Endocrine System Test
... D. Gland found in neck responsible for metabolism, resembles a butterfly E. Gland found in the inferior, anterior region of the brain, also referred to as the “master gland” F. Hormone which increases blood calcium G. Hormone which increases blood glucose level in times of prolonged stress H. Hormon ...
... D. Gland found in neck responsible for metabolism, resembles a butterfly E. Gland found in the inferior, anterior region of the brain, also referred to as the “master gland” F. Hormone which increases blood calcium G. Hormone which increases blood glucose level in times of prolonged stress H. Hormon ...
The Endocrine System - Discovery Education
... The pituitary gland is located just below the hypothalamus at the base of the brain. This gland controls bloood pressure, the overall chemical and physical activities of the body, growth, sexual development and reproduction. Because this gland is responsible for so much and it also controls many oth ...
... The pituitary gland is located just below the hypothalamus at the base of the brain. This gland controls bloood pressure, the overall chemical and physical activities of the body, growth, sexual development and reproduction. Because this gland is responsible for so much and it also controls many oth ...
ch_09_lecture_presentation
... •Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) •Regulates endocrine activity of the adrenal cortex •Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) •Influences growth and activity of the thyroid gland © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... •Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) •Regulates endocrine activity of the adrenal cortex •Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) •Influences growth and activity of the thyroid gland © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Thyroid Gland - Mr-Js-Science
... •Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) •Regulates endocrine activity of the adrenal cortex •Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) •Influences growth and activity of the thyroid gland © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... •Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) •Regulates endocrine activity of the adrenal cortex •Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) •Influences growth and activity of the thyroid gland © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Sheet#3,Dr.Alia , Sereen Alshawish
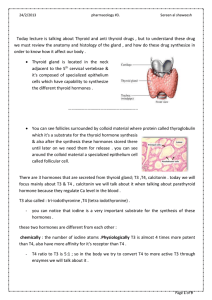
... every tissue affected by thyroid hormones , the major tissue affected : heart ,liver , kidney, skeletal muscle , pituitary gland and intestine because they have more receptors than other like spleen –not that much affected by these hormones -. 3- Control body temperature and the energy levels , how? ...
... every tissue affected by thyroid hormones , the major tissue affected : heart ,liver , kidney, skeletal muscle , pituitary gland and intestine because they have more receptors than other like spleen –not that much affected by these hormones -. 3- Control body temperature and the energy levels , how? ...
Lecture 11 Endocrine - Porterville College
... 4. What hormone targets the mammary glands? 5. What hormones target the gonads? 6. What are the targets cells of ACTH? 7. What is the action of the thyroid hormones? 8. What is the action of PTH 9. What is the purpose and action of Glucocorticoids? 10. What is the action of Epinephrine? What respons ...
... 4. What hormone targets the mammary glands? 5. What hormones target the gonads? 6. What are the targets cells of ACTH? 7. What is the action of the thyroid hormones? 8. What is the action of PTH 9. What is the purpose and action of Glucocorticoids? 10. What is the action of Epinephrine? What respons ...
Endocrine Emergencies
... We have reviewed this material in accordance with U.S. Copyright Law and have tried to maximize your ability to use, share, and adapt it. These lectures have been modified in the process of making a publicly shareable version. The citation key on the following slide provides information about how yo ...
... We have reviewed this material in accordance with U.S. Copyright Law and have tried to maximize your ability to use, share, and adapt it. These lectures have been modified in the process of making a publicly shareable version. The citation key on the following slide provides information about how yo ...
Hippocampus
... all parts of the cerebral cortex that is cognitive in nature, and another from the medial septum and parts of the hypothalamus and brain stem that is related in a general way to behavioral state. As illustrated in Fig. all sensory regions of the cerebral cortex have direct or indirect access to the ...
... all parts of the cerebral cortex that is cognitive in nature, and another from the medial septum and parts of the hypothalamus and brain stem that is related in a general way to behavioral state. As illustrated in Fig. all sensory regions of the cerebral cortex have direct or indirect access to the ...
L 1 Characters_Mechanisms_Pituitary Final
... - One hormone molecule does not trigger - the synthesis of just one enzyme molecule - It activates thousands of enzyme molecules through a cascade of called enzyme amplification - This enables a very small stimulus to produce a very large effect - Hormones are therefore needed in very small quantiti ...
... - One hormone molecule does not trigger - the synthesis of just one enzyme molecule - It activates thousands of enzyme molecules through a cascade of called enzyme amplification - This enables a very small stimulus to produce a very large effect - Hormones are therefore needed in very small quantiti ...
Trigeminal Nerve
... pons, laterally placed lesions at these levels produce a crossed picture of pain and temperature insensibility on the ipsilateral face and on the contralateral side of the body below the face. ...
... pons, laterally placed lesions at these levels produce a crossed picture of pain and temperature insensibility on the ipsilateral face and on the contralateral side of the body below the face. ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 39.1 Locomotor activity rhythm of a
... extensively to the shell. The major output of the SCN arises from the shell and is directed caudally to the subparaventricular zone (SPZ). The dorsal subparaventricular zone (dSPZ) projects to the medial preoptic area (MPOA), and is important for circadian regulation of core body temperature. Axons ...
... extensively to the shell. The major output of the SCN arises from the shell and is directed caudally to the subparaventricular zone (SPZ). The dorsal subparaventricular zone (dSPZ) projects to the medial preoptic area (MPOA), and is important for circadian regulation of core body temperature. Axons ...
Endocrine System Anatomy
... Gonadotropic = affects the male and female reproductive systems. – Follicle stimulating (luteinizing) = regulates development, growth and functions of the ovaries and testes. ...
... Gonadotropic = affects the male and female reproductive systems. – Follicle stimulating (luteinizing) = regulates development, growth and functions of the ovaries and testes. ...
Animal Models of Pediatric Combined Pituitary
... this mutation supports the hypothesis that the actions of LHX3 in the pituitary and nervous system are functionally separable, perhaps mediated by the different domains of the protein, and that the carboxyl terminus of LHX3 is essential for pituitary development. To further investigate this hypothes ...
... this mutation supports the hypothesis that the actions of LHX3 in the pituitary and nervous system are functionally separable, perhaps mediated by the different domains of the protein, and that the carboxyl terminus of LHX3 is essential for pituitary development. To further investigate this hypothes ...
Bio-Identical Hormone Replacement Therapy
... In most cases, it is beneficial to use a combination of estrogen and progesterone to obtain hormonal balance One without the other can lead to a dominance of one hormone Estrogen and Progesterone have reciprocal actions at the cellular level ...
... In most cases, it is beneficial to use a combination of estrogen and progesterone to obtain hormonal balance One without the other can lead to a dominance of one hormone Estrogen and Progesterone have reciprocal actions at the cellular level ...
The Endocrine System
... 2. When it has arrived at the target cell, the protein hormone binds with a specific receptor embedded in the cell membrane of target cell. (The number of receptors changes in response to the amount of hormone released -- “up-regulation” refers to the phenomenon where more receptors will be produced ...
... 2. When it has arrived at the target cell, the protein hormone binds with a specific receptor embedded in the cell membrane of target cell. (The number of receptors changes in response to the amount of hormone released -- “up-regulation” refers to the phenomenon where more receptors will be produced ...
Control and Coordination
... communication in human body but they have following limitations: 1. They reach only those cells that are connected by nervous tissue, not each and every cell in the animal body. 2. Cells cannot continually create and transmit electrical impulses. once an electrical impulse is generated in a cell and ...
... communication in human body but they have following limitations: 1. They reach only those cells that are connected by nervous tissue, not each and every cell in the animal body. 2. Cells cannot continually create and transmit electrical impulses. once an electrical impulse is generated in a cell and ...
Document
... control pituitary secretions and indirectly control secretions of other endocrine organs; controls adrenal medullae; secretes ADH and oxytocin • Several hormones affect neural metabolism; hormones help regulate fluid and electrolyte balance; reproductive hormones influence CNS development and behavi ...
... control pituitary secretions and indirectly control secretions of other endocrine organs; controls adrenal medullae; secretes ADH and oxytocin • Several hormones affect neural metabolism; hormones help regulate fluid and electrolyte balance; reproductive hormones influence CNS development and behavi ...
Altered functional resting-state hypothalamic connectivity and
... together” and allows for the quantification of how anatomically separated brain regions co-vary together while the brain is at rest, thus in the absence of any cognitive task. However, to date, there are limited studies performed in adults or children with PWS assessing global hypothalamic connectiv ...
... together” and allows for the quantification of how anatomically separated brain regions co-vary together while the brain is at rest, thus in the absence of any cognitive task. However, to date, there are limited studies performed in adults or children with PWS assessing global hypothalamic connectiv ...
independent work of the students
... chorionic gonadotropin, is only a temporary endocrine gland. The endocrine glands secrete chemicals known as hormones directly into the bloodstream. Because the glands have no ducts, they are sometimes called ductless glands, in contrast to exocrine, or duct glands. The autonomic nervous system con ...
... chorionic gonadotropin, is only a temporary endocrine gland. The endocrine glands secrete chemicals known as hormones directly into the bloodstream. Because the glands have no ducts, they are sometimes called ductless glands, in contrast to exocrine, or duct glands. The autonomic nervous system con ...
The Nervous System
... How the Nervous System Works (cont.) • Neurons are the long, thin cells of nerve tissues along which messages travel to and from the brain (much like a flame travels along a firecracker fuse). • Transmission between neurons, or nerve cells, occurs whenever the cells are stimulated past a minimum po ...
... How the Nervous System Works (cont.) • Neurons are the long, thin cells of nerve tissues along which messages travel to and from the brain (much like a flame travels along a firecracker fuse). • Transmission between neurons, or nerve cells, occurs whenever the cells are stimulated past a minimum po ...
Lecture 11 th week
... 1. Somatotropes—human growth hormone (hGH) 2. Corticotropes— adrenocorticotropin (ACTH) 3. Thyrotropes—thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) 4. Gonadotropes—gonadotropic hormones, which include both luteinizing hormone (LH) and folliclestimulating hormone (FSH) 5. Lactotropes—prolactin (PRL) ...
... 1. Somatotropes—human growth hormone (hGH) 2. Corticotropes— adrenocorticotropin (ACTH) 3. Thyrotropes—thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) 4. Gonadotropes—gonadotropic hormones, which include both luteinizing hormone (LH) and folliclestimulating hormone (FSH) 5. Lactotropes—prolactin (PRL) ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.