Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy: The Optimal QRS Duration
... detrimental. In patients with mild heart failure, CRT defibrillators (CRT-D) may also be beneficial in non-LBBB patients with PR interval prolongation and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) <30 %, but with a QRS duration ≥130 ms.6 Patients with QRS >130 ms may also respond to CRT even if LVEF ...
... detrimental. In patients with mild heart failure, CRT defibrillators (CRT-D) may also be beneficial in non-LBBB patients with PR interval prolongation and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) <30 %, but with a QRS duration ≥130 ms.6 Patients with QRS >130 ms may also respond to CRT even if LVEF ...
Cardiac Out Put
... In the veins, blood can be driven forward only as large veins have one way valve placed at 2 to 4 cm intervals. These valves prevent back flow of blood that tends to occur when a person stands up. ...
... In the veins, blood can be driven forward only as large veins have one way valve placed at 2 to 4 cm intervals. These valves prevent back flow of blood that tends to occur when a person stands up. ...
Clinical Investigations involving ECG Electrodes
... ECG measurements and were assigned to either the vacuum-systemgroup (150 patients) or the Ambu Blue Sensor SU-disposable-electrodegroup (150 patients). Microbiological samples of both electrodes were taken before the first session/patient of the day for each group. The vacuum system electrodes were ...
... ECG measurements and were assigned to either the vacuum-systemgroup (150 patients) or the Ambu Blue Sensor SU-disposable-electrodegroup (150 patients). Microbiological samples of both electrodes were taken before the first session/patient of the day for each group. The vacuum system electrodes were ...
Lab 8 - Creighton Biology
... referred to as “autorhythmicity.” A specialized bundle of tissue, known as the “pacemaker” (usually the sinoatrial, or SA, node), is responsible for setting the heartbeat rate since it fires inherently faster than the spontaneous rate of other heart cells. The activity of the SA node ultimately stim ...
... referred to as “autorhythmicity.” A specialized bundle of tissue, known as the “pacemaker” (usually the sinoatrial, or SA, node), is responsible for setting the heartbeat rate since it fires inherently faster than the spontaneous rate of other heart cells. The activity of the SA node ultimately stim ...
Top 10 Myths of Electrical Injury
... • Electrical injuries involve multiple body systems. • Entry and exit wounds fail to reflect the true extent of underlying tissue damage. • Electrical current may cause injuries distant from its apparent pathway through the victim. • Controversies exist regarding indications for admission and cardia ...
... • Electrical injuries involve multiple body systems. • Entry and exit wounds fail to reflect the true extent of underlying tissue damage. • Electrical current may cause injuries distant from its apparent pathway through the victim. • Controversies exist regarding indications for admission and cardia ...
CRRM1.11 - Embryology of the Heart
... A secondary septum forms alongside the primary septum but does not fuse completely, allowing limited blood flow through the foramen ovale into the left atrium ...
... A secondary septum forms alongside the primary septum but does not fuse completely, allowing limited blood flow through the foramen ovale into the left atrium ...
Biology 232
... 1) sinoatrial (SA) node – normal pacemaker in right atrial wall resting potential is not stable – spontaneously reaches threshold faster than any other autorhythmic cells threshold depolarization produces an action potential action potential propagates through both atrial walls via gap junctions 2) ...
... 1) sinoatrial (SA) node – normal pacemaker in right atrial wall resting potential is not stable – spontaneously reaches threshold faster than any other autorhythmic cells threshold depolarization produces an action potential action potential propagates through both atrial walls via gap junctions 2) ...
Flip and See ECG
... This book is humbly dedicated to Willem Einthoven, inventor of the electrocardiograph machine. For hundreds of years, the only known method for observing the beating of the heart was by opening the chest, breaking the sternum in half, and having a look. Sadly, the patients usually died. The discover ...
... This book is humbly dedicated to Willem Einthoven, inventor of the electrocardiograph machine. For hundreds of years, the only known method for observing the beating of the heart was by opening the chest, breaking the sternum in half, and having a look. Sadly, the patients usually died. The discover ...
Heart As An Endocrine Organ
... In addition to being a pump the heart has also been found to have an endocrine function, i.e. it sends hormonal signals which cause changes in the function of other organs and cells of the body. While many hormones which are also produced elsewhere in the body can be found in the heart, natriuretic ...
... In addition to being a pump the heart has also been found to have an endocrine function, i.e. it sends hormonal signals which cause changes in the function of other organs and cells of the body. While many hormones which are also produced elsewhere in the body can be found in the heart, natriuretic ...
Clinical monitoring of antiarrhythmics in critical care
... in particular pauses and conduction anomalies consecutive to sinoatrial node depression and the extension of AV conduction, are essential. The heart rate and PR interval must be recorded as well as any medicine-related post-administration symptom such as: hot flashes, histamine flush, dyspnea and ti ...
... in particular pauses and conduction anomalies consecutive to sinoatrial node depression and the extension of AV conduction, are essential. The heart rate and PR interval must be recorded as well as any medicine-related post-administration symptom such as: hot flashes, histamine flush, dyspnea and ti ...
here
... and death from cardiovascular diseases and stroke. Click here or copy and paste the URL below into your web browser to read the article and answer the question: http://www.heart.org/HEARTORG/Conditions/More/ConsumerHealthCare/Heart-HealthScreenings_UCM_428687_Article.jsp ...
... and death from cardiovascular diseases and stroke. Click here or copy and paste the URL below into your web browser to read the article and answer the question: http://www.heart.org/HEARTORG/Conditions/More/ConsumerHealthCare/Heart-HealthScreenings_UCM_428687_Article.jsp ...
The Heart Of An Athlete
... Example: a world class marathoner could have the same maximum heart rate as an average person, the difference being the marathoner’s heart pumps more blood with each beat. ...
... Example: a world class marathoner could have the same maximum heart rate as an average person, the difference being the marathoner’s heart pumps more blood with each beat. ...
New Options for Atrial Fibrillation Patients with
... achieving and maintaining a normal heart rhythm (rhythm control strategy) or may focus on maintaining a normal heart rate (rate control strategy). To obtain normal rhythm, anti-arrhythmic drugs, such as flecainide, sotalol, amiodarone and dofetilde are used. In most patients, rate control strategies ...
... achieving and maintaining a normal heart rhythm (rhythm control strategy) or may focus on maintaining a normal heart rate (rate control strategy). To obtain normal rhythm, anti-arrhythmic drugs, such as flecainide, sotalol, amiodarone and dofetilde are used. In most patients, rate control strategies ...
- American Heart Journal
... Accurate localization of intracardiac foreign bodies is essentialfor satisfactory operative removal. In somecases, despite localization by angiography, foreign bodies have been impossible to locate at operation.1.3Intracardiac foreign bodiesmay be accurately localized by two-dimensionalechocardiogra ...
... Accurate localization of intracardiac foreign bodies is essentialfor satisfactory operative removal. In somecases, despite localization by angiography, foreign bodies have been impossible to locate at operation.1.3Intracardiac foreign bodiesmay be accurately localized by two-dimensionalechocardiogra ...
Heart Failure
... -3. The upper border of the third right costal cartilage 1 cm from the right sternal line (upper right side of heart) -4. The lower border of the second left costal cartilage 2.5 cm from the left lateral sternal line (upper left side of heart) ...
... -3. The upper border of the third right costal cartilage 1 cm from the right sternal line (upper right side of heart) -4. The lower border of the second left costal cartilage 2.5 cm from the left lateral sternal line (upper left side of heart) ...
ATRIAL SEPTAL DEFECT
... Patients with small atrial shunts may live a normal life span. Large shunts usually cause disability by age 40 years. Because left-to-right shunts tend to increase with age-related changes in LV compliance, most clinicians believe that closure of all shunts over 1.5:1 should be accomplished. Increas ...
... Patients with small atrial shunts may live a normal life span. Large shunts usually cause disability by age 40 years. Because left-to-right shunts tend to increase with age-related changes in LV compliance, most clinicians believe that closure of all shunts over 1.5:1 should be accomplished. Increas ...
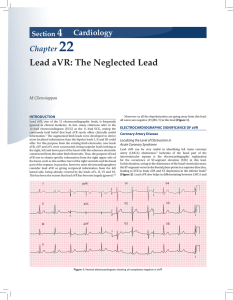
Lead aVR: The Neglected Lead - The Association of Physicians of
... INTRODUCTION Lead aVR, one of the 12 electrocardiographic leads, is frequently ignored in clinical medicine. In fact, many clinicians refer to the 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) as the 11-lead ECG, noting the commonly held belief that lead aVR rarely offers clinically useful information.1 The augme ...
... INTRODUCTION Lead aVR, one of the 12 electrocardiographic leads, is frequently ignored in clinical medicine. In fact, many clinicians refer to the 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) as the 11-lead ECG, noting the commonly held belief that lead aVR rarely offers clinically useful information.1 The augme ...
The Cardiovascular System Chapter 9
... blood into the ventricles ATRIOVENTRICULAR NODE is in the right atrium near the lower portion of the interatrial septum the electrical impulse from the SA node affects the AV node, which then transmits the impulse to the ...
... blood into the ventricles ATRIOVENTRICULAR NODE is in the right atrium near the lower portion of the interatrial septum the electrical impulse from the SA node affects the AV node, which then transmits the impulse to the ...
HEART DISEASE IN DOGS AND CATS
... when the supply of blood to the heart muscle is reduced or totally blocked. Whilst heart attacks are common in humans they rarely occur in other animals. Indeed dogs develop different heart conditions from cats, and within species heart conditions can occur more frequently in certain breeds. Heart d ...
... when the supply of blood to the heart muscle is reduced or totally blocked. Whilst heart attacks are common in humans they rarely occur in other animals. Indeed dogs develop different heart conditions from cats, and within species heart conditions can occur more frequently in certain breeds. Heart d ...
A novel genetic modifier for clarithromycin
... When ivabradine was administered intravenously (0.2 mg kg-1) to 14 patients (12 males, 2 females) with normal baseline electrophysiology, it was reported to lead to a heart rate reduction of 13-14 beats min-1 (at 0.5 and 1 hr following administration) and to prolong the QT interval, without changes ...
... When ivabradine was administered intravenously (0.2 mg kg-1) to 14 patients (12 males, 2 females) with normal baseline electrophysiology, it was reported to lead to a heart rate reduction of 13-14 beats min-1 (at 0.5 and 1 hr following administration) and to prolong the QT interval, without changes ...
Electrocardiography
Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG*) is the process of recording the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time using electrodes placed on a patient's body. These electrodes detect the tiny electrical changes on the skin that arise from the heart muscle depolarizing during each heartbeat.In a conventional 12 lead ECG, ten electrodes are placed on the patient's limbs and on the surface of the chest. The overall magnitude of the heart's electrical potential is then measured from twelve different angles (""leads"") and is recorded over a period of time (usually 10 seconds). In this way, the overall magnitude and direction of the heart's electrical depolarization is captured at each moment throughout the cardiac cycle. The graph of voltage versus time produced by this noninvasive medical procedure is referred to as an electrocardiogram (abbreviated ECG or EKG).During each heartbeat, a healthy heart will have an orderly progression of depolarization that starts with pacemaker cells in the sinoatrial node, spreads out through the atrium, passes through the atrioventricular node down into the bundle of His and into the Purkinje fibers spreading down and to the left throughout the ventricles. This orderly pattern of depolarization gives rise to the characteristic ECG tracing. To the trained clinician, an ECG conveys a large amount of information about the structure of the heart and the function of its electrical conduction system. Among other things, an ECG can be used to measure the rate and rhythm of heartbeats, the size and position of the heart chambers, the presence of any damage to the heart's muscle cells or conduction system, the effects of cardiac drugs, and the function of implanted pacemakers.