Endocrine System
... Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary Growth hormone (GH) General metabolic hormone Major effects are directed to growth of skeletal muscles and long bones Plays a role in determining final body size Causes amino acids to be built into proteins Causes fats to be broken down for a source of ...
... Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary Growth hormone (GH) General metabolic hormone Major effects are directed to growth of skeletal muscles and long bones Plays a role in determining final body size Causes amino acids to be built into proteins Causes fats to be broken down for a source of ...
The Endocrine System
... depending on the individual. Students can record the interview (with the interviewee’s permission) and play it back later to transcribe it. ...
... depending on the individual. Students can record the interview (with the interviewee’s permission) and play it back later to transcribe it. ...
topic13 - Bukowian metodyczka - misiek-puchatek
... Psychosocial dwarfism. Psychosocial, or deprivation, dwarfism is a term applied to children who are significantly retarded in growth because of environmental circumstances. Children from homes in which they receive little, if any, psychosocial stimulation display markedly delayed skeletal developmen ...
... Psychosocial dwarfism. Psychosocial, or deprivation, dwarfism is a term applied to children who are significantly retarded in growth because of environmental circumstances. Children from homes in which they receive little, if any, psychosocial stimulation display markedly delayed skeletal developmen ...
The Peripheral Endocrine Glands
... Tyrosine-containing Tg produced within the thyroid follicular cells by the endoplasmic reticulum–Golgi complex is transported by exocytosis into the colloid. Iodide is carried by secondary active transport from the blood into the colloid by symporters in the basolateral membrane of the follicular ce ...
... Tyrosine-containing Tg produced within the thyroid follicular cells by the endoplasmic reticulum–Golgi complex is transported by exocytosis into the colloid. Iodide is carried by secondary active transport from the blood into the colloid by symporters in the basolateral membrane of the follicular ce ...
anatomy of the pituitary gland
... 1) Anterior lobe (adenohypophysis): true gland, secretes hormones 2) Posterior lobe (neurohypophysis): connected to hypothalamus through hypothalamo-hypophyseal tract, stores hormones secreted by hypothalamic nuclei ...
... 1) Anterior lobe (adenohypophysis): true gland, secretes hormones 2) Posterior lobe (neurohypophysis): connected to hypothalamus through hypothalamo-hypophyseal tract, stores hormones secreted by hypothalamic nuclei ...
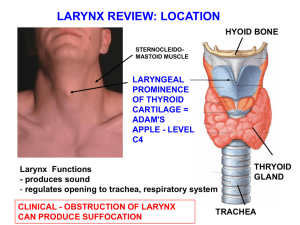
Larynx_mini_review_2012f
... OF CERVICAL VERTEBRAE CLINICAL: PALPATE CAROTID BIFURCATION LATERAL TO LARYNGEAL PROMINENCE - NERVES TO LARYNX CAN BE DAMAGED DURING CERVICAL DISC REPAIR ...
... OF CERVICAL VERTEBRAE CLINICAL: PALPATE CAROTID BIFURCATION LATERAL TO LARYNGEAL PROMINENCE - NERVES TO LARYNX CAN BE DAMAGED DURING CERVICAL DISC REPAIR ...
Chapter 10 - Hormonal and Reproductive Drugs
... messengers called hormones into the blood – Hormones are chemical substances produced by cells in one part of the body and transported to another part of the body where they influence cellular activity ...
... messengers called hormones into the blood – Hormones are chemical substances produced by cells in one part of the body and transported to another part of the body where they influence cellular activity ...
Neuroendocrine presentation
... release is controlled by neuroendocrine secretion in the posterior pituitary lobe. In addition addition, other hypothalamic neurons secrete releasing (RH) or release-inhibiting release inhibiting hormones (RIH) into the portal blood system that control hormone release from specific endocrine cells i ...
... release is controlled by neuroendocrine secretion in the posterior pituitary lobe. In addition addition, other hypothalamic neurons secrete releasing (RH) or release-inhibiting release inhibiting hormones (RIH) into the portal blood system that control hormone release from specific endocrine cells i ...
File
... Hormonal Stimuli • Hormones stimulate other endocrine organs to release their hormones – Hypothalamic hormones stimulate release of most anterior pituitary hormones – Anterior pituitary hormones stimulate targets to secrete still more hormones – Hypothalamic-pituitary-target endocrine organ feedbac ...
... Hormonal Stimuli • Hormones stimulate other endocrine organs to release their hormones – Hypothalamic hormones stimulate release of most anterior pituitary hormones – Anterior pituitary hormones stimulate targets to secrete still more hormones – Hypothalamic-pituitary-target endocrine organ feedbac ...
ORGANIZATION AND CONTROL OF ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... T3 (triiodothyronine) and Thyroid follicle → Secretion is increased by Increase basal T4 (thyroxine) or thyroid Follicular cells thyrotropin-releasing metabolic rate, hormones from follicular hormone (TRH), which stimulate cells stimulates release of thyroid- synthesis of stimulating hormone (TSH) i ...
... T3 (triiodothyronine) and Thyroid follicle → Secretion is increased by Increase basal T4 (thyroxine) or thyroid Follicular cells thyrotropin-releasing metabolic rate, hormones from follicular hormone (TRH), which stimulate cells stimulates release of thyroid- synthesis of stimulating hormone (TSH) i ...
Chapter 21: Blood Vessels and Circulation
... = TSH/thyroid-stimulating hormone = GH/growth hormone = FSH/follicle-stimulating hormone = MSH/melanocyte-stimulating hormone = LH/luteinizing hormone ...
... = TSH/thyroid-stimulating hormone = GH/growth hormone = FSH/follicle-stimulating hormone = MSH/melanocyte-stimulating hormone = LH/luteinizing hormone ...
Lesson 1
... too little or no insulin, resulting in high blood glucose levels. Symptoms include fatigue, weight loss, thirst, and frequent urination. ...
... too little or no insulin, resulting in high blood glucose levels. Symptoms include fatigue, weight loss, thirst, and frequent urination. ...
Hormone
... Transport and Regulation of TH Negative feedback regulation of TH release Rising TH levels provide negative feedback inhibition on release of TSH Hypothalamic thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) can overcome the negative feedback during pregnancy or exposure to cold ...
... Transport and Regulation of TH Negative feedback regulation of TH release Rising TH levels provide negative feedback inhibition on release of TSH Hypothalamic thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) can overcome the negative feedback during pregnancy or exposure to cold ...
Document
... too little or no insulin, resulting in high blood glucose levels. Symptoms include fatigue, weight loss, thirst, and frequent urination. ...
... too little or no insulin, resulting in high blood glucose levels. Symptoms include fatigue, weight loss, thirst, and frequent urination. ...
endocrine
... cells of the posterior pituitary The poterior pituitary is not strictly an endocrine gland, but does release hormones Slide 9.21 Edited by Dr. Ryan Lambert-Bellacov ...
... cells of the posterior pituitary The poterior pituitary is not strictly an endocrine gland, but does release hormones Slide 9.21 Edited by Dr. Ryan Lambert-Bellacov ...
Thyroid Gland - Mr-Js-Science
... •Caused by hypothyroidism in adults •Results in physical and mental slugishness •Graves’ disease •Caused by hyperthyroidism •Results in increased metabolism, heat intolerance, rapid heartbeat, weight loss, and exophthalmos © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... •Caused by hypothyroidism in adults •Results in physical and mental slugishness •Graves’ disease •Caused by hyperthyroidism •Results in increased metabolism, heat intolerance, rapid heartbeat, weight loss, and exophthalmos © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
ch_09_lecture_presentation
... •Caused by hypothyroidism in adults •Results in physical and mental slugishness •Graves’ disease •Caused by hyperthyroidism •Results in increased metabolism, heat intolerance, rapid heartbeat, weight loss, and exophthalmos © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... •Caused by hypothyroidism in adults •Results in physical and mental slugishness •Graves’ disease •Caused by hyperthyroidism •Results in increased metabolism, heat intolerance, rapid heartbeat, weight loss, and exophthalmos © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Chapter 18: The Endocrine System
... transfer information from cell to cell within a single tissue. ...
... transfer information from cell to cell within a single tissue. ...
The Endocrine System
... A) are small enough to pass directly through the membrane. B) are lipid-soluble in the bilayer. C) pass through special channels D) are water-soluble. E) dissolve in the cholesterol of the membranes. Question # 3 The reason that some individual hormones have so many different effects is that ...
... A) are small enough to pass directly through the membrane. B) are lipid-soluble in the bilayer. C) pass through special channels D) are water-soluble. E) dissolve in the cholesterol of the membranes. Question # 3 The reason that some individual hormones have so many different effects is that ...
Anatomy of Pituitary Gland
... C- Secretes hormones . 5-The Inferior hypophyseal artery supplies : A- Anterior lobe B- Posterior lobe C- infundibulum ...
... C- Secretes hormones . 5-The Inferior hypophyseal artery supplies : A- Anterior lobe B- Posterior lobe C- infundibulum ...
138 Hormones and the Body
... condition in which insufficient thyroid hormone is produced. The two thyroid hormones, T3 and T4 , both contain iodine. (T3 , or triiodothyronine, contains three iodine atoms, while T4 contains four iodine atoms.) If an iodine deficiency occurs, the body cannot make sufficient thyroid hormones, re ...
... condition in which insufficient thyroid hormone is produced. The two thyroid hormones, T3 and T4 , both contain iodine. (T3 , or triiodothyronine, contains three iodine atoms, while T4 contains four iodine atoms.) If an iodine deficiency occurs, the body cannot make sufficient thyroid hormones, re ...
Nerve activates contraction
... •Increasing heart rate, blood pressure, blood glucose levels •Dilating small passageways of lungs © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... •Increasing heart rate, blood pressure, blood glucose levels •Dilating small passageways of lungs © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Endocrine System
... Pituitary adenomas are composed of relatively uniform, polygonal cells arrayed in sheets, cords, or papillae. Supporting connective tissue, or reticulin, is sparse, accounting for the soft, gelatinous consistency of many of these tumors. The nuclei of the neoplastic cells may be uniform or pleomorph ...
... Pituitary adenomas are composed of relatively uniform, polygonal cells arrayed in sheets, cords, or papillae. Supporting connective tissue, or reticulin, is sparse, accounting for the soft, gelatinous consistency of many of these tumors. The nuclei of the neoplastic cells may be uniform or pleomorph ...
Thyroid

The thyroid gland, or simply the thyroid /ˈθaɪrɔɪd/, is one of the largest endocrine glands in the body, and consists of two connected lobes. It is found in the neck, below the laryngeal prominence (Adam's apple). The thyroid gland controls how quickly the body uses energy, makes proteins, and controls the body's sensitivity to other hormones. It participates in these processes by producing thyroid hormones, the principal ones being thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which is more active. These hormones regulate the growth and rate of function of many other systems in the body. T3 and T4 are synthesized from iodine and tyrosine. The thyroid also produces calcitonin, which plays a role in calcium homeostasis.Hormonal output from the thyroid is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) produced by the anterior pituitary, which itself is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) produced by the hypothalamus.The thyroid may be affected by some frequent thyroid diseases. Hyperthyroidism occurs when the gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones, the most common cause being Graves' disease—an autoimmune disorder. In contrast, hypothyroidism is a state of insufficient thyroid hormone production. Worldwide, the most common cause is iodine deficiency. Thyroid hormones are important for development, and hypothyroidism secondary to iodine deficiency remains the leading cause of preventable intellectual disability. In iodine-sufficient regions, the most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto's thyroiditis—also an autoimmune disease. In addition, the thyroid gland may also develop several types of nodules and cancer.