* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Note Sheet
Rigid rotor wikipedia , lookup
Host–guest chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Artificial photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Magnetorotational instability wikipedia , lookup
Process chemistry wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Debye–Hückel equation wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Computational chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Coupled cluster wikipedia , lookup
Rate equation wikipedia , lookup
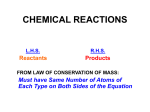
Roosevelt High School Chapter 3 Notes AP Chemistry Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations The Mole: Molecular Weight/Formula Weight: Mole Conversions: Grams to Moles: How many moles are in 24 g of CO2? Number to Moles: How many moles are in 1.54 x 1025 molecules of CO2? Volume at STP: How many moles of CO2 fit in a 100 L tank at STP? Percent Compositions: What is the percent composition of the elements in CO2? What is the mass of carbon in 50 g of CO2? **Empirical and Molecular Formulas: 1. 2. 3. 4. Starting with mass percentages, assume you have 100 g of the substance Convert grams of each element to moles Divide each number from #2 by the smallest of those from #2 Check to see if all the numbers are close to integer values-multiply through by a whole number to fix This is your EMPIRICAL FORMULA 5. To convert to a molecular formula, you must see how many times the mass of the empirical formula (#4) goes into the known molecular mass of the molecule. Use this number to multiply through the empirical formula. Example: A combustion analysis gives the following mass %: H= 9.15% molecular formula knowing that : molecular mass = 132.16 C = 54.53% O = 36.32% . Determine the Hydrates: If “Epsom salt,” MgSO4 · x H2O is heated to 250°C, all the water of hydration is lost. On heating a 1.687- g sample of the hydrate, 0.824 g of MgSO4 remains. What is the formula of Epsom salt? Combustion Reactions: Some Compound** + O2 → H2O + CO2 (**usually a hydrocarbon in AP Chemistry) Example 1: An organic compound contains the three elements carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Combustion of a 5.00 g sample of ethyl alcohol gives 9.55 g carbon dioxide and 5.87 g water. Roosevelt High School Chapter 3 Notes AP Chemistry Example 2 (gaining rounding experience): A compound containing only carbon, hydrogen and oxygen is found to be 48.38% carbon and 8.12% hydrogen by mass. What is its empirical formula? Example 3 (nitrogen): A 1.50 gram sample of cadaverine gives 3.23 g of CO2, 1.58 g of N2O5, and 1.865 g of H2O. Its molar mass is 102.2 g/mol. Determine the empirical and molecular formulas. Combination Reactions: Decomposition Reactions: Balancing Equations: 1. 2. 3. 4. Write a skeleton equation and make sure that formulas are correct Balance the atoms from complex to simple (You can only change coefficients!!) Make sure the coefficients are in the lowest whole number ratio Add the states of matter Example: Balance an equation for the combustion of propane (C3H8). Stoichiometry: Using the “mole-ratio” Example: How many grams of CO2 are made when 12.5g of propane are completely combusted in excess oxygen? Limiting Reactant: The reactant that “runs out” first determines the amount of product. Example: A 2.00 g sample of ammonia is mixed with 4.00 g of oxygen. Which is the limiting reactant and how much excess reactant remains after the reaction has stopped? 4 NH3(g) + 5 O2(g) Percent Yield: 4 NO(g) + 6 H2O(g) Divide the amount actually created in a lab by the theoretical yield and multiply 100%. Calculate the theoretical yield of C2H5Cl if 112 g of C2H5OH is reacted with 34.7 g of PCl3 based on the reaction below. If 23.7 g of C2H5Cl is produced, what is the percent yield? 3 C2H5OH + PCl3 ==> 3 C2H5Cl + H3PO3