Adrenal medulla
... • Hypopituitarism: deficiency of one or more hormones resulting in metabolic and sexual dysfunction • Panhypopituitarism: decreased production of all anterior pituitary hormones • Hyperpituitarism: hormone oversecretion – ACTH secretion of MSH – PRL(prolactin) inhibits secretion of gonadotropins and ...
... • Hypopituitarism: deficiency of one or more hormones resulting in metabolic and sexual dysfunction • Panhypopituitarism: decreased production of all anterior pituitary hormones • Hyperpituitarism: hormone oversecretion – ACTH secretion of MSH – PRL(prolactin) inhibits secretion of gonadotropins and ...
DIRECTIONS: Each of the questions or incomplete statements
... (B) PFA mobilization is increased due to reduced lipoprotein lipase activity (C) Triglyceride formation is limited by availability of glucose (D) Muscle protein catabolism leads to an increase in the circulating levels of ketogenic ...
... (B) PFA mobilization is increased due to reduced lipoprotein lipase activity (C) Triglyceride formation is limited by availability of glucose (D) Muscle protein catabolism leads to an increase in the circulating levels of ketogenic ...
isolated adrenocorticotropic hormone (acth)
... adrenal insufficiency with low cortisol production and normal secretion of pituitary hormones other than ACTH. Isolated ACTH deficiency has rare association with Hashimoto’s disease which is characterized by autoimmune origin. This suggests the possibility of common autoimmune process affecting both ...
... adrenal insufficiency with low cortisol production and normal secretion of pituitary hormones other than ACTH. Isolated ACTH deficiency has rare association with Hashimoto’s disease which is characterized by autoimmune origin. This suggests the possibility of common autoimmune process affecting both ...
Endocrine System Notes
... changes within the target cell through chemical reactions • Most hormones have primary effects that directly regulate target cells and many secondary effects that influence or modulate other regulatory mechanisms in target cells • Endocrine glands produce more hormone molecules than are needed; the ...
... changes within the target cell through chemical reactions • Most hormones have primary effects that directly regulate target cells and many secondary effects that influence or modulate other regulatory mechanisms in target cells • Endocrine glands produce more hormone molecules than are needed; the ...
Endocrine system Review What governs magnitude of hormone
... treat too much pituitary thyrotropin (Fig ...
... treat too much pituitary thyrotropin (Fig ...
Your Amazing Brain:
... Your brain makes up about 2% of body weight yet takes 20% of the body’s blood supply Brain does not fully mature until age 25-30 years ...
... Your brain makes up about 2% of body weight yet takes 20% of the body’s blood supply Brain does not fully mature until age 25-30 years ...
Endocrine and Nervous System
... Hormones are chemicals released in one part of the body that travel through the bloodstream and affect the activities of cells in other parts of the body. ...
... Hormones are chemicals released in one part of the body that travel through the bloodstream and affect the activities of cells in other parts of the body. ...
The Endocrine System 2
... For example, thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) binds to receptors on cells of the thyroid gland, but it does not bind to cells of the ovaries because ovarian cells do not have TSH receptors. Receptors, like other cellular proteins, are constantly being synthesized and broken down. Generally, a targe ...
... For example, thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) binds to receptors on cells of the thyroid gland, but it does not bind to cells of the ovaries because ovarian cells do not have TSH receptors. Receptors, like other cellular proteins, are constantly being synthesized and broken down. Generally, a targe ...
chapter 45 - Fort Bend ISD
... The other major communication and control system is the nervous system, a network of specialized cells called neurons that transmit signals along dedicated pathways. These signals in turn regulate other cells, including neurons, muscle cells, and endocrine cells. ...
... The other major communication and control system is the nervous system, a network of specialized cells called neurons that transmit signals along dedicated pathways. These signals in turn regulate other cells, including neurons, muscle cells, and endocrine cells. ...
The pituitary gland and hypothalamus
... form the pituitary stalk. The neurohypophysis strictly consists of three parts: the median eminence, which is the neural tissue of the hypothalamus from which the pituitary protrudes, the posterior pituitary itself, and the infundibular stem, which connects the two. The anterior pituitary gland play ...
... form the pituitary stalk. The neurohypophysis strictly consists of three parts: the median eminence, which is the neural tissue of the hypothalamus from which the pituitary protrudes, the posterior pituitary itself, and the infundibular stem, which connects the two. The anterior pituitary gland play ...
chemical coordination and integration
... Four parathyroid glands are present on the back side of thyroid gland, one pair each in the 2 lobes of the thyroid gland. The glands secrete parathormone. The hormone maintains optimum level of blood calcium and phosphorus by reducing their excretion and mobilization from bones when required. Parath ...
... Four parathyroid glands are present on the back side of thyroid gland, one pair each in the 2 lobes of the thyroid gland. The glands secrete parathormone. The hormone maintains optimum level of blood calcium and phosphorus by reducing their excretion and mobilization from bones when required. Parath ...
Brain Gender Identity
... critical time without disrupting the reproductive axis. This has been shown in mice exposed to DES in-utero. (Warita, 2006) ...
... critical time without disrupting the reproductive axis. This has been shown in mice exposed to DES in-utero. (Warita, 2006) ...
Nervous System Lecture
... Neurons are the building blocks of the nervous system There are approximately 100 billion of them in the nervous system All neurons have the same basic structures – Cell body (contains all of the DNA and controls cellular functions) – Axon (take information away from the cell body) • Some neurons ca ...
... Neurons are the building blocks of the nervous system There are approximately 100 billion of them in the nervous system All neurons have the same basic structures – Cell body (contains all of the DNA and controls cellular functions) – Axon (take information away from the cell body) • Some neurons ca ...
Neuroscience and Behavior Notes 2-2 (obj 7-10)
... Interconnected neurons form networks in the brain. Theses networks are complex and modify with growth and experience. ...
... Interconnected neurons form networks in the brain. Theses networks are complex and modify with growth and experience. ...
Endocrine System
... • Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) – Females: • Stimulates growth & development of an ovum that is released each month during ovulation • Stimulate estrogen release from the ovaries ...
... • Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) – Females: • Stimulates growth & development of an ovum that is released each month during ovulation • Stimulate estrogen release from the ovaries ...
Pituitary and Adrenal Gland Dysfunction
... Disorders of the Anterior Pituitary Gland Target tissue Thyroid, adrenal cortex, ovary, testes, uterus, mammary glands and kidney ...
... Disorders of the Anterior Pituitary Gland Target tissue Thyroid, adrenal cortex, ovary, testes, uterus, mammary glands and kidney ...
Notes - Scioly.org
... Note: Although autonomic motor nerves control (sympathetic) rate/strength of the heart beat (ex: in order to increase oxygen circulation during exercise), contraction is triggered by the heart itself. 2 Picture showing the pathway the heart uses to trigger its own contractions: ...
... Note: Although autonomic motor nerves control (sympathetic) rate/strength of the heart beat (ex: in order to increase oxygen circulation during exercise), contraction is triggered by the heart itself. 2 Picture showing the pathway the heart uses to trigger its own contractions: ...
Biol 155 Human Physiology
... Primarily under inhibitory control. This means that if there is an injury to the hypophyseal portal system which blocks hypothalamic regulation of the pituitary gland, PRL levels increase. All other pituitary hormone levels decrease when this happens. ...
... Primarily under inhibitory control. This means that if there is an injury to the hypophyseal portal system which blocks hypothalamic regulation of the pituitary gland, PRL levels increase. All other pituitary hormone levels decrease when this happens. ...
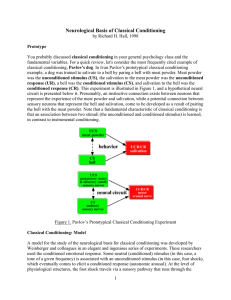
Neurological Basis of Classical Conditioning
... In order to test the viability of the neurological model presented above, Weinberger and colleagues began by establishing the tonotopic frequency of a set of neurons within the auditory system, in particular the auditory cortex. Many cells in the auditory system are "tuned" to a given frequency, tha ...
... In order to test the viability of the neurological model presented above, Weinberger and colleagues began by establishing the tonotopic frequency of a set of neurons within the auditory system, in particular the auditory cortex. Many cells in the auditory system are "tuned" to a given frequency, tha ...
Estrogen
... the ovaries, and during pregnancy, the placenta. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimulates the ovarian production of estrogens by the granulosa cells of the ovarian follicles and corpora lutea. Some estrogens are also produced in smaller amounts by other tissues such as the liver, adrenal glands ...
... the ovaries, and during pregnancy, the placenta. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimulates the ovarian production of estrogens by the granulosa cells of the ovarian follicles and corpora lutea. Some estrogens are also produced in smaller amounts by other tissues such as the liver, adrenal glands ...
Lab 01 - Endocrine Anatomy
... signal the anterior lobe to secrete tropic hormones that target other endocrine glands, inducing them to produce and secrete their own hormones. The posterior lobe does not produce hormones. Instead, its function is to store and release antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and oxytocin (OT), which are both pr ...
... signal the anterior lobe to secrete tropic hormones that target other endocrine glands, inducing them to produce and secrete their own hormones. The posterior lobe does not produce hormones. Instead, its function is to store and release antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and oxytocin (OT), which are both pr ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.