* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download G06: Heart (Weyrich)
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
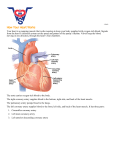
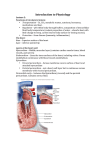
A patient is diagnosed with ischemia (i.e., lack of blood flow) in a left lobar pulmonary vein. The attending physician determines that the ischemia is due to a vasospastic episode. Constriction of this left lobar pulmonary vein is controlled by ____________. A. B. C. D. E. Efferent fibers from the phrenic nerve. Post-ganglionic fibers from T1-T4 sympathetic trunks Post-ganglionic fibers from the vagus n. Afferent fibers from the phrenic nerve Sympathetic fibers from the vagus n. 0 of 5 ef fe re nt fib sy er m s pa fro th m et t.. ic pa fib ra sy er m s fr. pa . af th fe et re i c nt fib fib er er ... sy s m fro pa m th th et ... ic fib er s fr. . 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% Heart • Surface anatomy and heart sounds -Dry lecture -Gray’s 169, 203-205 • Heart -Gray’s pp. 153-181 -Gray’s dissector pp. 84-101 1 Subdivisions of the Mediastinum The Heart 2 The Heart Pericardium Pericardium 1. Fibrous pericardium (external sac) 2. Serous pericardium (internal sac) (parietal layer– lines the inner surface of the fibrous) (visceral layer [epicardium] – adheres to the heart) Syllabus p. 41 3 Vessels and Nerves of the Pericardium A patient is diagnosed with cardiac tamponade. Pericardiocentesis is needed to drain fluid from the pericardial cavity to relieve pressure on the heart. To remove fluid a wide bore needle is inserted through the ________ intercostal space near the ____________ and passed superoposteriorly. 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% or 6t h, st 5t er h nu or m 6t ,i h, n. C .. m .2 i d nd -a xi ,s lla te ry rn D ... al .2 an nd g ,s le te ,. .. rn E. al 5t an h gl or e, 6t ... h, m id -v er ... 0 of 5 5th or 6th, infrasternal angle 5th or 6th, mid-axillary line 2nd, sternal angle 2nd, jugular notch 5th or 6th, mid-vertebral line 5t h A. B. C. D. E. 4 Cardiac Tamponade Walls of the Heart Syllabus p. 41 5 General Features of the Heart Arterial Supply of the Heart Syllabus p. 42 6 Coronary Angiography Arterial Supply of the Heart Venous Drainage of the Heart 7 Chambers of the Heart Right Atrium Syllabus p. 44 8 Tricuspid Valve and Right Ventricle Left Atrium and Ventricle 9 Heart Valves (Diastole) Ventricular Filling MV and TC valves close Syllabus p. 45 Heart Valves (Systole) Ventricular Contraction Semilunar valves close Syllabus p. 45 10 Sympathetic Innervation of the Heart Syllabus p. 46 Parasympathetic Innervation of the Heart 11 Referred Pain Innervation of the Heart • Sympathetic Innervation -Increases heart rate and force of contraction -Dilates coronary arteries • Parasympathetic Fibers -Decreases heart rate and force of contraction -Constricts coronary arteries 12 Conduction System of the Heart Syllabus p. 48 Blood Flow to and from the Heart 13 An aneurysm in the aortic arch compresses the left vagus nerve and alters its activity. Stimulation of parasympathetic vagus nerves __________. 40% A. B. C. D. 20% 20% 20% 0% In cr ea D se ila s te he s ar co tr r at on C e .C ar y on ar st te ric rie D ts s .I co nc ro re na as r.. es E. . th C e on fo st rc ric e ts .. pu lm on ... E. Increases heart rate Dilates coronary arteries Constricts coronary arteries Increases the force of the heartbeat Constricts pulmonary arteries A thrombus develops in the right atrium of a patient and eventually lodges itself in the sinuatrial nodal branch artery. Identify the course of the thrombus from the right atrium to the sinuatrial nodal branch artery. D. E. 0 of 5 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% at riu m ,t ric at us riu pi m ... C , m .R itr ig al ht va at ... D riu .R m ig ,t ht ric at u. riu E. .. m R ig ,m ht i tra at riu l.. . m ,t ric us ... C. R ig ht B. Right atrium, tricuspid valve, right ventricle, aortic valve, right coronary artery, sinuatrial nodal branch artery Right atrium, mitral valve, right ventricle, aortic valve, right coronary artery, sinuatrial nodal branch artery. Right atrium, tricuspid valve, right ventricle, aortic valve, left coronary artery, sinuatrial nodal branch artery. Right atrium, mitral valve, right ventricle, aortic valve, left coronary artery, sinuatrial nodal branch artery Right atrium, tricuspid valve, right ventricle, aortic valve, right coronary artery, right marginal branch, sinuatrial nodal branch artery R ig ht A. 14 SCREEN 2 Subdivisions of the Mediastinum 15 Pericardial Parts 16 Vessels and Nerves of the Pericardium 17 Cardiac Tamponade Walls of the Heart 18 General Features of the Heart Arterial Supply of the Heart 19 Venous Drainage of the Heart 20 Blood Flow to and from the Heart Tricuspid Valve and Right Ventricle 21 Left Atrium and Ventricle Heart Valves (Cardiac Cycle) 22 Sympathetic Innervation of the Heart Sympathetic Innervation of the Heart 23 Parasympathetic Innervation of the Heart Visceral Sensory Fibers from the Heart Syllabus p. 47 24 Referred Pain Conduction System of the Heart 25 Blood Flow to and from the Heart Syllabus p. 49 26