Slide 1
... cells that act to regulate the activity of other cells in the body. – Hormones affect all cells in the body and are made and secreted by endocrine glands. • Endocrine glands are ductless organs that secret hormones either into the bloodstream or the fluid around cells. • The endocrine glands can be ...
... cells that act to regulate the activity of other cells in the body. – Hormones affect all cells in the body and are made and secreted by endocrine glands. • Endocrine glands are ductless organs that secret hormones either into the bloodstream or the fluid around cells. • The endocrine glands can be ...
hormones
... cells that act to regulate the activity of other cells in the body. – Hormones affect all cells in the body and are made and secreted by endocrine glands. • Endocrine glands are ductless organs that secret hormones either into the bloodstream or the fluid around cells. • The endocrine glands can be ...
... cells that act to regulate the activity of other cells in the body. – Hormones affect all cells in the body and are made and secreted by endocrine glands. • Endocrine glands are ductless organs that secret hormones either into the bloodstream or the fluid around cells. • The endocrine glands can be ...
Lesson Plan - Colorado FFA
... b. Animals must have proper levels of all nutrients, especially minerals, for proper functioning. c. These hormones produce gradual change, instead of immediate change like the nervous system. i. Football player: nervous system directs him to run and catch pass, endocrine system causes rate of growt ...
... b. Animals must have proper levels of all nutrients, especially minerals, for proper functioning. c. These hormones produce gradual change, instead of immediate change like the nervous system. i. Football player: nervous system directs him to run and catch pass, endocrine system causes rate of growt ...
The Endocrine System
... Regulates or supports a variety of important cardiovascular, metabolic, immunologic, and homeostatic functions including water balance People with adrenal insufficiency: these stresses can cause hypotension, shock and death: must give glucocorticoids, eg for surgery or if have infection, etc.24 ...
... Regulates or supports a variety of important cardiovascular, metabolic, immunologic, and homeostatic functions including water balance People with adrenal insufficiency: these stresses can cause hypotension, shock and death: must give glucocorticoids, eg for surgery or if have infection, etc.24 ...
Bovine Reproductive Physiology and Endocrinology
... Causes behavioral changes in the cow Causes LH surge just prior to release of follicle Coordinates acceptance of bull and release of follicle Necessary to ensure that sperm and egg meet Stimulates muscular contractions that move egg into oviduct and contractions in vagina, cervix, and uterus to move ...
... Causes behavioral changes in the cow Causes LH surge just prior to release of follicle Coordinates acceptance of bull and release of follicle Necessary to ensure that sperm and egg meet Stimulates muscular contractions that move egg into oviduct and contractions in vagina, cervix, and uterus to move ...
chapter 50 endocrine systems
... Lipid hormone receptors Receptors located within the cell (in cytosol or nucleus) Steroid hormone-receptor complex acts as transcriptional activator to enhance particular genes Transcription of gene enhance and more of that gene’s product produced Can influence a number of genes within a sing ...
... Lipid hormone receptors Receptors located within the cell (in cytosol or nucleus) Steroid hormone-receptor complex acts as transcriptional activator to enhance particular genes Transcription of gene enhance and more of that gene’s product produced Can influence a number of genes within a sing ...
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... Identify the thyroid gland in the neck of the torso model, with two lobes lateral to the trachea connected by a midline isthmus which lies anterior to the trachea. Although not shown on this torso model, attached to its posterior surface are four parathyroid glands. From Figure 17.10 in your Saladi ...
... Identify the thyroid gland in the neck of the torso model, with two lobes lateral to the trachea connected by a midline isthmus which lies anterior to the trachea. Although not shown on this torso model, attached to its posterior surface are four parathyroid glands. From Figure 17.10 in your Saladi ...
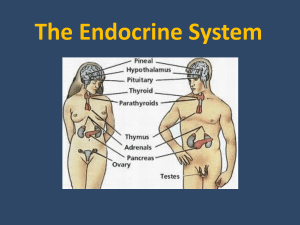
Overview of the structures of the endocrine system
... regular cycle determined by hormonal secretions (covered in later lectures). Functions of ovarian hormones and their secretions are tied to secretion of FSH and LH from anterior pituitary gland. ESTROGENS – stimulate development of female sex organs and sexual characteristics. PROGESTERONE + ESTROGE ...
... regular cycle determined by hormonal secretions (covered in later lectures). Functions of ovarian hormones and their secretions are tied to secretion of FSH and LH from anterior pituitary gland. ESTROGENS – stimulate development of female sex organs and sexual characteristics. PROGESTERONE + ESTROGE ...
The Endocrine System
... Type 1 diabetes is when the body doesn’t produce insulin. Most patience develop this disorder before the age of 40. People who have this will need to take insulin injections their whole lives. ...
... Type 1 diabetes is when the body doesn’t produce insulin. Most patience develop this disorder before the age of 40. People who have this will need to take insulin injections their whole lives. ...
Endocrine System Part 2
... Developmental Aspects of the Endocrine System Most endocrine organs operate smoothly until old age Menopause is brought about by lack of efficiency of the ovaries Problems associated with reduced estrogen are common Growth hormone production declines with age Many endocrine glands decreas ...
... Developmental Aspects of the Endocrine System Most endocrine organs operate smoothly until old age Menopause is brought about by lack of efficiency of the ovaries Problems associated with reduced estrogen are common Growth hormone production declines with age Many endocrine glands decreas ...
Endocrine and Special Senses practice Questions Scioly 2016
... A) form the basement membrane of the olfactory epithelium. B) produce a pigmented mucus that covers the olfactory epithelium. C) are sensitive to aromatic molecules in the air. D) contain the neural receptors for the sense of smell. E) form structures called olfactory bulbs. ...
... A) form the basement membrane of the olfactory epithelium. B) produce a pigmented mucus that covers the olfactory epithelium. C) are sensitive to aromatic molecules in the air. D) contain the neural receptors for the sense of smell. E) form structures called olfactory bulbs. ...
Nerve activates contraction
... secondary female characteristics – Matures female reproductive organs – Helps prepare uterus to receive a fertilized egg – Helps maintain pregnancy – Prepares breasts to produce milk ...
... secondary female characteristics – Matures female reproductive organs – Helps prepare uterus to receive a fertilized egg – Helps maintain pregnancy – Prepares breasts to produce milk ...
Introduction to the Endocrine System
... 6. Some glands have endocrine and non‐endocrine regions, which function differently. True False 7. Growth hormone is a protein that stimulates the growth of bones, muscles, and other organs by promoting protein synthesis. This hormone is produced by the pituitary gland. True False 8. The ad ...
... 6. Some glands have endocrine and non‐endocrine regions, which function differently. True False 7. Growth hormone is a protein that stimulates the growth of bones, muscles, and other organs by promoting protein synthesis. This hormone is produced by the pituitary gland. True False 8. The ad ...
Slide 1
... • Releasing hormones prompt anterior lobe to release hormones • Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) produced & secreted by specific neurons of hypothalamus cause release of FSH & LH • Inhibiting hormones turn off secretion of anterior lobe hormones ...
... • Releasing hormones prompt anterior lobe to release hormones • Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) produced & secreted by specific neurons of hypothalamus cause release of FSH & LH • Inhibiting hormones turn off secretion of anterior lobe hormones ...
III Semester Botany MODULE 7 ENDOCRINOLOGY
... posterior surface of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is composed of a large number of follicles, each a small spherical structure made of thyroid cells filled with triiodothyronine (T3), which contains three iodine atoms, and thyroxine (T4), which contains four iodine atoms. These are the two f ...
... posterior surface of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is composed of a large number of follicles, each a small spherical structure made of thyroid cells filled with triiodothyronine (T3), which contains three iodine atoms, and thyroxine (T4), which contains four iodine atoms. These are the two f ...
45_InstGuide_AR
... Describe the nature and location of intracellular receptors for hormones that pass easily through cell membranes. Explain how their role compares to the signal-transduction pathway noted above, and describe the changes they are likely to trigger within the target cell. ...
... Describe the nature and location of intracellular receptors for hormones that pass easily through cell membranes. Explain how their role compares to the signal-transduction pathway noted above, and describe the changes they are likely to trigger within the target cell. ...
The Endocrine System
... Mostly ______________________ (male sex hormones) are made but some __________________ (female sex hormones) are also formed ...
... Mostly ______________________ (male sex hormones) are made but some __________________ (female sex hormones) are also formed ...
Hormones and the Endocrine System Intercellular communication
... • Estrogens, most importantly estradiol, are responsible for maintenance of the female reproductive system and the development of female secondary sex characteristics • In mammals, progestins, which include progesterone, are primarily involved in preparing and maintaining the uterus • Synthesis of t ...
... • Estrogens, most importantly estradiol, are responsible for maintenance of the female reproductive system and the development of female secondary sex characteristics • In mammals, progestins, which include progesterone, are primarily involved in preparing and maintaining the uterus • Synthesis of t ...
system physiology-animal
... Love and hormones: falling in love and having babies change hormonal levels in both men and women! When women fall in love, their testosterone levels spike but they produce less estrogen. For men, it's the other way around. This is nature's way of reducing the differences between the sexes, making t ...
... Love and hormones: falling in love and having babies change hormonal levels in both men and women! When women fall in love, their testosterone levels spike but they produce less estrogen. For men, it's the other way around. This is nature's way of reducing the differences between the sexes, making t ...
releasing hormones
... • Nonsteroid Hormones • Usually proteins or peptides that are not fat soluble • Relies on two messengers to produce an effect • First messenger (hormone) binds to the plasma membrane • Binding triggers the release of membrane enzymes that lead to cAMP (second messenger) formation • cAMP activates ...
... • Nonsteroid Hormones • Usually proteins or peptides that are not fat soluble • Relies on two messengers to produce an effect • First messenger (hormone) binds to the plasma membrane • Binding triggers the release of membrane enzymes that lead to cAMP (second messenger) formation • cAMP activates ...
H1 Hormones - TASIS IB Biology
... Peptide and protein hormones • Soluble in plasma but cannot cross the lipid membrane • Act on cell surface receptors • Binding with the receptor leads to activtion of a ‘second messenger’ cascade ...
... Peptide and protein hormones • Soluble in plasma but cannot cross the lipid membrane • Act on cell surface receptors • Binding with the receptor leads to activtion of a ‘second messenger’ cascade ...
Chapter 25 The Endocrine Glands
... • Nonfunctional tumors: do not produce hormones but exert other effects • May encroach on important structures adjacent to optic chiasm; disrupt hormone-producing functions of anterior lobe cells ...
... • Nonfunctional tumors: do not produce hormones but exert other effects • May encroach on important structures adjacent to optic chiasm; disrupt hormone-producing functions of anterior lobe cells ...
The submandibular gland
... mandible. Most benign neoplasms are found within the superficial lobe and can be removed by a superficial parotidectomy. Tumours arising in the deep lobe of the parotid gland can grow and extend laterally, displacing the overlying superficial lobe without direct involvement. These parapharyngeal tum ...
... mandible. Most benign neoplasms are found within the superficial lobe and can be removed by a superficial parotidectomy. Tumours arising in the deep lobe of the parotid gland can grow and extend laterally, displacing the overlying superficial lobe without direct involvement. These parapharyngeal tum ...
IVA_ Endocrine_System_Chemical_Co_Ordination
... Hypothalamus is situated below the thalamus. It connects the neural and endocrine systems, as it closely tied to the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus is the master control centre of the endocrine system, as it contains several groups of neurosecretary cells called nuclei, which produce hormones cal ...
... Hypothalamus is situated below the thalamus. It connects the neural and endocrine systems, as it closely tied to the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus is the master control centre of the endocrine system, as it contains several groups of neurosecretary cells called nuclei, which produce hormones cal ...
Mammary gland

A mammary gland is an organ in female mammals that produces milk to feed young offspring. Mammals get their name from the word ""mammary."" In humans, the mammary glands are situated in the breasts. In ruminants such as cows, goats, and deer, the mammary glands are contained in the udders. The mammary glands of mammals other than primates, such as dogs and cats, are sometimes called dugs.