Tuberoinfundibular peptid 39 and its receptor in the central nervous
... The PTH2 receptor shows a constant expression in the brain throughout the lifespan while TIP39 is abundantly expressed only in the early postnatal life, and rapidly decreases after puberty and reactivates only under special physiological conditions. ...
... The PTH2 receptor shows a constant expression in the brain throughout the lifespan while TIP39 is abundantly expressed only in the early postnatal life, and rapidly decreases after puberty and reactivates only under special physiological conditions. ...
Endocrinology First Day
... extend of hormone defic, what they are and how long they have been deficient Hyperpituitarism is more distinct because, most often hyper involves the over production of a sinlge hormone, the clinical result is more confined and characteristic can be primary or secondary can reactive or conpensatory ...
... extend of hormone defic, what they are and how long they have been deficient Hyperpituitarism is more distinct because, most often hyper involves the over production of a sinlge hormone, the clinical result is more confined and characteristic can be primary or secondary can reactive or conpensatory ...
Snímek 1
... from the blood and it is actively transported to colloid - It is oxidized by peroxidase to molecular iodine, it is then bound to the amino acid tyrosin contained in the molecule of thyreoglobulin - It is called iodine organification - Condensation of iodine on T3 and T4 ...
... from the blood and it is actively transported to colloid - It is oxidized by peroxidase to molecular iodine, it is then bound to the amino acid tyrosin contained in the molecule of thyreoglobulin - It is called iodine organification - Condensation of iodine on T3 and T4 ...
Endocrine System - Northwest ISD Moodle
... The Endocrine System All hormones circulate to virtually every tissue but a given hormone influences the activity of only certain tissue cells called target cells Protein receptors are found on the plasma membrane that respond to only a specific hormone When the binding occurs the hormone influence ...
... The Endocrine System All hormones circulate to virtually every tissue but a given hormone influences the activity of only certain tissue cells called target cells Protein receptors are found on the plasma membrane that respond to only a specific hormone When the binding occurs the hormone influence ...
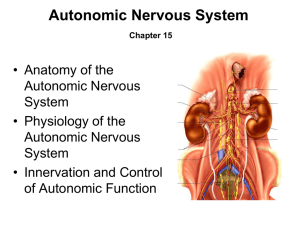
Autonomic Nervous System
... • An Adrenal Gland sits above each kidney • Adrenal Cortex secretes steroid hormones for chronic stress • Adrenal Medulla is a modified sympathetic ganglion that secretes neurotransmitters (catecholamine hormones) into the blood in response to acute stress. – catecholamines secreted by the adrenal m ...
... • An Adrenal Gland sits above each kidney • Adrenal Cortex secretes steroid hormones for chronic stress • Adrenal Medulla is a modified sympathetic ganglion that secretes neurotransmitters (catecholamine hormones) into the blood in response to acute stress. – catecholamines secreted by the adrenal m ...
attitude - Dr. Roberta Dev Anand
... products onto epithelial surfaces through tiny tubes called ducts. ...
... products onto epithelial surfaces through tiny tubes called ducts. ...
Monkey social depriv-brain I - University of Illinois Archives
... movements, self-directed behaviors, and psychosocial abnormalities, but neurobiological mechanisms underlying the behaviors of socially deprived (SD) monkeys are unknown. Monkeys were reared in total social deprivation for the first 9 months of life; control monkeys were reared socially (SR) with mo ...
... movements, self-directed behaviors, and psychosocial abnormalities, but neurobiological mechanisms underlying the behaviors of socially deprived (SD) monkeys are unknown. Monkeys were reared in total social deprivation for the first 9 months of life; control monkeys were reared socially (SR) with mo ...
BIO 12 EXAM OUTLINE
... rate at which they occur in a population Male and female sex chromosomes- what they look like, how they are different The cell cycle and what happens at each stage Terms/ definitions - crossing over, segregation, homologous chromosomes, chromatids, centromere, synapsis, monosomy, trisomy ...
... rate at which they occur in a population Male and female sex chromosomes- what they look like, how they are different The cell cycle and what happens at each stage Terms/ definitions - crossing over, segregation, homologous chromosomes, chromatids, centromere, synapsis, monosomy, trisomy ...
MODULE 8 : Endocrine System - Rajarata University of Sri Lanka
... 2.2.5. Recall that growth hormone is a single polypeptide of 70,000 MW that acts on the membrane by phosphorylation of the receptor 2.2.6. Recall that growth hormone is essential for post natal growth and for normal carbohydrate, protein, lipid and mineral metabolism 2.2.7. Recall that growth relate ...
... 2.2.5. Recall that growth hormone is a single polypeptide of 70,000 MW that acts on the membrane by phosphorylation of the receptor 2.2.6. Recall that growth hormone is essential for post natal growth and for normal carbohydrate, protein, lipid and mineral metabolism 2.2.7. Recall that growth relate ...
The following are possible
... portion of the colloid, remove thyroglobin from T3 and T4 and secrete the free hormones into the blood. ...
... portion of the colloid, remove thyroglobin from T3 and T4 and secrete the free hormones into the blood. ...
Nerve activates contraction
... Produce several androgens Testosterone is the most important androgen Responsible for adult male secondary sex characteristics Promotes growth and maturation of male reproductive system Required for sperm cell production Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummi ...
... Produce several androgens Testosterone is the most important androgen Responsible for adult male secondary sex characteristics Promotes growth and maturation of male reproductive system Required for sperm cell production Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummi ...
Endocrine Web Practice - Oakland Schools Moodle
... b. parathyroid glands secrete a hormone that causes bone to release calcium into the blood. c. thyroid gland releases calcium into the blood. d. pancreas releases insulin, which causes the cells to absorb glucose from the blood. ____ 15. Excessive production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland ...
... b. parathyroid glands secrete a hormone that causes bone to release calcium into the blood. c. thyroid gland releases calcium into the blood. d. pancreas releases insulin, which causes the cells to absorb glucose from the blood. ____ 15. Excessive production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland ...
The Endocrine System
... can become cancerous resulting in Hodgkin disease or nonHodgkin lymphomas ...
... can become cancerous resulting in Hodgkin disease or nonHodgkin lymphomas ...
Thyroid Pharmacology
... MOA: Does not effect exogenous thyroid hormone, inhibits the synthesis of thyroid hormone by inhibiting iodide incorporation into tyrosine and the coupling of iodotyrosines * inhibits the conversion of T4 to T3 ...
... MOA: Does not effect exogenous thyroid hormone, inhibits the synthesis of thyroid hormone by inhibiting iodide incorporation into tyrosine and the coupling of iodotyrosines * inhibits the conversion of T4 to T3 ...
Nerve activates contraction
... •Regulate hormonal activity of the gonads •Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) ...
... •Regulate hormonal activity of the gonads •Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) ...
Assessment and Management of Patients With Endocrine Disorders
... Compare hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism: their causes, clinical manifestations, management, and nursing ...
... Compare hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism: their causes, clinical manifestations, management, and nursing ...
Hormonal Regulation of Fluid and Electrolytes: Adrenal Cortex
... Hormonal Regulation of Fluid and Electrolytes: Posterior Pituitary • Posterior pituitary – Secretes antidiuretic hormone (ADH), oxytocin – Produced in hypothalamus, travels to posterior pituitary – Secreted upon neural signal from hypothalamus ...
... Hormonal Regulation of Fluid and Electrolytes: Posterior Pituitary • Posterior pituitary – Secretes antidiuretic hormone (ADH), oxytocin – Produced in hypothalamus, travels to posterior pituitary – Secreted upon neural signal from hypothalamus ...
Graves Disease
... Follicular Cells - Deficiency - May lead to Hypothyroidism &/or Goitre - Maternal Deficiency leads to Cretinism in Child - Limits T3/T4 Synthesis - If in Excess Thyroid limits uptake ...
... Follicular Cells - Deficiency - May lead to Hypothyroidism &/or Goitre - Maternal Deficiency leads to Cretinism in Child - Limits T3/T4 Synthesis - If in Excess Thyroid limits uptake ...
The Thyroid Gland
... Type 2 – provides intracellular T3 (brain, pituitary, adipose) Type 3 - inactivates T3 and T4 ...
... Type 2 – provides intracellular T3 (brain, pituitary, adipose) Type 3 - inactivates T3 and T4 ...
17-BASAL GANGLIA
... Caudate & Lentiform nuclei are functionally related to each other & called “Corpus striatum”:Part of extrapyramidal motor system, principally involved in the control of posture and movements (primarily by inhibiting motor functions) ...
... Caudate & Lentiform nuclei are functionally related to each other & called “Corpus striatum”:Part of extrapyramidal motor system, principally involved in the control of posture and movements (primarily by inhibiting motor functions) ...
Interstitial Cell-Stimulating Hormone Activities in the
... Interstitial Cell-Stimulating Hormone Activities in the Pituitary Gland and Peripheral Blood of Immature and Mature Male Dogs ...
... Interstitial Cell-Stimulating Hormone Activities in the Pituitary Gland and Peripheral Blood of Immature and Mature Male Dogs ...
Lesson 1 - I-Board Allied Schools
... Cerebellum: the large posterior part of the brain. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF): clear fluid that surrounds the brain and is present in the spinal cord. Cerebrum: the largest part of the brain; it is responsible for thought, personality, movement, and memory. Thalamus: lies deep within the diencephalon ...
... Cerebellum: the large posterior part of the brain. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF): clear fluid that surrounds the brain and is present in the spinal cord. Cerebrum: the largest part of the brain; it is responsible for thought, personality, movement, and memory. Thalamus: lies deep within the diencephalon ...
pineal gland
... Section C: The Vertebrate Endocrine System 1. The hypothalamus and pituitary integrate many functions of the vertebrate endocrine system 2. The pineal gland is involved in biorhythms 3. Thyroid hormones function in development, bioenergetics, and homeostasis 4. Parathyroid hormone and calcitonin bal ...
... Section C: The Vertebrate Endocrine System 1. The hypothalamus and pituitary integrate many functions of the vertebrate endocrine system 2. The pineal gland is involved in biorhythms 3. Thyroid hormones function in development, bioenergetics, and homeostasis 4. Parathyroid hormone and calcitonin bal ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.