Chapter 45 Worksheet Sy Ha Hormones and the Endocrine System
... neurotransmitter and local regulator. For example, when oxygen levels fall in blood, NO is released which activates enzyme that relaxes smooth muscle cells, resulting in better blood flow. Prostaglandins, modified fatty acids, also have many modified activities. For example, during sex, prostagland ...
... neurotransmitter and local regulator. For example, when oxygen levels fall in blood, NO is released which activates enzyme that relaxes smooth muscle cells, resulting in better blood flow. Prostaglandins, modified fatty acids, also have many modified activities. For example, during sex, prostagland ...
SChapter9
... -Precise changes in a cell following hormone binding are specific to the hormone and cell, but typically one or more of the following occur: ...
... -Precise changes in a cell following hormone binding are specific to the hormone and cell, but typically one or more of the following occur: ...
No Slide Title
... – reacts quickly (1 - 10 msec), stops quickly – reacts slowly (seconds to days), may continue long after stimulus stops ...
... – reacts quickly (1 - 10 msec), stops quickly – reacts slowly (seconds to days), may continue long after stimulus stops ...
Hormones - SITH ITB
... The gonads secrete sex hormones • Sex hormones include – estrogens, which maintain the female reproductive system and promote the development of female characteristics, – progestins, such as progesterone, which prepare and maintain the uterus to support a developing embryo, and – androgens, suc ...
... The gonads secrete sex hormones • Sex hormones include – estrogens, which maintain the female reproductive system and promote the development of female characteristics, – progestins, such as progesterone, which prepare and maintain the uterus to support a developing embryo, and – androgens, suc ...
hormones - WordPress.com
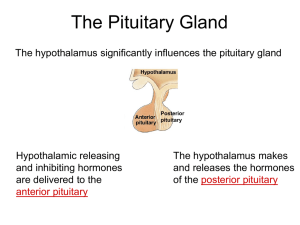
... • Hypothalamus controls synthesis and release of MANY hormones from the anterior pituitary (via releasing factors and portal circulation) • Hypothalamic neurosecretory cells release hormones (oxytocin, ADH) from the posterior pituitary gland • Negative feedback plays a major role ...
... • Hypothalamus controls synthesis and release of MANY hormones from the anterior pituitary (via releasing factors and portal circulation) • Hypothalamic neurosecretory cells release hormones (oxytocin, ADH) from the posterior pituitary gland • Negative feedback plays a major role ...
No Slide Title
... – reacts quickly (1 - 10 msec), stops quickly – reacts slowly (seconds to days), may continue long after stimulus stops ...
... – reacts quickly (1 - 10 msec), stops quickly – reacts slowly (seconds to days), may continue long after stimulus stops ...
Introduction to Endocrinology
... – Any substance normally produced by specialized cells in some part of the body, carried by the blood stream to another part, where it effects the body as a whole – Vehicles for intracellular & extracellular communication ...
... – Any substance normally produced by specialized cells in some part of the body, carried by the blood stream to another part, where it effects the body as a whole – Vehicles for intracellular & extracellular communication ...
Pineal Gland - Meridian Kinesiology
... The Pineal Gland is intricately connected to the Suprachiasmatic Nucleus (SCN) of the Hypothalamus (this accounts for its involvement in Circadian Rhythm). The Pineal Gland translates input signals such as Light and Temperature into Nerve Impulses for transmission to other parts of the Brain and bod ...
... The Pineal Gland is intricately connected to the Suprachiasmatic Nucleus (SCN) of the Hypothalamus (this accounts for its involvement in Circadian Rhythm). The Pineal Gland translates input signals such as Light and Temperature into Nerve Impulses for transmission to other parts of the Brain and bod ...
Unit 21.3 Human Endocrine System
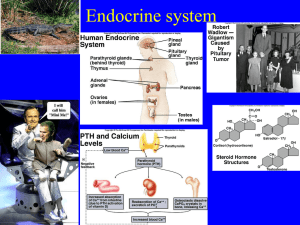
... Endocrine glands: synthesize and secrete hormones (ductless) Hormones ≡ chemicals secreted in one area of body which affect responses in other areas. The circulatory system aids in the distribution of these hormones Delivered to target tissue which recognize specific hormones by receptor cells ...
... Endocrine glands: synthesize and secrete hormones (ductless) Hormones ≡ chemicals secreted in one area of body which affect responses in other areas. The circulatory system aids in the distribution of these hormones Delivered to target tissue which recognize specific hormones by receptor cells ...
Keshara Senanayake Audesirk Chapter 33
... >lack of insulin production of the failure of target cells to respond to insulin results in diabetes mellitus >sex organs secrete steroid hormones >sex organs do far more than produce sperm or eggs -> the testes in males and ovaries in females are important endocrine organs -> testes secrete several ...
... >lack of insulin production of the failure of target cells to respond to insulin results in diabetes mellitus >sex organs secrete steroid hormones >sex organs do far more than produce sperm or eggs -> the testes in males and ovaries in females are important endocrine organs -> testes secrete several ...
chemical coordination and integration
... The adrenal medulla secretes two hormones called adrenaline or epinephrine and noradrenaline or norepinephrine. These are commonly called as catecholamines. Adrenaline and noradrenaline are rapidly secreted in response to stress of any kind and during emergency situations and are called emergency ho ...
... The adrenal medulla secretes two hormones called adrenaline or epinephrine and noradrenaline or norepinephrine. These are commonly called as catecholamines. Adrenaline and noradrenaline are rapidly secreted in response to stress of any kind and during emergency situations and are called emergency ho ...
Parotid Region
... • Buccal pad of fat • Buccopharyngeal fascia • Buccinator muscle & • Buccal mucosa • Opens into the vestibule of mouth on a small papilla, opposite the second upper molar tooth ...
... • Buccal pad of fat • Buccopharyngeal fascia • Buccinator muscle & • Buccal mucosa • Opens into the vestibule of mouth on a small papilla, opposite the second upper molar tooth ...
17. Pituitary and Adrenal Glands
... TSH – stimulates secretion of thyroid hormone and the growth of the thyroid gland. Important regulator of metabolic activity in the body. ...
... TSH – stimulates secretion of thyroid hormone and the growth of the thyroid gland. Important regulator of metabolic activity in the body. ...
Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System
... Some endocrine glands (such as the thyroid) primarily secrete hormones into the blood. Other glands (such as the pancreas) have endocrine and nonendocrine functions. Other organs (such as the stomach) are primarily nonendocrine but have some cells that secrete hormones. ...
... Some endocrine glands (such as the thyroid) primarily secrete hormones into the blood. Other glands (such as the pancreas) have endocrine and nonendocrine functions. Other organs (such as the stomach) are primarily nonendocrine but have some cells that secrete hormones. ...
Chapter 18
... cytosolic enzymes or DNA. But, first, the hormones identify the target cells by the receptors on the membrane (epinephrine, Norepinephrine, peptide hormones) or in the cytoplasm (steroid hormones) or the nucleus (thyroid hormones). The hormones which attack the target receptors on the membrane do no ...
... cytosolic enzymes or DNA. But, first, the hormones identify the target cells by the receptors on the membrane (epinephrine, Norepinephrine, peptide hormones) or in the cytoplasm (steroid hormones) or the nucleus (thyroid hormones). The hormones which attack the target receptors on the membrane do no ...
Document
... 3) Paracrine hormones. Example: prostaglandins. Derived from cholesterol • Many functions: one is to promote inflammation (pain, fever) • Aspirin, ibuprofen, celebrex: inhibit prostaglandin production but vary in side effects (some can cause _____________ in small intestine, etc) ...
... 3) Paracrine hormones. Example: prostaglandins. Derived from cholesterol • Many functions: one is to promote inflammation (pain, fever) • Aspirin, ibuprofen, celebrex: inhibit prostaglandin production but vary in side effects (some can cause _____________ in small intestine, etc) ...
You Light Up My Life - Teaching Learning Center
... Hormones are secreted by endocrine glands, endocrine cells, and some neurons. Local signaling molecules are released by some cells; these work only on nearby tissues. Pheromones are signaling molecules that have targets outside the body and which are used to integrate behaviors. ...
... Hormones are secreted by endocrine glands, endocrine cells, and some neurons. Local signaling molecules are released by some cells; these work only on nearby tissues. Pheromones are signaling molecules that have targets outside the body and which are used to integrate behaviors. ...
Hormones and the Endocrine System
... through cell membranes, while water-soluble hormones (polypeptides and amines) do not • The solubility of a hormone correlates with the location of receptors inside or on the surface of target cells ...
... through cell membranes, while water-soluble hormones (polypeptides and amines) do not • The solubility of a hormone correlates with the location of receptors inside or on the surface of target cells ...
I. General Characteristics of the Endocrine System
... amplified through second messengers. D. Prostaglandins 1. Prostaglandins are paracrine substances that act locally. 2. Some prostaglandins regulate cellular responses to hormones. 3. The variety of effects prostaglandins can produce include relaxation of smooth muscle in airway and blood vessels, co ...
... amplified through second messengers. D. Prostaglandins 1. Prostaglandins are paracrine substances that act locally. 2. Some prostaglandins regulate cellular responses to hormones. 3. The variety of effects prostaglandins can produce include relaxation of smooth muscle in airway and blood vessels, co ...
parotid gland and duct
... • Although the CN VII is embedded within the gland the CN VII does not provide innervation to the gland . the auriculotemporal nerve , a branch of CN V3 (mandibular branch of trigeminal N.) , is closely related to the parotid gland and passes superior to it with the superficial temporal vessels. The ...
... • Although the CN VII is embedded within the gland the CN VII does not provide innervation to the gland . the auriculotemporal nerve , a branch of CN V3 (mandibular branch of trigeminal N.) , is closely related to the parotid gland and passes superior to it with the superficial temporal vessels. The ...
CHAPTER 13: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... produces 2 closely related catecholamine hormones, which function in the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system: ...
... produces 2 closely related catecholamine hormones, which function in the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system: ...
Chapter 15-B Endocrine Glands
... function of the gonads; ovaries and testes • Two gonadotrophins secrete from ant. Pituitary are: • LH (Luteinizing hormone) & FSH (Follicle stimulating hormone) : – Both hormones regulate production of gametes sperm cells in testes and oocytes in ovaries – And reproductive hormones • Testosterone in ...
... function of the gonads; ovaries and testes • Two gonadotrophins secrete from ant. Pituitary are: • LH (Luteinizing hormone) & FSH (Follicle stimulating hormone) : – Both hormones regulate production of gametes sperm cells in testes and oocytes in ovaries – And reproductive hormones • Testosterone in ...
Mammary gland

A mammary gland is an organ in female mammals that produces milk to feed young offspring. Mammals get their name from the word ""mammary."" In humans, the mammary glands are situated in the breasts. In ruminants such as cows, goats, and deer, the mammary glands are contained in the udders. The mammary glands of mammals other than primates, such as dogs and cats, are sometimes called dugs.