
management of patients with acute heart failure and atrial fibrillation
... disease, pulmonary disease or infection may also require specific therapy.6 The Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure Trial has shown no benefit associated with a rhythm control strategy.7 However, in patients with new- or recent-onset AF, an attempt at cardioversion and drug therapy is reasonable, ...
... disease, pulmonary disease or infection may also require specific therapy.6 The Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure Trial has shown no benefit associated with a rhythm control strategy.7 However, in patients with new- or recent-onset AF, an attempt at cardioversion and drug therapy is reasonable, ...
G06: Heart (Weyrich)
... 2. Serous pericardium (internal sac) (parietal layer– lines the inner surface of the fibrous) (visceral layer [epicardium] – adheres to the heart) ...
... 2. Serous pericardium (internal sac) (parietal layer– lines the inner surface of the fibrous) (visceral layer [epicardium] – adheres to the heart) ...
Blood Vessels - cloudfront.net
... inserted into the artery and a balloon is used to stretch the walls open. A bypass can also treat clogged arteries, a vein is used to replace a clogged artery. Coronary bypass refers to a procedure where the coronary artery is bypassed to supply blood to the heart. (The phrase “quadruple bypass” mea ...
... inserted into the artery and a balloon is used to stretch the walls open. A bypass can also treat clogged arteries, a vein is used to replace a clogged artery. Coronary bypass refers to a procedure where the coronary artery is bypassed to supply blood to the heart. (The phrase “quadruple bypass” mea ...
Cardiovascular System
... Why Get an EKG • Unexplained chest pain, or reduced blood flow to the heart (ischemia), shortness of breath, dizziness, fainting, or rapid and irregular heartbeats (palpitations). • Identify ventricle hypertrophy and other changes of the myocardium. • Check how well mechanical devices, such as pace ...
... Why Get an EKG • Unexplained chest pain, or reduced blood flow to the heart (ischemia), shortness of breath, dizziness, fainting, or rapid and irregular heartbeats (palpitations). • Identify ventricle hypertrophy and other changes of the myocardium. • Check how well mechanical devices, such as pace ...
DOC - Gericareonline.net
... takes a motion picture of the inside of the heart as it pumps. It is commonly used for patients with heart failure. It tells the doctor more about how the person’s heart is working. Echocardiography is very safe. It does not use x-rays, and you do not need an injection. This test uses the same metho ...
... takes a motion picture of the inside of the heart as it pumps. It is commonly used for patients with heart failure. It tells the doctor more about how the person’s heart is working. Echocardiography is very safe. It does not use x-rays, and you do not need an injection. This test uses the same metho ...
presentation source
... The P Waves Appear & Are Not Connected To Any QRS Complex The QRS Are Abherrantly Wide Ultimate Ventricular Rate Is Often Very Bradycardic ...
... The P Waves Appear & Are Not Connected To Any QRS Complex The QRS Are Abherrantly Wide Ultimate Ventricular Rate Is Often Very Bradycardic ...
CARDIOVASCULAR INTERACTIONS
... This learning package, for both teachers and students, consists of a Lab Book, a Model, and an Information File. The Lab Book is an interactive tutorial for exploring the relative influences of parameter changes on the cardiovascular system. Consequences of heart failure, hemorrhage, and exercise ca ...
... This learning package, for both teachers and students, consists of a Lab Book, a Model, and an Information File. The Lab Book is an interactive tutorial for exploring the relative influences of parameter changes on the cardiovascular system. Consequences of heart failure, hemorrhage, and exercise ca ...
emergency Drugs lab 7
... dilation, cycloplegia, and photophobia - sinus tachycardia (at higher doses), bradycardia (initially or at very low doses), hypertension, hypotension, arrhythmias (ectopic complexes), and circulatory failure. ...
... dilation, cycloplegia, and photophobia - sinus tachycardia (at higher doses), bradycardia (initially or at very low doses), hypertension, hypotension, arrhythmias (ectopic complexes), and circulatory failure. ...
Left Axis Deviation in Inferior Infarction
... in group B of the present series. (2) The second example (Fig 4 ) is that of a patient admitted to the coronary care unit for an episode of acute inferior wall infarction. Aberrantly conducted ventricular beats were obtained in this case by introduction of artificially induced atrial premature beats ...
... in group B of the present series. (2) The second example (Fig 4 ) is that of a patient admitted to the coronary care unit for an episode of acute inferior wall infarction. Aberrantly conducted ventricular beats were obtained in this case by introduction of artificially induced atrial premature beats ...
Congestive heart failure
... sphironolactone in patients with severe CHF ↓↓ morbidity & mortality in patients who were also receiving standard therapy (diuretics, ACE inhibitors) • This shows that aldosterone plays a pathological role in the progression of CHF – other than that of Na+ retention i.e prevents re-modelling • Low d ...
... sphironolactone in patients with severe CHF ↓↓ morbidity & mortality in patients who were also receiving standard therapy (diuretics, ACE inhibitors) • This shows that aldosterone plays a pathological role in the progression of CHF – other than that of Na+ retention i.e prevents re-modelling • Low d ...
Cardiovascular System
... ejection phase. After the aortic valve closes, an incisura occurs because of sudden cessation of back-flow toward left ventricle. Aortic pressure decreases slowly during diastole because of the elasticity of the aorta. ...
... ejection phase. After the aortic valve closes, an incisura occurs because of sudden cessation of back-flow toward left ventricle. Aortic pressure decreases slowly during diastole because of the elasticity of the aorta. ...
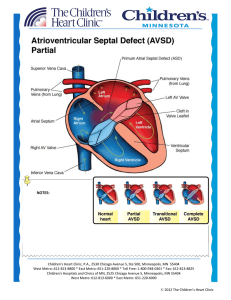
Atrioventricular Septal Defect AVSD
... symptoms of congestive heart failure. Diagnostics: EKG: First degree heart block (prolonged PR interval) and left axis deviation may be present. Chest x-ray: Cardiomegaly and prominent pulmonary vasculature and main pulmonary artery. The left ventricular outflow tract is elongated and narrowed, ...
... symptoms of congestive heart failure. Diagnostics: EKG: First degree heart block (prolonged PR interval) and left axis deviation may be present. Chest x-ray: Cardiomegaly and prominent pulmonary vasculature and main pulmonary artery. The left ventricular outflow tract is elongated and narrowed, ...
New onset atrial fibrillation after initiating amphetamine
... Literature review was unrevealing for linkage of amphetamine stimulants to atrial fibrillation specifically. However, there are reports associating amphetamines to atrial flutter.[4] Additionally, recreational use of amphetamines can cause electrical instability of the myocardium potentially leading ...
... Literature review was unrevealing for linkage of amphetamine stimulants to atrial fibrillation specifically. However, there are reports associating amphetamines to atrial flutter.[4] Additionally, recreational use of amphetamines can cause electrical instability of the myocardium potentially leading ...
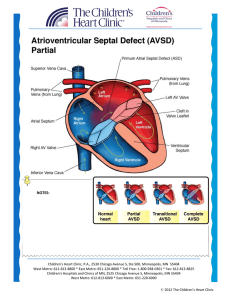
Atrioventricular Septal Defect AVSD
... symptoms of congestive heart failure. Diagnostics: EKG: First degree heart block (prolonged PR interval) and left axis deviation may be present. Chest x-ray: Cardiomegaly and prominent pulmonary vasculature and main pulmonary artery. The left ventricular outflow tract is elongated and narrowed, ...
... symptoms of congestive heart failure. Diagnostics: EKG: First degree heart block (prolonged PR interval) and left axis deviation may be present. Chest x-ray: Cardiomegaly and prominent pulmonary vasculature and main pulmonary artery. The left ventricular outflow tract is elongated and narrowed, ...
Outline Chapters 15-16 - Mead`s Fabulous Weebly
... ◦ Signal spreads from Sa node to atria; Atria contract 2. QRS Complex = Ventricle depolarization ◦ Signal spreads through ventricles; Soon after, ventricles contract 3. T = Ventricle repolarization : Ventricles relax C. Cardiac Cycle: 3 phases 1. Relaxation period - Diastole All 4 chambers relaxed ...
... ◦ Signal spreads from Sa node to atria; Atria contract 2. QRS Complex = Ventricle depolarization ◦ Signal spreads through ventricles; Soon after, ventricles contract 3. T = Ventricle repolarization : Ventricles relax C. Cardiac Cycle: 3 phases 1. Relaxation period - Diastole All 4 chambers relaxed ...
INTRODUCTION TO SPORT SCIENCE
... pumping force for the circulatory system Both ventricles contract together 100% of blood from R ventricle goes to the lungs where it is oxygenated Returned to L atria (receptacle) and flows to L ventricle Pumped from L ventricle to the rest of the body ...
... pumping force for the circulatory system Both ventricles contract together 100% of blood from R ventricle goes to the lungs where it is oxygenated Returned to L atria (receptacle) and flows to L ventricle Pumped from L ventricle to the rest of the body ...
Sinus Node
... resynchronize contraction of the heart (both interventricular resynchyronization and intraventricular LV resynchronization) ...
... resynchronize contraction of the heart (both interventricular resynchyronization and intraventricular LV resynchronization) ...
Presentation
... pre-existing EKG abnormalities. More info than EKG. Less expensive than nuclear. ...
... pre-existing EKG abnormalities. More info than EKG. Less expensive than nuclear. ...
3MP Anatomy Exam 2 Review
... Cardiac valves – open and close due to pressure changes in the cardiac chambers Chemoreceptors – detect changes in carbon dioxide and oxygen levels in the blood Contractility – force of ventricular ejection; greatly affected by a weak left ventricle Coronary arteries – receive blood when both ventri ...
... Cardiac valves – open and close due to pressure changes in the cardiac chambers Chemoreceptors – detect changes in carbon dioxide and oxygen levels in the blood Contractility – force of ventricular ejection; greatly affected by a weak left ventricle Coronary arteries – receive blood when both ventri ...
Electrocardiography
Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG*) is the process of recording the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time using electrodes placed on a patient's body. These electrodes detect the tiny electrical changes on the skin that arise from the heart muscle depolarizing during each heartbeat.In a conventional 12 lead ECG, ten electrodes are placed on the patient's limbs and on the surface of the chest. The overall magnitude of the heart's electrical potential is then measured from twelve different angles (""leads"") and is recorded over a period of time (usually 10 seconds). In this way, the overall magnitude and direction of the heart's electrical depolarization is captured at each moment throughout the cardiac cycle. The graph of voltage versus time produced by this noninvasive medical procedure is referred to as an electrocardiogram (abbreviated ECG or EKG).During each heartbeat, a healthy heart will have an orderly progression of depolarization that starts with pacemaker cells in the sinoatrial node, spreads out through the atrium, passes through the atrioventricular node down into the bundle of His and into the Purkinje fibers spreading down and to the left throughout the ventricles. This orderly pattern of depolarization gives rise to the characteristic ECG tracing. To the trained clinician, an ECG conveys a large amount of information about the structure of the heart and the function of its electrical conduction system. Among other things, an ECG can be used to measure the rate and rhythm of heartbeats, the size and position of the heart chambers, the presence of any damage to the heart's muscle cells or conduction system, the effects of cardiac drugs, and the function of implanted pacemakers.