Physiology is an Integrated Science
... >1 cell function may be turned on by one hormone hormone affects on target cell change plasma membrane permeability activate / deactivate genes activate / deactivate enzymes control protein synthesis stimulate secretion mitosis level of response depends on blood levels of hormone long term effects o ...
... >1 cell function may be turned on by one hormone hormone affects on target cell change plasma membrane permeability activate / deactivate genes activate / deactivate enzymes control protein synthesis stimulate secretion mitosis level of response depends on blood levels of hormone long term effects o ...
Chapter 16 – The Endocrine System
... • Required for adrenal cortex to ______________________ its hormone Gonadotrophic hormones • Target cells: ____________________ (testes & ovaries) • Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) – Females: • Stimulates growth & development of an ___________ that is released each month during _______________ • ...
... • Required for adrenal cortex to ______________________ its hormone Gonadotrophic hormones • Target cells: ____________________ (testes & ovaries) • Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) – Females: • Stimulates growth & development of an ___________ that is released each month during _______________ • ...
Endocrine System Disorders
... • The word hormone is derived from the Greek “hormao” meaning “I excite or arouse” • Hormones communicate this effect by their unique chemical structures recognized by specific receptors on their target cells, by their patterns of secretion and their concentrations in the general or ...
... • The word hormone is derived from the Greek “hormao” meaning “I excite or arouse” • Hormones communicate this effect by their unique chemical structures recognized by specific receptors on their target cells, by their patterns of secretion and their concentrations in the general or ...
Unit P: Endocrine System
... d. When blood level of hormone increases, brain hormones stop 2. Nervous control – in some cases, sympathetic nervous system causes direct release of hormone from gland (for example, when stress causes the adrenal medulla to secrete adrenalin) ...
... d. When blood level of hormone increases, brain hormones stop 2. Nervous control – in some cases, sympathetic nervous system causes direct release of hormone from gland (for example, when stress causes the adrenal medulla to secrete adrenalin) ...
internal structure of the brain stem
... 7.Where are fibers of the corticospinal tract located in the medulla? A .Inferior olivary nucleus B. Pyramid C. Medial lemniscus 8. What is the only cranial nerve that exits dorsally ? A. Trochlear B. Oculomotor C. Abducent 9. Through which cerebral peduncle do cerebellar efferent enter the midbrain ...
... 7.Where are fibers of the corticospinal tract located in the medulla? A .Inferior olivary nucleus B. Pyramid C. Medial lemniscus 8. What is the only cranial nerve that exits dorsally ? A. Trochlear B. Oculomotor C. Abducent 9. Through which cerebral peduncle do cerebellar efferent enter the midbrain ...
Endocrine System Puberty PowerPoint
... • state physical, mental/emotional and social changes an adolescent experiences ...
... • state physical, mental/emotional and social changes an adolescent experiences ...
Chapter Two Part Two - K-Dub
... messages, just like the nervous system, but it sends them through the bloodstream instead of across synapses. These molecules, called hormones, are produced in various glands around the body. The messages go to the brain and other tissues. ...
... messages, just like the nervous system, but it sends them through the bloodstream instead of across synapses. These molecules, called hormones, are produced in various glands around the body. The messages go to the brain and other tissues. ...
Chapter Two Part Two PPT
... messages, just like the nervous system, but it sends them through the bloodstream instead of across synapses. These molecules, called hormones, are produced in various glands around the body. The messages go to the brain and other tissues. ...
... messages, just like the nervous system, but it sends them through the bloodstream instead of across synapses. These molecules, called hormones, are produced in various glands around the body. The messages go to the brain and other tissues. ...
Element Meaning - s3.amazonaws.com
... the blood is high, the islet cells of the pancreas release insulin. This hormone stimulates body cells to take up more glucose, thus lowering glucose levels in the blood. Thus, negative feedback mechanisms reverse increasing or decreasing to maintain a state of balance. In addition to negative feedb ...
... the blood is high, the islet cells of the pancreas release insulin. This hormone stimulates body cells to take up more glucose, thus lowering glucose levels in the blood. Thus, negative feedback mechanisms reverse increasing or decreasing to maintain a state of balance. In addition to negative feedb ...
Lecture 9: Chemical signals in animals
... system involving hormones • Hormone – Chemical signal secreted into body fluids (usually blood) – Effective in minute amounts ...
... system involving hormones • Hormone – Chemical signal secreted into body fluids (usually blood) – Effective in minute amounts ...
Clinical Manifestations
... melanin-stimulating hormone like effects on the skin. • - Sparse body hair in women, if the adrenal cells producing androgens are destroyed . • - Inability to respond to stressful situations, perhaps leading to severe hypotension. ...
... melanin-stimulating hormone like effects on the skin. • - Sparse body hair in women, if the adrenal cells producing androgens are destroyed . • - Inability to respond to stressful situations, perhaps leading to severe hypotension. ...
3 Endocrinology
... The pea-size pituitary gland is enclosed by sella turcica (Turk's saddle) of the sphenoid bone and is connected to the hypothalamus by a funnel-shaped infundibulum. In humans, the pituitary gland has two major lobes: the anterior lobe or adenohypophysis, composed of glandular tissue and the site of ...
... The pea-size pituitary gland is enclosed by sella turcica (Turk's saddle) of the sphenoid bone and is connected to the hypothalamus by a funnel-shaped infundibulum. In humans, the pituitary gland has two major lobes: the anterior lobe or adenohypophysis, composed of glandular tissue and the site of ...
endocr
... The pea-size pituitary gland is enclosed by sella turcica (Turk's saddle) of the sphenoid bone and is connected to the hypothalamus by a funnel-shaped infundibulum. In humans, the pituitary gland has two major lobes: the anterior lobe or adenohypophysis, composed of glandular tissue and the site of ...
... The pea-size pituitary gland is enclosed by sella turcica (Turk's saddle) of the sphenoid bone and is connected to the hypothalamus by a funnel-shaped infundibulum. In humans, the pituitary gland has two major lobes: the anterior lobe or adenohypophysis, composed of glandular tissue and the site of ...
Endocrine System - Mercer Island School District
... Pituitary Gland: Produces hormones that control many functions Thyroid Gland: Produces thyroid hormones that regulate the body’s metabolism Adrenals: Inner part produces, hormones called catecholamines which help the body cope with physical and emotional stress ...
... Pituitary Gland: Produces hormones that control many functions Thyroid Gland: Produces thyroid hormones that regulate the body’s metabolism Adrenals: Inner part produces, hormones called catecholamines which help the body cope with physical and emotional stress ...
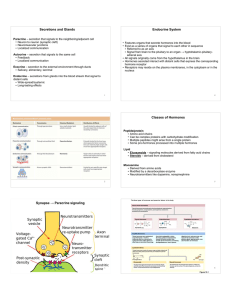
Secretions and Glands Endocrine System Classes of Hormones
... ● Has neurons that secrete two hormones released from posterior pituitary ● Antidiuretic hormone (from supraoptic nucleus) aka Vasopressin ● Oxytocin (from paraventricular nucleus) ● Secretes regulatory hormones or tropic hormones that control anterior pituitary gland endocrine cells ● Released from ...
... ● Has neurons that secrete two hormones released from posterior pituitary ● Antidiuretic hormone (from supraoptic nucleus) aka Vasopressin ● Oxytocin (from paraventricular nucleus) ● Secretes regulatory hormones or tropic hormones that control anterior pituitary gland endocrine cells ● Released from ...
Increases blood calcium levels Parathyroid Hormone
... The islets of Langerhans are the region of the pancreas that contain its endocrine cells. Can you remember what hormones are produced here? ...
... The islets of Langerhans are the region of the pancreas that contain its endocrine cells. Can you remember what hormones are produced here? ...
Thyroid Cancer Treatment
... stimulate the production of TRH and subsequently higher levels of TSH and thyroid hormones. High levels of thyroid hormones inhibit the production of TRH, which lowers TSH, thereby regulating thyroid function. ...
... stimulate the production of TRH and subsequently higher levels of TSH and thyroid hormones. High levels of thyroid hormones inhibit the production of TRH, which lowers TSH, thereby regulating thyroid function. ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM STUDY GUIDE
... 1. What gland is found on the posterior side of the thyroid gland? What hormone does this gland secrete? 2. What does PTH regulate? What does PTH in the blood cause to happen? 3. What does hypercalcemic mean? What does hypocalcemic mean? 4. How do PTH and calcitonin work together to control blood ca ...
... 1. What gland is found on the posterior side of the thyroid gland? What hormone does this gland secrete? 2. What does PTH regulate? What does PTH in the blood cause to happen? 3. What does hypercalcemic mean? What does hypocalcemic mean? 4. How do PTH and calcitonin work together to control blood ca ...
Anterior pituitary insufficiency
... development during pregnancy and to induce lactation Prolactin also binds to specific receptors in the gonads, lymphoid cells, and liver Secretion is pulsatile; it increases with sleep, stress, pregnancy, and chest wall stimulation or trauma ...
... development during pregnancy and to induce lactation Prolactin also binds to specific receptors in the gonads, lymphoid cells, and liver Secretion is pulsatile; it increases with sleep, stress, pregnancy, and chest wall stimulation or trauma ...
Endocrine System
... a. Blood level of hormone falls b. Brains gets message and sends out hormone to stimulate gland c. Gland secretes more hormone d. When blood level of hormone increases, brain hormones stop 2. Nervous control – in some cases, sympathetic nervous system causes direct release of hormone from gland (for ...
... a. Blood level of hormone falls b. Brains gets message and sends out hormone to stimulate gland c. Gland secretes more hormone d. When blood level of hormone increases, brain hormones stop 2. Nervous control – in some cases, sympathetic nervous system causes direct release of hormone from gland (for ...
Chapter 21: Blood Vessels and Circulation
... • Endocrine glands are ductless glands • Communicate with other cells/organs/ systems in the body through release of hormones • Endocrine cells hormone (chemical messenger) interstitial fluid or circulatory system target cells ...
... • Endocrine glands are ductless glands • Communicate with other cells/organs/ systems in the body through release of hormones • Endocrine cells hormone (chemical messenger) interstitial fluid or circulatory system target cells ...
The Nervous System Part 2
... target glands and organs – One of its major functions is to stimulate the medulla of the adrenal glands to release a hormone called epinephrine – The resulting hormone rush is more commonly known as adrenaline ...
... target glands and organs – One of its major functions is to stimulate the medulla of the adrenal glands to release a hormone called epinephrine – The resulting hormone rush is more commonly known as adrenaline ...
the PDF file
... receptors will be disrupted. As both these signals meet in a bundle in spinal cord so there is any spinal cord injury then both these signals are disrupted. 8. How does chemical coordination occur in plants? Answer Chemical coordination occurs in plants with the help of plant hormones. Different pla ...
... receptors will be disrupted. As both these signals meet in a bundle in spinal cord so there is any spinal cord injury then both these signals are disrupted. 8. How does chemical coordination occur in plants? Answer Chemical coordination occurs in plants with the help of plant hormones. Different pla ...
Document
... • The receptor neurons synapse with mitral cells at a junction called the glomeruli. • Axons from neurons bearing the same kind of stimulus, for example the smell of perfume, converge on a given type of glomerulus, each glomerulus receives only one type of odor signal. • Mitral cells refine the sig ...
... • The receptor neurons synapse with mitral cells at a junction called the glomeruli. • Axons from neurons bearing the same kind of stimulus, for example the smell of perfume, converge on a given type of glomerulus, each glomerulus receives only one type of odor signal. • Mitral cells refine the sig ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.