Chapter 15-B Endocrine Glands
... function of the gonads; ovaries and testes • Two gonadotrophins secrete from ant. Pituitary are: • LH (Luteinizing hormone) & FSH (Follicle stimulating hormone) : – Both hormones regulate production of gametes sperm cells in testes and oocytes in ovaries – And reproductive hormones • Testosterone in ...
... function of the gonads; ovaries and testes • Two gonadotrophins secrete from ant. Pituitary are: • LH (Luteinizing hormone) & FSH (Follicle stimulating hormone) : – Both hormones regulate production of gametes sperm cells in testes and oocytes in ovaries – And reproductive hormones • Testosterone in ...
CRYDERS-Endocrine System
... • A. Osmoreceptors (specialized neurons of hypothalamus monitor changes in intercellular osmolality) monitor the solute concentration of the blood • With high solutes, ADH secretion increases • ADH stimulates kidney to retain water • With low solutes, ADH is not released, thus causing ...
... • A. Osmoreceptors (specialized neurons of hypothalamus monitor changes in intercellular osmolality) monitor the solute concentration of the blood • With high solutes, ADH secretion increases • ADH stimulates kidney to retain water • With low solutes, ADH is not released, thus causing ...
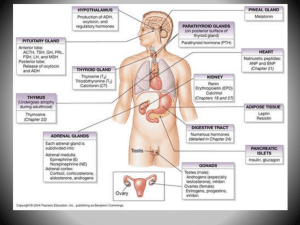
Thymus Pineal Thyroid Parathyroid
... • Description: – Large in infants/children – Decreases in size throughout adulthood – Made of fibrous connective tissue and fat ...
... • Description: – Large in infants/children – Decreases in size throughout adulthood – Made of fibrous connective tissue and fat ...
Ch13
... secretes a hormone called dopamine which inhibits the production of prolactin. In late pregnancy, an increase in the hormone estrogen will stimulate prolactin production. Also, after a child is born breast feeding stimulates nerve endings in the nipples which stimulates the hypothalamus to release p ...
... secretes a hormone called dopamine which inhibits the production of prolactin. In late pregnancy, an increase in the hormone estrogen will stimulate prolactin production. Also, after a child is born breast feeding stimulates nerve endings in the nipples which stimulates the hypothalamus to release p ...
Unit 12 Chp 45 Animal Endocrine System Notes
... B. Chemical Signals and Their Modes of Action 1. A variety of local regulators affect neighboring target cells ...
... B. Chemical Signals and Their Modes of Action 1. A variety of local regulators affect neighboring target cells ...
Endocrine System - Bellefonte Area School District
... U.S. environment since 1979. We do not know the extent to which they can interfere with the endocrine system and cause endocrine system diseases. Based on our knowledge of the effects of certain synthetic chemicals, such as DDT, diethylstilbestrol and PCBs, and the increasing evidence that reproduct ...
... U.S. environment since 1979. We do not know the extent to which they can interfere with the endocrine system and cause endocrine system diseases. Based on our knowledge of the effects of certain synthetic chemicals, such as DDT, diethylstilbestrol and PCBs, and the increasing evidence that reproduct ...
The Endocrine System
... secretes a hormone called dopamine which inhibits the production of prolactin. In late pregnancy, an increase in the hormone estrogen will stimulate prolactin production. Also, after a child is born breast feeding stimulates nerve endings in the nipples which stimulates the hypothalamus to release p ...
... secretes a hormone called dopamine which inhibits the production of prolactin. In late pregnancy, an increase in the hormone estrogen will stimulate prolactin production. Also, after a child is born breast feeding stimulates nerve endings in the nipples which stimulates the hypothalamus to release p ...
The Endocrine System
... secretes a hormone called dopamine which inhibits the production of prolactin. In late pregnancy, an increase in the hormone estrogen will stimulate prolactin production. Also, after a child is born breast feeding stimulates nerve endings in the nipples which stimulates the hypothalamus to release p ...
... secretes a hormone called dopamine which inhibits the production of prolactin. In late pregnancy, an increase in the hormone estrogen will stimulate prolactin production. Also, after a child is born breast feeding stimulates nerve endings in the nipples which stimulates the hypothalamus to release p ...
Chapter 30
... • The CNS regulates the body’s hormones through a chain of command. • For example, the hypothalamus controls the pituitary gland with thyrotropic-releasing hormone (TRH). • This causes the pituitary to release or thyroidstimulating hormone (TSH). • TSH then causes the thyroid gland to release thyroi ...
... • The CNS regulates the body’s hormones through a chain of command. • For example, the hypothalamus controls the pituitary gland with thyrotropic-releasing hormone (TRH). • This causes the pituitary to release or thyroidstimulating hormone (TSH). • TSH then causes the thyroid gland to release thyroi ...
Chapter 13 – The Endocrine System
... secretes a hormone called dopamine which inhibits the production of prolactin. In late pregnancy, an increase in the hormone estrogen will stimulate prolactin production. Also, after a child is born breast feeding stimulates nerve endings in the nipples which stimulates the hypothalamus to release p ...
... secretes a hormone called dopamine which inhibits the production of prolactin. In late pregnancy, an increase in the hormone estrogen will stimulate prolactin production. Also, after a child is born breast feeding stimulates nerve endings in the nipples which stimulates the hypothalamus to release p ...
The Endocrine System
... secretes a hormone called dopamine which inhibits the production of prolactin. In late pregnancy, an increase in the hormone estrogen will stimulate prolactin production. Also, after a child is born breast feeding stimulates nerve endings in the nipples which stimulates the hypothalamus to release p ...
... secretes a hormone called dopamine which inhibits the production of prolactin. In late pregnancy, an increase in the hormone estrogen will stimulate prolactin production. Also, after a child is born breast feeding stimulates nerve endings in the nipples which stimulates the hypothalamus to release p ...
Hormones - hellosehat
... endocrine tissues. All anterior pituitary hormones are tropins. Releasing hormones: GHRH. Growth hormone-releasing hormone. Causes the anterior pituitary to release growth hormone. TRH. Thyroid-releasing hormone. Causes the anterior pituitary to release thyroidstimulating hormone (TSH). CRH. ...
... endocrine tissues. All anterior pituitary hormones are tropins. Releasing hormones: GHRH. Growth hormone-releasing hormone. Causes the anterior pituitary to release growth hormone. TRH. Thyroid-releasing hormone. Causes the anterior pituitary to release thyroidstimulating hormone (TSH). CRH. ...
Female Reproductive System
... The uterus measures about 7.5 cm. in length, 5 cm. in breadth, at its upper part, and nearly 2.5 cm. in thickness; it weighs from 30 to 40 gm. It is divisible into two portions. On the surface, about midway between the body and the cervix, is a slight constriction known as the isthmus, and correspon ...
... The uterus measures about 7.5 cm. in length, 5 cm. in breadth, at its upper part, and nearly 2.5 cm. in thickness; it weighs from 30 to 40 gm. It is divisible into two portions. On the surface, about midway between the body and the cervix, is a slight constriction known as the isthmus, and correspon ...
1 Chapter 2: The Endocrine System Chemical Communication
... G-proteins can also open ion channels, letting calcium into cell, which eventually stimulates cAMP production which then activates specific kinases G-coupled protein receptors have 7 transmembrane domains – For glucagon, oxytocin, and vasopressin receptors ...
... G-proteins can also open ion channels, letting calcium into cell, which eventually stimulates cAMP production which then activates specific kinases G-coupled protein receptors have 7 transmembrane domains – For glucagon, oxytocin, and vasopressin receptors ...
Power Point - Science Olympiad
... Parathyroid These four little glands are embedded in the thyroid gland They secrete parathyroid hormone which regulates the amount of calcium in the blood and its absorption by bones ...
... Parathyroid These four little glands are embedded in the thyroid gland They secrete parathyroid hormone which regulates the amount of calcium in the blood and its absorption by bones ...
The PowerPoint - helpmemrr.com
... Hormones (from Greek Harmon – to excite) : are chemical signals that are secreted into body fluids (most often the blood) and communicate regulatory messages within the body Target cells : Cells that are equipped to respond to hormones ...
... Hormones (from Greek Harmon – to excite) : are chemical signals that are secreted into body fluids (most often the blood) and communicate regulatory messages within the body Target cells : Cells that are equipped to respond to hormones ...
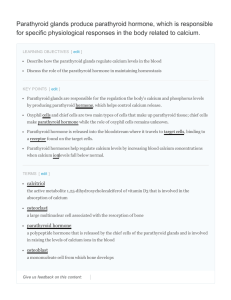
Parathyroid glands produce parathyroid hormone, which
... parathyroid hormone. Most people have four parathyroid glands; however, the number can vary from two to six. These glands are located on the posterior surface of the thyroid gland. Normally, there is a superior gland and an inferior gland associated with each of the thyroid's two ...
... parathyroid hormone. Most people have four parathyroid glands; however, the number can vary from two to six. These glands are located on the posterior surface of the thyroid gland. Normally, there is a superior gland and an inferior gland associated with each of the thyroid's two ...
The Endocrine System (Chapter 16)
... synthesis and secretion of T3 and T4 from follicular cells. Explain what thyroxine is and which thyroid hormone is the active form circulating in the blood. Explain the physiological basis for the endocrine abnormalities seen in hyperthyroidism due to Grave’s disease and in hypothyroidism due to iod ...
... synthesis and secretion of T3 and T4 from follicular cells. Explain what thyroxine is and which thyroid hormone is the active form circulating in the blood. Explain the physiological basis for the endocrine abnormalities seen in hyperthyroidism due to Grave’s disease and in hypothyroidism due to iod ...
Hormone review
... Type II diabetes is caused by a deficiency in insulin production or by changes in insulin receptors on the target cells. In either case, blood glucose level may be high because cells do not receive the message to metabolize glucose. This form of diabetes usually becomes noticeable in middle age. It ...
... Type II diabetes is caused by a deficiency in insulin production or by changes in insulin receptors on the target cells. In either case, blood glucose level may be high because cells do not receive the message to metabolize glucose. This form of diabetes usually becomes noticeable in middle age. It ...
Hormones & the Endocrine System
... Animals have 2 systems of internal communication Endocrine system: the collection of hormone secreting cells Nervous system: conveys high speed electrical signals along specialized cells called neurons The endocrine system and the nervous system act ...
... Animals have 2 systems of internal communication Endocrine system: the collection of hormone secreting cells Nervous system: conveys high speed electrical signals along specialized cells called neurons The endocrine system and the nervous system act ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 85,29 КБ
... soluble and lipid-soluble hormones. Each of these classes of hormones has specific mechanisms for their function that dictate how they affect their target cells. Water-soluble hormones: Water-soluble hormones include the peptide and amino-acid hormones such as insulin, epinephrine, HGH, and oxytocin ...
... soluble and lipid-soluble hormones. Each of these classes of hormones has specific mechanisms for their function that dictate how they affect their target cells. Water-soluble hormones: Water-soluble hormones include the peptide and amino-acid hormones such as insulin, epinephrine, HGH, and oxytocin ...
Unit 08 Endocrine System Outline
... NEW YORK — Ted James and Lysa Grant hit it off immediately when they met at a study group for a psychology class. The two students at New York University knew something was special, and four years later they are now engaged. James, 24, vividly remembers the first thing he noticed about Grant. "I jus ...
... NEW YORK — Ted James and Lysa Grant hit it off immediately when they met at a study group for a psychology class. The two students at New York University knew something was special, and four years later they are now engaged. James, 24, vividly remembers the first thing he noticed about Grant. "I jus ...
Ch. 45 - Ltcconline.net
... The focus of this chapter is on the chemical signals that make our organ systems function in a coordinated manner. Our overriding theme, however, is homeostasis- how chemical signals maintain an animal’s steady state. I. ...
... The focus of this chapter is on the chemical signals that make our organ systems function in a coordinated manner. Our overriding theme, however, is homeostasis- how chemical signals maintain an animal’s steady state. I. ...
Mammary gland

A mammary gland is an organ in female mammals that produces milk to feed young offspring. Mammals get their name from the word ""mammary."" In humans, the mammary glands are situated in the breasts. In ruminants such as cows, goats, and deer, the mammary glands are contained in the udders. The mammary glands of mammals other than primates, such as dogs and cats, are sometimes called dugs.