PDF - International Journal of Advanced Research
... the upper border of thyroid cartilage to be the level of bifurcation. According to Ilic, 58%cases displayed same level of origin whereas Espalieu found it to be true in 65% and Golth and Poisel in 67% of cases [6]. Zumre et al have related the bifurcation of CCA to vertebral levels. They have docume ...
... the upper border of thyroid cartilage to be the level of bifurcation. According to Ilic, 58%cases displayed same level of origin whereas Espalieu found it to be true in 65% and Golth and Poisel in 67% of cases [6]. Zumre et al have related the bifurcation of CCA to vertebral levels. They have docume ...
Endocrine System Power point use for study cards
... • Travel through portal veins • Enter anterior pituitary at capillaries Tortora & Grabowski 9/e 2000 JWS ...
... • Travel through portal veins • Enter anterior pituitary at capillaries Tortora & Grabowski 9/e 2000 JWS ...
Multiple endocrine neoplasia
... 3. Describe the transport of gases in the blood 4. Understand the metabolic processes involved in the maintenance of metabolic fuel supplies 5. Describe the basic features of endocrine cells 6. Describe and understand the molecular mechanisms involved in hormone action upon target tissues Identify a ...
... 3. Describe the transport of gases in the blood 4. Understand the metabolic processes involved in the maintenance of metabolic fuel supplies 5. Describe the basic features of endocrine cells 6. Describe and understand the molecular mechanisms involved in hormone action upon target tissues Identify a ...
ANTHONY B. OLINGER, PhD - Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott
... This work is provided “as is,” and the publisher disclaims any and all warranties, express or implied, including any warranties as to accuracy, comprehensiveness, or currency of the content of this work. This work is no substitute for individual patient assessment based upon healthcare professionals ...
... This work is provided “as is,” and the publisher disclaims any and all warranties, express or implied, including any warranties as to accuracy, comprehensiveness, or currency of the content of this work. This work is no substitute for individual patient assessment based upon healthcare professionals ...
Week 1 - Miss Cunanan`s medical Class
... Causes: removal of thyroid gland; radiation treatments to neck; obesity; may be congenital © 2014 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, ...
... Causes: removal of thyroid gland; radiation treatments to neck; obesity; may be congenital © 2014 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, ...
Hormones
... Causes: removal of thyroid gland; radiation treatments to neck; obesity; may be congenital © 2014 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, ...
... Causes: removal of thyroid gland; radiation treatments to neck; obesity; may be congenital © 2014 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, ...
17 | the endocrine system
... Patients who are referred to endocrinologists may have signs and symptoms or blood test results that suggest excessive or impaired functioning of an endocrine gland or endocrine cells. The endocrinologist may order additional blood tests to determine whether the patient’s hormonal levels are abnorma ...
... Patients who are referred to endocrinologists may have signs and symptoms or blood test results that suggest excessive or impaired functioning of an endocrine gland or endocrine cells. The endocrinologist may order additional blood tests to determine whether the patient’s hormonal levels are abnorma ...
Biochemistry of Hormones-A case oriented approach 2012
... More specifically, when a receptor becomes bound to a hormone, it undergoes a conformational change which allows it to interact productively with other components of the cells, leading ultimately to an alteration in the physiologic state of the cell. Despite the molecular diversity of hormones, all ...
... More specifically, when a receptor becomes bound to a hormone, it undergoes a conformational change which allows it to interact productively with other components of the cells, leading ultimately to an alteration in the physiologic state of the cell. Despite the molecular diversity of hormones, all ...
File
... a. glycogen is stored in large quantities. b. insulin levels still increase. c. cells do not receive glucose. d. None of the above ANS: C ...
... a. glycogen is stored in large quantities. b. insulin levels still increase. c. cells do not receive glucose. d. None of the above ANS: C ...
The Endocrine System
... or the body to maintain homeostasis, cells must be able to communicate and integrate their activities with each other. For the last five chapters, we have examined how this is achieved through the nervous system. We now turn to two modes of chemical communication called endocrine and paracrine signa ...
... or the body to maintain homeostasis, cells must be able to communicate and integrate their activities with each other. For the last five chapters, we have examined how this is achieved through the nervous system. We now turn to two modes of chemical communication called endocrine and paracrine signa ...
Gl Glands, Hormones Diabetes
... Hormone), LH (Luteinising Hormone), prolactin (released when female is suckled during lactation) and growth hormones. It also produces other hormones that control the adrenal and thyroid glands. The thyroid gland is located on the front of the trachea in the neck just below the Adam’s apple. It rele ...
... Hormone), LH (Luteinising Hormone), prolactin (released when female is suckled during lactation) and growth hormones. It also produces other hormones that control the adrenal and thyroid glands. The thyroid gland is located on the front of the trachea in the neck just below the Adam’s apple. It rele ...
Document
... Effect on active mammary glands: Stimulation of teat/nipple by nursing or milking causes oxytocin release into bloodstream Causes contraction of musclelike myoepithelial cells around mammary gland alveoli and small ducts Forces milk into lower parts of gland, making it accessible for nursing/m ...
... Effect on active mammary glands: Stimulation of teat/nipple by nursing or milking causes oxytocin release into bloodstream Causes contraction of musclelike myoepithelial cells around mammary gland alveoli and small ducts Forces milk into lower parts of gland, making it accessible for nursing/m ...
The Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland
... of rats, oxytocin has been shown to selectively act on inhibitory interneurons reducing background noise and improving signal transmission within speci c brain circuits. These studies indicate that oxytocin helps the brain focus in on socially relevant sensory input. It also is becoming clear that o ...
... of rats, oxytocin has been shown to selectively act on inhibitory interneurons reducing background noise and improving signal transmission within speci c brain circuits. These studies indicate that oxytocin helps the brain focus in on socially relevant sensory input. It also is becoming clear that o ...
endocrine system
... more mRNA molecules are transcribed, the more new protein molecules are formed, and thus the greater the magnitude of the regulatory effect. In short, the amount of steroid hormone present determines the magnitude of a target cell’s response. Also, because transcription and protein synthesis take so ...
... more mRNA molecules are transcribed, the more new protein molecules are formed, and thus the greater the magnitude of the regulatory effect. In short, the amount of steroid hormone present determines the magnitude of a target cell’s response. Also, because transcription and protein synthesis take so ...
Ch41_Endocrine Function - University of Perpetual Help System
... slavishly adhered to these teachings, many of which were the products of the early Greeks (such as Aristotle and Galen), even though personal experience provided them with contradictory evidence. The endocrine system fell victim to the outdated theories postulated long before. Even when some of its ...
... slavishly adhered to these teachings, many of which were the products of the early Greeks (such as Aristotle and Galen), even though personal experience provided them with contradictory evidence. The endocrine system fell victim to the outdated theories postulated long before. Even when some of its ...
140 Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland
... their target cells. For example, thyroidstimulating hormone (TSH) is a tropic hormone because it stimulates the release of the thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T3 ) and thyroxine (T4 ) from the thyroid gland. Some hormones, such as growth hormone (GH), exhibit both tropic and nontropic effects. ...
... their target cells. For example, thyroidstimulating hormone (TSH) is a tropic hormone because it stimulates the release of the thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T3 ) and thyroxine (T4 ) from the thyroid gland. Some hormones, such as growth hormone (GH), exhibit both tropic and nontropic effects. ...
Lesson Overview
... Calcitonin’s opposing hormone is parathyroid hormone, which is released by the four parathyroid glands located on the back surface of the thyroid. Parathyroid hormone (PTH) increases the calcium levels in the blood by promoting the release of calcium from bone, the reabsorption of calcium in the kid ...
... Calcitonin’s opposing hormone is parathyroid hormone, which is released by the four parathyroid glands located on the back surface of the thyroid. Parathyroid hormone (PTH) increases the calcium levels in the blood by promoting the release of calcium from bone, the reabsorption of calcium in the kid ...
Direct stimulation from the nervous system
... long (via bloodstream) short (across synaptic space) Mosby items and derived items © 2008 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. ...
... long (via bloodstream) short (across synaptic space) Mosby items and derived items © 2008 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. ...
39-1 The Endocrine System
... The hypothalamus is also sensitive to temperature. If body temperature drops, it produces extra TRH. TSH is released, which causes the release of more thyroxine. Thyroxine increases oxygen consumption and cellular metabolism. Increased metabolic activity maintains a core temperature. Slide 34 of 44 ...
... The hypothalamus is also sensitive to temperature. If body temperature drops, it produces extra TRH. TSH is released, which causes the release of more thyroxine. Thyroxine increases oxygen consumption and cellular metabolism. Increased metabolic activity maintains a core temperature. Slide 34 of 44 ...
012609.KChristensen.Histology-Endocrine
... We have reviewed this material in accordance with U.S. Copyright Law and have tried to maximize your ability to use, share, and adapt it. The citation key on the following slide provides information about how you may share and adapt this material. Copyright holders of content included in this materi ...
... We have reviewed this material in accordance with U.S. Copyright Law and have tried to maximize your ability to use, share, and adapt it. The citation key on the following slide provides information about how you may share and adapt this material. Copyright holders of content included in this materi ...
Structure and Development of the Parotoid Gland in
... ules, about 20 Ctmin diameter, that vary from basophilic to eosinophilic. Both types of granules stain positively for proteins and give a slightly positive PAS reaction for neutral carbohydrates. Nuclei are flattened and are limited to the periphery of the gland. Usually a distinction between cytopl ...
... ules, about 20 Ctmin diameter, that vary from basophilic to eosinophilic. Both types of granules stain positively for proteins and give a slightly positive PAS reaction for neutral carbohydrates. Nuclei are flattened and are limited to the periphery of the gland. Usually a distinction between cytopl ...
Syllabus - Etoos India
... 1. They are produced at one site and are passed by blood to another site for action. ...
... 1. They are produced at one site and are passed by blood to another site for action. ...
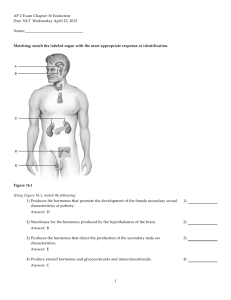
AP 2 Exam Chapter 16 Endocrine Due: NLT Wednesday April 23
... B) entering some cells and binding to intracellular receptors within the nuclei C) acting to decrease basal metabolic rate D) exerting only a minor effect on body metabolism Answer: B ...
... B) entering some cells and binding to intracellular receptors within the nuclei C) acting to decrease basal metabolic rate D) exerting only a minor effect on body metabolism Answer: B ...
Variable Origin of the Superior Laryngeal Artery and Its - al
... In the present study the external diameter of the SLA was 1.34±0.07 mm on the left side and was 1.36±0.05mm on the right side. Ozgur et al. (2009) found the external diameter of the SLA was 1.42 ± 0.47mm in their study. Lang et al. (1987) observed the average external diameter of SLA was 1.23 mm on ...
... In the present study the external diameter of the SLA was 1.34±0.07 mm on the left side and was 1.36±0.05mm on the right side. Ozgur et al. (2009) found the external diameter of the SLA was 1.42 ± 0.47mm in their study. Lang et al. (1987) observed the average external diameter of SLA was 1.23 mm on ...
29.6 The Endocrine System and Hormones
... 29.6 The Endocrine System and Hormones • There are many glands located throughout the body. Hypothalamus: makes hormones that stimulate other glands to release hormones Pituitary: controls growth and water in blood Thyroid: metabolism, energy levels, digestion Thymus: helps white blood cells fight ...
... 29.6 The Endocrine System and Hormones • There are many glands located throughout the body. Hypothalamus: makes hormones that stimulate other glands to release hormones Pituitary: controls growth and water in blood Thyroid: metabolism, energy levels, digestion Thymus: helps white blood cells fight ...
Thyroid

The thyroid gland, or simply the thyroid /ˈθaɪrɔɪd/, is one of the largest endocrine glands in the body, and consists of two connected lobes. It is found in the neck, below the laryngeal prominence (Adam's apple). The thyroid gland controls how quickly the body uses energy, makes proteins, and controls the body's sensitivity to other hormones. It participates in these processes by producing thyroid hormones, the principal ones being thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which is more active. These hormones regulate the growth and rate of function of many other systems in the body. T3 and T4 are synthesized from iodine and tyrosine. The thyroid also produces calcitonin, which plays a role in calcium homeostasis.Hormonal output from the thyroid is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) produced by the anterior pituitary, which itself is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) produced by the hypothalamus.The thyroid may be affected by some frequent thyroid diseases. Hyperthyroidism occurs when the gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones, the most common cause being Graves' disease—an autoimmune disorder. In contrast, hypothyroidism is a state of insufficient thyroid hormone production. Worldwide, the most common cause is iodine deficiency. Thyroid hormones are important for development, and hypothyroidism secondary to iodine deficiency remains the leading cause of preventable intellectual disability. In iodine-sufficient regions, the most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto's thyroiditis—also an autoimmune disease. In addition, the thyroid gland may also develop several types of nodules and cancer.