groups (families) vs rows
... If 4.04g of N combine with 11.46g of O to produce a compound with a formula mass of 108.0 amu, what is the molecular formula of this compound? ...
... If 4.04g of N combine with 11.46g of O to produce a compound with a formula mass of 108.0 amu, what is the molecular formula of this compound? ...
Physics 880.06: Problem Set 5
... (b). Calculate the extra free energy of the superconductor associated with the wall. In other words, calculate the difference between the above free energy and the analogous free energy for a uniform system occupying the half-space z > 0. Assume no vector potential and no ...
... (b). Calculate the extra free energy of the superconductor associated with the wall. In other words, calculate the difference between the above free energy and the analogous free energy for a uniform system occupying the half-space z > 0. Assume no vector potential and no ...
Parameterization for solvent molecules around a
... The MD simulation was performed with a Buckyball (C60) hydrated by 1380 water molecules A 3.5 x 3.5 x 3.5 cubic box was used, which was periodic in all dimensions ...
... The MD simulation was performed with a Buckyball (C60) hydrated by 1380 water molecules A 3.5 x 3.5 x 3.5 cubic box was used, which was periodic in all dimensions ...
Review Packet
... 31. Anything that takes up space and has mass is called a. matter b. mass c. volume d. stuff 32. A change in the force of Earth’s gravity on an object will affect its a. mass b. density c. weight d. kinetic energy 33. Chemical proprieties a. include changes of state of a substance b. include mass an ...
... 31. Anything that takes up space and has mass is called a. matter b. mass c. volume d. stuff 32. A change in the force of Earth’s gravity on an object will affect its a. mass b. density c. weight d. kinetic energy 33. Chemical proprieties a. include changes of state of a substance b. include mass an ...
Packet
... 31. Anything that takes up space and has mass is called a. matter b. mass c. volume d. stuff 32. A change in the force of Earth’s gravity on an object will affect its a. mass b. density c. weight d. kinetic energy 33. Chemical proprieties a. include changes of state of a substance b. include mass an ...
... 31. Anything that takes up space and has mass is called a. matter b. mass c. volume d. stuff 32. A change in the force of Earth’s gravity on an object will affect its a. mass b. density c. weight d. kinetic energy 33. Chemical proprieties a. include changes of state of a substance b. include mass an ...
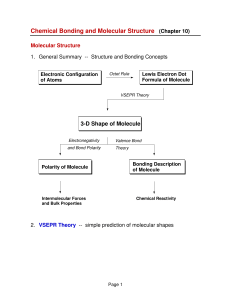
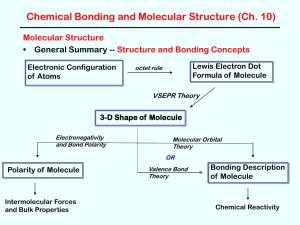
3-D Shape of Molecule
... Fill in MO diagram for C2, N2, O2, F2, and Ne2 and determine bond order for each: molecule ...
... Fill in MO diagram for C2, N2, O2, F2, and Ne2 and determine bond order for each: molecule ...
401
... where f I {ri A } , r ij denotes the functions composed of the products of x i A, yi A, z i A, r i A, and r ij, where i runs electrons, A denotes nuclei in the molecule, and r ij denotes the interelectron distance between the electrons i and j. Now, we have a picture that an electron is captured in ...
... where f I {ri A } , r ij denotes the functions composed of the products of x i A, yi A, z i A, r i A, and r ij, where i runs electrons, A denotes nuclei in the molecule, and r ij denotes the interelectron distance between the electrons i and j. Now, we have a picture that an electron is captured in ...
Review Sheet for Chemistry* First Semester Final
... Review Sheet for Chemistry* First Semester Final Refer to your class notes, worksheets, and the textbook to complete this review sheet. Study early so that you will have time to ask questions about what you don’t understand. ...
... Review Sheet for Chemistry* First Semester Final Refer to your class notes, worksheets, and the textbook to complete this review sheet. Study early so that you will have time to ask questions about what you don’t understand. ...
Review Sheet: Unit 6 Name__________________ CHEMISTRY: A
... information about the chemical composition of a compound. Consequently, chemists rely on a chemical ____________ when representing a chemical compound. ____________ compounds are composed of a metal and a nonmetal while ____________ compounds are formed between nonmetals. In formulas for binary ioni ...
... information about the chemical composition of a compound. Consequently, chemists rely on a chemical ____________ when representing a chemical compound. ____________ compounds are composed of a metal and a nonmetal while ____________ compounds are formed between nonmetals. In formulas for binary ioni ...
Green Chemistry: Principles and Practice
... Principle 6 Energy requirements should be recognized for their environmental and economic impacts and should be minimized. Synthetic methods should be conducted at ambient temperature and pressure. ...
... Principle 6 Energy requirements should be recognized for their environmental and economic impacts and should be minimized. Synthetic methods should be conducted at ambient temperature and pressure. ...
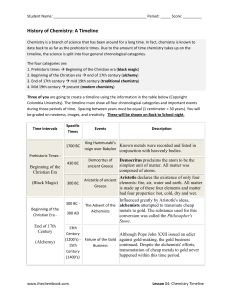
Word - The Chemistry Book
... elements. They were given the 1935 Nobel Prize. Albert Einstein and Enrico Fermi both warned the United States about Germany's extensive research on atomic fission reaction. Manhattan Project Below the football field at the University of Chicago, the United States developed the very first working nu ...
... elements. They were given the 1935 Nobel Prize. Albert Einstein and Enrico Fermi both warned the United States about Germany's extensive research on atomic fission reaction. Manhattan Project Below the football field at the University of Chicago, the United States developed the very first working nu ...
Che-30042 Lecture 1 - Rob Jackson`s Website
... • For Be, the ordering of the orbitals will not be affected, but in the case of K and Ca, the energy of the 4s orbital will be found to be lower than 3d at the end of the calculation, explaining the orbital occupancies. • A problem with the SCF method is that it does not treat electron correlation ( ...
... • For Be, the ordering of the orbitals will not be affected, but in the case of K and Ca, the energy of the 4s orbital will be found to be lower than 3d at the end of the calculation, explaining the orbital occupancies. • A problem with the SCF method is that it does not treat electron correlation ( ...