01 - ALCA
... - INSERT picture of the placement of the endocrine glands & get two different map/marker colors. - The first color represents the ‘true’ endocrine glands, which means this is the only job…to be an endocrine gland. - The second color represents glands that have other functions, but also have endocrin ...
... - INSERT picture of the placement of the endocrine glands & get two different map/marker colors. - The first color represents the ‘true’ endocrine glands, which means this is the only job…to be an endocrine gland. - The second color represents glands that have other functions, but also have endocrin ...
20. Endocrine System
... 3. Explain the relationships between the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland. The pituitary (pi-too í -tār-ē) gland, or hypophysis (hı̄-pof í -sis; undergrowth), lies inferior to the hypothalamus (figure 20.4). The small, slightly oval gland is housed within the hypophyseal fossa in the sella t ...
... 3. Explain the relationships between the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland. The pituitary (pi-too í -tār-ē) gland, or hypophysis (hı̄-pof í -sis; undergrowth), lies inferior to the hypothalamus (figure 20.4). The small, slightly oval gland is housed within the hypophyseal fossa in the sella t ...
The Endocrine System: Regulating the Body`s
... the response of turning on a furnace. The heat from the furnace raises the temperature, causing the furnace to turn off. Ask students how negative feedback works in the example in the video of the boy shivering in the cold. If students have trouble, help them by reminding them that the hypothalamus ...
... the response of turning on a furnace. The heat from the furnace raises the temperature, causing the furnace to turn off. Ask students how negative feedback works in the example in the video of the boy shivering in the cold. If students have trouble, help them by reminding them that the hypothalamus ...
power pt notes endo - Aurora City School
... activate G proteins. They exert their effects on target cells through a second messenger, such as cAMP, which alters the activity of enzymes present in the cell. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... activate G proteins. They exert their effects on target cells through a second messenger, such as cAMP, which alters the activity of enzymes present in the cell. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Document
... with endocrine system • Chemical structures similar to those of some hormones • Examples: pesticides, herbicides, etc. ...
... with endocrine system • Chemical structures similar to those of some hormones • Examples: pesticides, herbicides, etc. ...
hormones - Zanichelli
... norepinephrine, which have a short-term effect. The adrenal cortex secretes hormones that provide long-term responses to stress (sex hormones, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids). ...
... norepinephrine, which have a short-term effect. The adrenal cortex secretes hormones that provide long-term responses to stress (sex hormones, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids). ...
hormones - Zanichelli
... norepinephrine, which have a short-term effects. The adrenal cortex secretes hormones that provide long-term responses to stress (sex hormones, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids). ...
... norepinephrine, which have a short-term effects. The adrenal cortex secretes hormones that provide long-term responses to stress (sex hormones, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids). ...
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... Adrenalcorticoids hormones ~ corticosteroids Eicosanoids (eye cos an oids) Increase inflammation & cause swelling NON-CIRCULATING hormones ~ act locally only Released from most cell membranes & have a highly localized response Prostaglandins ~ most common ...
... Adrenalcorticoids hormones ~ corticosteroids Eicosanoids (eye cos an oids) Increase inflammation & cause swelling NON-CIRCULATING hormones ~ act locally only Released from most cell membranes & have a highly localized response Prostaglandins ~ most common ...
hormones
... b. Identify the nine pituitary hormones and their target tissues. c. In a dehydrated person, how would the amount of ADH released by the posterior pituitary change? © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... b. Identify the nine pituitary hormones and their target tissues. c. In a dehydrated person, how would the amount of ADH released by the posterior pituitary change? © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Focused Endocrine Assessment
... Conflict of Interest and Commercial Support RN.com strives to present content in a fair and unbiased manner at all times, and has a full and fair disclosure policy that requires course faculty to declare any real or apparent commercial affiliation related to the content of this presentation. Note: C ...
... Conflict of Interest and Commercial Support RN.com strives to present content in a fair and unbiased manner at all times, and has a full and fair disclosure policy that requires course faculty to declare any real or apparent commercial affiliation related to the content of this presentation. Note: C ...
2,3,4-Anterior Pituitary 12017-02-05 00:361.9 MB
... • Outline neuroendocrine control of growth hormone secretion • List stimuli that increase and decrease growth hormone secretion • Describe the role of prolactin in milk secretion. • Discuss regulation of prolactin secretion. ...
... • Outline neuroendocrine control of growth hormone secretion • List stimuli that increase and decrease growth hormone secretion • Describe the role of prolactin in milk secretion. • Discuss regulation of prolactin secretion. ...
I. General Characteristics of the Endocrine System
... Exocrine gland = a gland that secretes substances into ducts which then leave the body (i.e. sweat/sebaceous glands) or into a internal space or lumen (i.e. digestive glands). Exocrine glands are not part of the endocrine system! ...
... Exocrine gland = a gland that secretes substances into ducts which then leave the body (i.e. sweat/sebaceous glands) or into a internal space or lumen (i.e. digestive glands). Exocrine glands are not part of the endocrine system! ...
The Endocrine System
... • Exchange of ions and molecules between adjacent cells across gap junctions • Occurs between two cells of same type • Highly specialized and relatively rare ...
... • Exchange of ions and molecules between adjacent cells across gap junctions • Occurs between two cells of same type • Highly specialized and relatively rare ...
Overivew notes
... Hormone that targets the kidney and decreases water loss. Hormone that stimulates contraction of uterine muscles during labor and delivery, as well as contraction of cell surrounding milk secretory cells in mammary glands. ...
... Hormone that targets the kidney and decreases water loss. Hormone that stimulates contraction of uterine muscles during labor and delivery, as well as contraction of cell surrounding milk secretory cells in mammary glands. ...
2-Anterior pituitary hormones
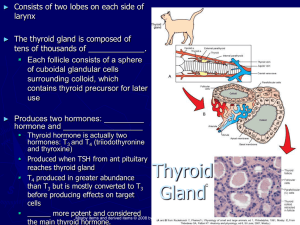
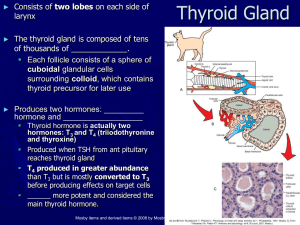
... wrapped around the front of the trachea.It composed of many spherical structures called follicles, each consisting of a single layer of epithelial cell surrounding an extracellular central space filled with a glycoprotein colloid called amine hormones- thyroxine (T4) and triiododothyronine (T3), par ...
... wrapped around the front of the trachea.It composed of many spherical structures called follicles, each consisting of a single layer of epithelial cell surrounding an extracellular central space filled with a glycoprotein colloid called amine hormones- thyroxine (T4) and triiododothyronine (T3), par ...
Dissection of the Brain, Hypothalamus and Pituitary
... 2) To introduce the anatomical, neural, and vascular relationships between the hypothalamus and the pituitary (anterior and posterior), which allow them to communicate with each other. ...
... 2) To introduce the anatomical, neural, and vascular relationships between the hypothalamus and the pituitary (anterior and posterior), which allow them to communicate with each other. ...
Document
... the hormone glucagon which causes the breakdown of stored glycogen in the liver and thereby increases the glucose level in the blood ...
... the hormone glucagon which causes the breakdown of stored glycogen in the liver and thereby increases the glucose level in the blood ...
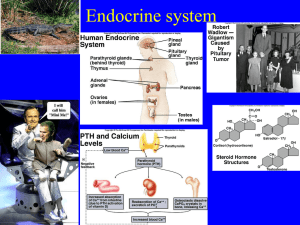
Endocrine Lecture
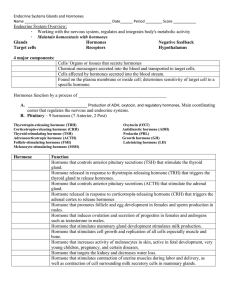
... Purpose of Endocrine system • A system consisting of glands throughout the body that secrete specialized endocrine cells within each gland. • The secretion of these specialized cells are HORMONES. • IMP.. Hormones are either stimulatory or inhibitory!!!!! • Each of the glands produces, synthesizes ...
... Purpose of Endocrine system • A system consisting of glands throughout the body that secrete specialized endocrine cells within each gland. • The secretion of these specialized cells are HORMONES. • IMP.. Hormones are either stimulatory or inhibitory!!!!! • Each of the glands produces, synthesizes ...
Thyroid Gland
... Produced by C cells (parafollicular cells) located between thyroid follicles Maintains homeostasis of blood _______________ levels Calcium is necessary for muscle contraction, blood clotting, milk secretion, and formation/maintenance of skeleton. Calcium levels must be kept within a narrow range t ...
... Produced by C cells (parafollicular cells) located between thyroid follicles Maintains homeostasis of blood _______________ levels Calcium is necessary for muscle contraction, blood clotting, milk secretion, and formation/maintenance of skeleton. Calcium levels must be kept within a narrow range t ...
Thyroid Gland - Claire Simms, DVM VTI
... Produced by C cells (parafollicular cells) located between thyroid follicles Maintains homeostasis of blood _______________ levels Calcium is necessary for muscle contraction, blood clotting, milk secretion, and formation/maintenance of skeleton. Calcium levels must be kept within a narrow range t ...
... Produced by C cells (parafollicular cells) located between thyroid follicles Maintains homeostasis of blood _______________ levels Calcium is necessary for muscle contraction, blood clotting, milk secretion, and formation/maintenance of skeleton. Calcium levels must be kept within a narrow range t ...
Presentation - Online Veterinary Anatomy Museum
... Where are ‘C’ cells located? C cells also called parafollicular cells are derived from the neural crest; they occur singly amongst the follicle cells or more usually are found in small groups between the follicles. ...
... Where are ‘C’ cells located? C cells also called parafollicular cells are derived from the neural crest; they occur singly amongst the follicle cells or more usually are found in small groups between the follicles. ...
Biochemistry of hormones derived from amino acids and proteins
... reticulum) - removal of the pre-sequence, sometimes glycosylation - resulting in prohormones the prohormones - packaged into membrane-bound secretory vesicles - secreted from the cell by exocytosis in response to specific stimuli mature peptide hormones diffuse through the blood to all of the ce ...
... reticulum) - removal of the pre-sequence, sometimes glycosylation - resulting in prohormones the prohormones - packaged into membrane-bound secretory vesicles - secreted from the cell by exocytosis in response to specific stimuli mature peptide hormones diffuse through the blood to all of the ce ...
Endocrine System
... Endocrine System There are several endocrine glands located throughout the body. Other glands, called exocrine glands, are different in that they do not empty into the bloodstream, but rather release their secretions through narrow tubes, or ducts. The pancreas is a gland that serves a dual r ...
... Endocrine System There are several endocrine glands located throughout the body. Other glands, called exocrine glands, are different in that they do not empty into the bloodstream, but rather release their secretions through narrow tubes, or ducts. The pancreas is a gland that serves a dual r ...
Steroid Hormones - Dr-Manar-KSU
... Hyperthyroidism: the excessive secretion of thyroid hormones causes: ...
... Hyperthyroidism: the excessive secretion of thyroid hormones causes: ...
Hypothalamic and Pituitary Hormones
... • Four (4) of these ones are called Tropic Hormones as they stimulate the growth, nutrition and function of : • other endocrine glands • TSH : regulates Thyroid gland secretion • ACTH : controls secretion of Adrenal Cortex • FSH : maintains female sex hormones level and follicle growth • LH : regula ...
... • Four (4) of these ones are called Tropic Hormones as they stimulate the growth, nutrition and function of : • other endocrine glands • TSH : regulates Thyroid gland secretion • ACTH : controls secretion of Adrenal Cortex • FSH : maintains female sex hormones level and follicle growth • LH : regula ...
Thyroid

The thyroid gland, or simply the thyroid /ˈθaɪrɔɪd/, is one of the largest endocrine glands in the body, and consists of two connected lobes. It is found in the neck, below the laryngeal prominence (Adam's apple). The thyroid gland controls how quickly the body uses energy, makes proteins, and controls the body's sensitivity to other hormones. It participates in these processes by producing thyroid hormones, the principal ones being thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which is more active. These hormones regulate the growth and rate of function of many other systems in the body. T3 and T4 are synthesized from iodine and tyrosine. The thyroid also produces calcitonin, which plays a role in calcium homeostasis.Hormonal output from the thyroid is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) produced by the anterior pituitary, which itself is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) produced by the hypothalamus.The thyroid may be affected by some frequent thyroid diseases. Hyperthyroidism occurs when the gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones, the most common cause being Graves' disease—an autoimmune disorder. In contrast, hypothyroidism is a state of insufficient thyroid hormone production. Worldwide, the most common cause is iodine deficiency. Thyroid hormones are important for development, and hypothyroidism secondary to iodine deficiency remains the leading cause of preventable intellectual disability. In iodine-sufficient regions, the most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto's thyroiditis—also an autoimmune disease. In addition, the thyroid gland may also develop several types of nodules and cancer.