Chapter 7
... Uncertainty Principle – location and momentum of particle are complimentary; can’t both be known simultaneously with precision; can’t specify precise location of particle if it behaves like a wave Developed an equation that describes the wavelike properties of matter, we use the wave function to exp ...
... Uncertainty Principle – location and momentum of particle are complimentary; can’t both be known simultaneously with precision; can’t specify precise location of particle if it behaves like a wave Developed an equation that describes the wavelike properties of matter, we use the wave function to exp ...
Unit 01 Qual Chem
... Physical Change = a change that does not alter the identity of a substance (shape, size, ...
... Physical Change = a change that does not alter the identity of a substance (shape, size, ...
Deconstructed HS-PS1-2
... Understand that electronegativity describes the tendency of an element to attract electrons to it. ...
... Understand that electronegativity describes the tendency of an element to attract electrons to it. ...
Final
... Perform molarity calculations and conversions Be able to develop a precipitation and acid/base neutralization reaction given the names of the starting materials Determine whether a material is soluble or insoluble Determine whether a precipitation and acid/base neutralization reaction occurs Write c ...
... Perform molarity calculations and conversions Be able to develop a precipitation and acid/base neutralization reaction given the names of the starting materials Determine whether a material is soluble or insoluble Determine whether a precipitation and acid/base neutralization reaction occurs Write c ...
Final Exam Chemistry B2A Mr. Kimball`s Class 2003
... a) a type of chemical bond formed by the transfer of one or more electrons b) holds together (a) cation(s) and (an) anion(s). c) forms because all the charges attract each other d) results in the bonded atoms usually satisfying the Rule of Eight and Rule of Two e) the force of attraction between ion ...
... a) a type of chemical bond formed by the transfer of one or more electrons b) holds together (a) cation(s) and (an) anion(s). c) forms because all the charges attract each other d) results in the bonded atoms usually satisfying the Rule of Eight and Rule of Two e) the force of attraction between ion ...
Regents_Chem_Core_for_review
... increases. When an atom loses one or more electrons, it becomes a positive ion and its radius decreases. (5.2c) IV.7 When a bond is broken, energy is absorbed. When a bond is formed, energy is released. (5.2i) IV.8 Atoms attain a stable valence electron configuration by bonding with other atoms. Nob ...
... increases. When an atom loses one or more electrons, it becomes a positive ion and its radius decreases. (5.2c) IV.7 When a bond is broken, energy is absorbed. When a bond is formed, energy is released. (5.2i) IV.8 Atoms attain a stable valence electron configuration by bonding with other atoms. Nob ...
CHEMISTry is life - World of Teaching
... -Too often kids get to high school chemistry and they are scared before they even begin. -My goal is to shape a positive image in their minds about chemistry so that they can be more prepared mentally for high school. -I will do this by showing them how applicable chemistry is to every day life. It ...
... -Too often kids get to high school chemistry and they are scared before they even begin. -My goal is to shape a positive image in their minds about chemistry so that they can be more prepared mentally for high school. -I will do this by showing them how applicable chemistry is to every day life. It ...
Unit 5 Power Point
... nucleus. These orbits correspond to certain definite amounts of energy. • An electron in a permitted orbit has a specific energy and is in an allowed energy state. It will not spiral into the nucleus. • Energy is emitted or absorbed by an electron as it changes from one energy state to another . Thi ...
... nucleus. These orbits correspond to certain definite amounts of energy. • An electron in a permitted orbit has a specific energy and is in an allowed energy state. It will not spiral into the nucleus. • Energy is emitted or absorbed by an electron as it changes from one energy state to another . Thi ...
gr11chemreview
... 16. Determine the molar mass for the following compounds. A) Mg(SCN)2 B) SrCl2∙ 4H2O ...
... 16. Determine the molar mass for the following compounds. A) Mg(SCN)2 B) SrCl2∙ 4H2O ...
S3 Chemistry - eduBuzz.org
... Calculate the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in an atom Identify whether a species has an equal or unequal number of protons and electrons and use this to state whether it is an atom or ion. State the charge of an ion. Calculate the charge on a ion using nuclide notation Use the ...
... Calculate the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in an atom Identify whether a species has an equal or unequal number of protons and electrons and use this to state whether it is an atom or ion. State the charge of an ion. Calculate the charge on a ion using nuclide notation Use the ...
Learning Outcomes for Chemical Reactions and
... • Calculate the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in an atom • Identify whether a species has an equal or unequal number of protons and electrons and use this to state whether it is an atom or ion. • State the charge of an ion. • Calculate the charge on a ion using nuclide notation • Use the ...
... • Calculate the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in an atom • Identify whether a species has an equal or unequal number of protons and electrons and use this to state whether it is an atom or ion. • State the charge of an ion. • Calculate the charge on a ion using nuclide notation • Use the ...
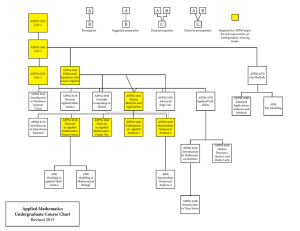
Chart of Course Options
... Required for APPM major. For full requirements see Undergraduate Advising Guide. ...
... Required for APPM major. For full requirements see Undergraduate Advising Guide. ...
Chapter 2 Outline
... E. A change in the number of protons results in a change of element F. A change in the number of neutrons results in an isotope G. A change in the number of electrons results in an ion IV. Compounds and mixtures A. When two or more atoms bond covalently, they form a molecule B. A compound is formed ...
... E. A change in the number of protons results in a change of element F. A change in the number of neutrons results in an isotope G. A change in the number of electrons results in an ion IV. Compounds and mixtures A. When two or more atoms bond covalently, they form a molecule B. A compound is formed ...
Unit 1 - Measurement Atomic Theory
... (i) Substance must absorb in the visible range (400 – 700 nm) (ii) Color comes from visible light NOT absorbed. (d) OTHER PROPERTIES: (i) Boiling Point, Melting Point, Malleability, Ductility, Specific Gravity, luster, vapor pressure, etc. ...
... (i) Substance must absorb in the visible range (400 – 700 nm) (ii) Color comes from visible light NOT absorbed. (d) OTHER PROPERTIES: (i) Boiling Point, Melting Point, Malleability, Ductility, Specific Gravity, luster, vapor pressure, etc. ...
Review for Exam 1
... Determine how many of each ion type is needed for an overall charge of zero. When the cation and anion have different charges, use the ion charges to determine the number of ions of each needed. ...
... Determine how many of each ion type is needed for an overall charge of zero. When the cation and anion have different charges, use the ion charges to determine the number of ions of each needed. ...
Electron Configuration Class Notes
... Energy moves in waves, but it can act as particles (photons). Louie de Broglie – “matter waves” Postulated that since light shows a “dual nature” – has wave properties as well as particulate properties, then matter should also be able to move - not only as particles - but also as waves! - this prope ...
... Energy moves in waves, but it can act as particles (photons). Louie de Broglie – “matter waves” Postulated that since light shows a “dual nature” – has wave properties as well as particulate properties, then matter should also be able to move - not only as particles - but also as waves! - this prope ...
CHEM IB Lecture notes as of 8-29-06
... transformations that they undergo 2 a : the composition and chemical properties of a substance b : chemical
processes and phenomena (as of an organism)
3 a : a strong mutual attraction, attachment, or sympathy b :
interaction ...
... transformations that they undergo 2 a : the composition and chemical properties of a substance
Chemistry 12 Curriculum Review
... Kinetics, Equilibrium and Solutions Students are Students are expected to expected to have understand how an understanding energy is involved of the rate of in various systems. chemical Students will reactions which develop their can be described planning, using equations, recording, calculations, a ...
... Kinetics, Equilibrium and Solutions Students are Students are expected to expected to have understand how an understanding energy is involved of the rate of in various systems. chemical Students will reactions which develop their can be described planning, using equations, recording, calculations, a ...
Chapter 10 - HCC Learning Web
... The number of molecular orbitals formed is always equal to the number of atomic orbitals combined. A molecular orbital can accommodate up to two electrons. When electrons are added to orbitals of the same energy, the most stable arrangement is predicted by Hund's rule. Low-energy molecular orbitals ...
... The number of molecular orbitals formed is always equal to the number of atomic orbitals combined. A molecular orbital can accommodate up to two electrons. When electrons are added to orbitals of the same energy, the most stable arrangement is predicted by Hund's rule. Low-energy molecular orbitals ...