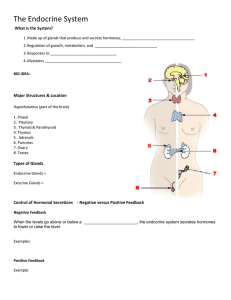
Endocrine System Introduction
... • Gigantism is caused by too much growth hormone during adolescence and puberty. ...
... • Gigantism is caused by too much growth hormone during adolescence and puberty. ...
Sample Questions Chapter 16
... ____ 25. Once an ovum is released from an ovary, a. a zygote forms. b. it enters the fallopian tubes. c. menstruation starts. d. ovarian cysts form. Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. ____ 26 ...
... ____ 25. Once an ovum is released from an ovary, a. a zygote forms. b. it enters the fallopian tubes. c. menstruation starts. d. ovarian cysts form. Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. ____ 26 ...
The Endocrine System (Chap 11)
... The thyroid hormones control your _________________________, which is the body's ability to break down food and store it as energy Thyroid Hormones Thyroxin (T4) & Tri-iodothyronine (T3) - increase the rate at which cells release energy from carbohydrates Calcitonin – regulates the blood concentrati ...
... The thyroid hormones control your _________________________, which is the body's ability to break down food and store it as energy Thyroid Hormones Thyroxin (T4) & Tri-iodothyronine (T3) - increase the rate at which cells release energy from carbohydrates Calcitonin – regulates the blood concentrati ...
Thyroid Gland - Fort Bend ISD
... Contains islands of cells called the Islets of Langerhans which secrete glucagon and insulin Glucagon – stimulates the liver to break down glycogen, Raises ...
... Contains islands of cells called the Islets of Langerhans which secrete glucagon and insulin Glucagon – stimulates the liver to break down glycogen, Raises ...
Endocrine System
... The Anterior part produces two hormones, ADH and Oxytocin. ADH is involved in water level control in the blood. Oxytocin controls lactation (milk let down) and is released from the pituitary when an animal is suckled. The Posterior part of the Pituitary produces a number of important hormones. These ...
... The Anterior part produces two hormones, ADH and Oxytocin. ADH is involved in water level control in the blood. Oxytocin controls lactation (milk let down) and is released from the pituitary when an animal is suckled. The Posterior part of the Pituitary produces a number of important hormones. These ...
The Endocrine and Reproductive System
... The Menstrual Cycle • Before an egg is released, the body prepares to have a baby. • The uterus’s wall thickens with blood in case an egg is fertilized. – If the egg is fertilized, the blood gives nutrients to the egg. – If the egg is not fertilized, the blood and egg are flushed out of the bo ...
... The Menstrual Cycle • Before an egg is released, the body prepares to have a baby. • The uterus’s wall thickens with blood in case an egg is fertilized. – If the egg is fertilized, the blood gives nutrients to the egg. – If the egg is not fertilized, the blood and egg are flushed out of the bo ...
Endocrine System
... – Brain gets message and sends out hormone to stimulate gland – Gland stimulates more hormone – When blood levels of hormone increase, the brain hormones stop ...
... – Brain gets message and sends out hormone to stimulate gland – Gland stimulates more hormone – When blood levels of hormone increase, the brain hormones stop ...
The Human Endocrine System: The Glands and Their Hormones
... Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) – stimulates the thyroid to release thyroxine Adreno-corticotropic hormone (ACTH) – stimulates the release of hormones from the adrenal glands Growth hormone (GH) – indirectly controls the growth of bone and cartilage Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH) – s ...
... Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) – stimulates the thyroid to release thyroxine Adreno-corticotropic hormone (ACTH) – stimulates the release of hormones from the adrenal glands Growth hormone (GH) – indirectly controls the growth of bone and cartilage Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH) – s ...
Principles of Endocrinology
... junctions, synaptic transmission, paracrine/autocrine, and endocrine ...
... junctions, synaptic transmission, paracrine/autocrine, and endocrine ...
Endocrine Glands
... and stress in general 5. Follicle-stimulating hormone and 6. Luteinizing hormone In females they stimulate ovarian follicle development and estrogen production In males they stimulate sperm production and testosterone production Released in response to gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) from the ...
... and stress in general 5. Follicle-stimulating hormone and 6. Luteinizing hormone In females they stimulate ovarian follicle development and estrogen production In males they stimulate sperm production and testosterone production Released in response to gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) from the ...
Endocrine System Jeopardy Round 1
... Increased thyroxine would cause a decrease in the amount of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) as a result of negative feedback. ...
... Increased thyroxine would cause a decrease in the amount of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) as a result of negative feedback. ...
Chapter 1: Animal Agriculture
... • Pregnant mare serum • Equine chorionic gonadotropin • Human chorionic gonadotropins ...
... • Pregnant mare serum • Equine chorionic gonadotropin • Human chorionic gonadotropins ...
The Endocrine System - BIOLOGY and HONORS PHYSIOLOGY Mr
... In addition to ‘releasing hormones,’ the hypothalamus secretes inhibitory hormones which halt the secreation of various stimulatng hormones into the capillary beds of the pituitary. ...
... In addition to ‘releasing hormones,’ the hypothalamus secretes inhibitory hormones which halt the secreation of various stimulatng hormones into the capillary beds of the pituitary. ...
Lab 1 Functional Anatomy of the Endocrine Glands
... ______________________ Many releasing hormones (TRH, CRH, GHRH etc.) ______________________ FSH, LH, GH, ACTH, Prolactin, TSH, ______________________ T-cell stimulating hormones ______________________ Melatonin ______________________ Mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, androgens, epinephrine and no ...
... ______________________ Many releasing hormones (TRH, CRH, GHRH etc.) ______________________ FSH, LH, GH, ACTH, Prolactin, TSH, ______________________ T-cell stimulating hormones ______________________ Melatonin ______________________ Mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, androgens, epinephrine and no ...
Endocrine System Guide
... when the body ____________________to insulin b. In other words, glucose ____________________to be used in energy production i. They produce enough insulin but the ____________________ c. The ____________________form of diabetes i. ____________________ Unit Four – Regulatory ...
... when the body ____________________to insulin b. In other words, glucose ____________________to be used in energy production i. They produce enough insulin but the ____________________ c. The ____________________form of diabetes i. ____________________ Unit Four – Regulatory ...
I can File
... explain that science and technology have both intended and unintended consequences for humans and the environment (hormone synthesis for diabetes mellitus, dwarfism, milk yield in cows) evaluate the use of hormone therapy in the treatment of humans (growth hormone and aging, anabolic steroids and ...
... explain that science and technology have both intended and unintended consequences for humans and the environment (hormone synthesis for diabetes mellitus, dwarfism, milk yield in cows) evaluate the use of hormone therapy in the treatment of humans (growth hormone and aging, anabolic steroids and ...
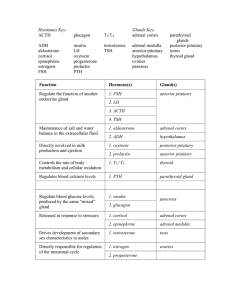
Hormones Key: Glands Key: ACTH glucagon T3/T4 adrenal cortex
... Regulate the function of another endocrine gland ...
... Regulate the function of another endocrine gland ...
IB BIO endocrine system
... The endocrine glands are also known as ductless glands. They secrete certain chemical substances which guide and control the various metabolic activities, the growth and differentiation of various systems and thereby bringing about a correct physiological balance between them. Such substances are al ...
... The endocrine glands are also known as ductless glands. They secrete certain chemical substances which guide and control the various metabolic activities, the growth and differentiation of various systems and thereby bringing about a correct physiological balance between them. Such substances are al ...
Chapter 18 Essays
... 8. Give a step-by-step, real-life example (i.e. for a specific hormone) showing how a receptor, a G-protein and a second messenger are involved in a hormone’s effect on a target cell’s metabolic activity. The best answers will include a diagram (as in Spotlight 18-3) and an explanation of the diagra ...
... 8. Give a step-by-step, real-life example (i.e. for a specific hormone) showing how a receptor, a G-protein and a second messenger are involved in a hormone’s effect on a target cell’s metabolic activity. The best answers will include a diagram (as in Spotlight 18-3) and an explanation of the diagra ...
Endocrine (regulatory) System
... how a toxic chemical affects hormone balance? How is a hormone defined in the video and how do these chemicals control metabolic activities in animals? What two structures in the brain does Dr. Catherine Rivier explore that relates to stress? How is the endocrine system similar to the nervous system ...
... how a toxic chemical affects hormone balance? How is a hormone defined in the video and how do these chemicals control metabolic activities in animals? What two structures in the brain does Dr. Catherine Rivier explore that relates to stress? How is the endocrine system similar to the nervous system ...
Calm Your Hormones or Everything You Should Know About
... • Your sex hormones interact with cortisol (stress hormone) and insulin (glucose regulator) • They are made by pregnenolone, the memory hormone • They interact with thyroid hormones (metabolism) • Hormone levels influence each other and change over time • Environment, diet, toxins and life stage are ...
... • Your sex hormones interact with cortisol (stress hormone) and insulin (glucose regulator) • They are made by pregnenolone, the memory hormone • They interact with thyroid hormones (metabolism) • Hormone levels influence each other and change over time • Environment, diet, toxins and life stage are ...
документ
... stature of a person is very small. Dwarfism is the condition of being undersized, or less than 127 cm (50 in) in height. Some dwarfs have been less than 64 cm (24 in) in height when fully grown. The word midget is usually applied to dwarfs. Another growth disorder disease is Cretinism which is a res ...
... stature of a person is very small. Dwarfism is the condition of being undersized, or less than 127 cm (50 in) in height. Some dwarfs have been less than 64 cm (24 in) in height when fully grown. The word midget is usually applied to dwarfs. Another growth disorder disease is Cretinism which is a res ...