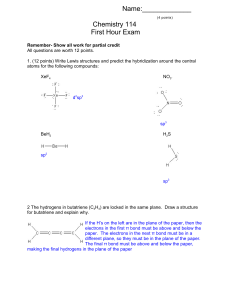
Review 3rd Qtr KEY
... Given calculations with the calculator answer, write the answers with the appropriate # of significant figures. ...
... Given calculations with the calculator answer, write the answers with the appropriate # of significant figures. ...
chemistry - cloudfront.net
... Group 1: alkali metals (except H), soft, very reactive metal (usually exists as compounds; easily lose their one valence electron); forms a “base” (or alkali) when reacting with water (not just dissolved!) Group 2: alkaline earth metals; also form bases with water; do not dissolve well, reactive (lo ...
... Group 1: alkali metals (except H), soft, very reactive metal (usually exists as compounds; easily lose their one valence electron); forms a “base” (or alkali) when reacting with water (not just dissolved!) Group 2: alkaline earth metals; also form bases with water; do not dissolve well, reactive (lo ...
SG5 Chemical Reactions and Quantities
... a) Multiply each atomic weight by the number of atoms of that type in the formula b) Add up the resulting weights for all elements present; total is called Molecular Weight (MW) c) Divide the weight of each element by the total ( x 100%) to find percentage composition 8) Determine empirical formulas ...
... a) Multiply each atomic weight by the number of atoms of that type in the formula b) Add up the resulting weights for all elements present; total is called Molecular Weight (MW) c) Divide the weight of each element by the total ( x 100%) to find percentage composition 8) Determine empirical formulas ...
First Semester Final - Review Questions
... 27. Describe the bonding characteristics of carbon. How many bonds can carbon form? What types of covalent bonds can carbon form? 28. What type of bond is found in most large organic molecules? 29. What monomers make up proteins? What monomers make up DNA? 30. What is the chemical structure of an am ...
... 27. Describe the bonding characteristics of carbon. How many bonds can carbon form? What types of covalent bonds can carbon form? 28. What type of bond is found in most large organic molecules? 29. What monomers make up proteins? What monomers make up DNA? 30. What is the chemical structure of an am ...
AP Chemistry Syllabus 2013 Mawhiney
... final results. Lastly, students identify the major chemical principles used in the lab and the lab results that support those principles. Although the teacher uses many demonstrations throughout the year, they do not take the place of laboratory work by the students nor are they treated as a lab in ...
... final results. Lastly, students identify the major chemical principles used in the lab and the lab results that support those principles. Although the teacher uses many demonstrations throughout the year, they do not take the place of laboratory work by the students nor are they treated as a lab in ...
Chemistry Final Study Guide
... 43. The three major categories of elements on the periodic table are the __________, __________, and __________. 44. The first group on the periodic table is called the __________ __________, and they are very reactive due to the fact that they tend to lose one __________. 45. Electrons in the outer ...
... 43. The three major categories of elements on the periodic table are the __________, __________, and __________. 44. The first group on the periodic table is called the __________ __________, and they are very reactive due to the fact that they tend to lose one __________. 45. Electrons in the outer ...
Bonding Challenge
... in the ground state. Indicate the number of unpaired electrons in the ground-state atom, and explain your reasoning. b) In terms of atomic structure, explain why the first ionization energy of selenium is (i) less than that of bromine (atomic number 35), and (ii) greater than that of tellurium (atom ...
... in the ground state. Indicate the number of unpaired electrons in the ground-state atom, and explain your reasoning. b) In terms of atomic structure, explain why the first ionization energy of selenium is (i) less than that of bromine (atomic number 35), and (ii) greater than that of tellurium (atom ...
HW-1-Ch1-Atomic-structure-W16
... 8. How long would it take for a sample of 222Rn that weighs 0.750 g to decay to 0.100 g? Assume a half-life for 222Rn of 3.823 days? ...
... 8. How long would it take for a sample of 222Rn that weighs 0.750 g to decay to 0.100 g? Assume a half-life for 222Rn of 3.823 days? ...
Midterm Review File
... 19. Answer the following questions about the periodic table. a. Explain why noble gases are inert and do not form ions. b. Identify the name of the group that contains the element fluorine _______________ c. Give the name of the element in the alkali group that has the greatest electron affinity ___ ...
... 19. Answer the following questions about the periodic table. a. Explain why noble gases are inert and do not form ions. b. Identify the name of the group that contains the element fluorine _______________ c. Give the name of the element in the alkali group that has the greatest electron affinity ___ ...
Note Sheet
... Example 2 (gaining rounding experience): A compound containing only carbon, hydrogen and oxygen is found to be 48.38% carbon and 8.12% hydrogen by mass. What is its empirical formula? ...
... Example 2 (gaining rounding experience): A compound containing only carbon, hydrogen and oxygen is found to be 48.38% carbon and 8.12% hydrogen by mass. What is its empirical formula? ...
Early Research Award
... chemical systems and efficient molecular dynamics simulation for drug design. For science problems involving the estimate of statistical averages, a conventional approach is to run multiple, non‐ communicating copies of the simulation and then to average the resul ...
... chemical systems and efficient molecular dynamics simulation for drug design. For science problems involving the estimate of statistical averages, a conventional approach is to run multiple, non‐ communicating copies of the simulation and then to average the resul ...
Materials Science for Chemical Engineers
... one electron is places in all orbitals of equal energy before two electrons are placed in any one of these orbitals. Rule 3. Pauli Exclusion principle a maximum of two electrons can occupy an orbital. No two electrons can have the same four quantum numbers. ...
... one electron is places in all orbitals of equal energy before two electrons are placed in any one of these orbitals. Rule 3. Pauli Exclusion principle a maximum of two electrons can occupy an orbital. No two electrons can have the same four quantum numbers. ...
Name: Period
... 3. What are the shapes of an s and p orbitals? 4. What is a principal energy level, sublevel and atomic orbital? 5. What is the maximum number in each s, p, d and f orbitals? 6. What types of atomic orbitals are in the 1st, 2nd and 3rd principal energy levels? 7. If the spin of one electron is clock ...
... 3. What are the shapes of an s and p orbitals? 4. What is a principal energy level, sublevel and atomic orbital? 5. What is the maximum number in each s, p, d and f orbitals? 6. What types of atomic orbitals are in the 1st, 2nd and 3rd principal energy levels? 7. If the spin of one electron is clock ...
Chemistry ~ Fall Final Review
... 8. Describe the models of the atom: Democritus, Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Bohr, Electron Cloud. 9. Use a diagram to define wavelength and frequency. Write the equations that relate wavelength & frequency and frequency & energy. What is “c”? What is “h”? 10. A beam of light has an energy of 2.34 ...
... 8. Describe the models of the atom: Democritus, Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Bohr, Electron Cloud. 9. Use a diagram to define wavelength and frequency. Write the equations that relate wavelength & frequency and frequency & energy. What is “c”? What is “h”? 10. A beam of light has an energy of 2.34 ...
How Good Is the Quantum Mechanical Explanation of the Periodic
... should be strictly deducible from quantum mechanics. Although I am not in a position to propose a better explanation, I do not think that we should be complacent about what the present explanation achieves. As I have tried to argue, in terms of deduction from theoretical principles, the present semi ...
... should be strictly deducible from quantum mechanics. Although I am not in a position to propose a better explanation, I do not think that we should be complacent about what the present explanation achieves. As I have tried to argue, in terms of deduction from theoretical principles, the present semi ...
AP Chemistry Syllabus
... either would like to earn college credit (by AP examination) or would like to prepare for college chemistry while in high school. This is accomplished through an intensive, in-depth approach. It is highly recommended that the student take the College Board's Advance Placement test in Chemistry. The ...
... either would like to earn college credit (by AP examination) or would like to prepare for college chemistry while in high school. This is accomplished through an intensive, in-depth approach. It is highly recommended that the student take the College Board's Advance Placement test in Chemistry. The ...