Endocrine System Notes
... Longer lasting action of hormones is _______________________. hypothalamus The ____________________, which maintains homeostasis in the body, controls most of the glands of the endocrine system. ...
... Longer lasting action of hormones is _______________________. hypothalamus The ____________________, which maintains homeostasis in the body, controls most of the glands of the endocrine system. ...
inferior thyroid a.
... the size of a small pea (about 0.5x0.8 cm ovoids) They are important because of their role in calcium metabolism. They secrete parathormone that mobilizes bone calcium and increases gut and kidney calcium absorption ...
... the size of a small pea (about 0.5x0.8 cm ovoids) They are important because of their role in calcium metabolism. They secrete parathormone that mobilizes bone calcium and increases gut and kidney calcium absorption ...
Nerve Supply
... The parathyroid glands are ovoid bodies measuring about 6 mm long in their greatest diameter. They are four in number and are closely related to the posterior border of the thyroid gland, lying within its fascial capsule. The two superior parathyroid glands are the more constant in position and lie ...
... The parathyroid glands are ovoid bodies measuring about 6 mm long in their greatest diameter. They are four in number and are closely related to the posterior border of the thyroid gland, lying within its fascial capsule. The two superior parathyroid glands are the more constant in position and lie ...
8.2 Major Endocrine Organs
... – acts on uterus, causes contractions – acts on breast, causes secretion of milk © Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. ...
... – acts on uterus, causes contractions – acts on breast, causes secretion of milk © Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. ...
The Endocrine System Chapter 10
... within their structure, but the organ’s primary function is not endocrine (ie: heart, kidney, digestive organs, pancreas hypothalamus, gonads, thymus) Some organs are primarily endocrine organs (endocrine glands) (ie. pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pineal) ...
... within their structure, but the organ’s primary function is not endocrine (ie: heart, kidney, digestive organs, pancreas hypothalamus, gonads, thymus) Some organs are primarily endocrine organs (endocrine glands) (ie. pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pineal) ...
Human Anatomy & Physiology
... • Thyroxine (T4) = more abundant than T3, but less potent • Triiodothyronine (T3) = more potent than T4 • Calcitonin ...
... • Thyroxine (T4) = more abundant than T3, but less potent • Triiodothyronine (T3) = more potent than T4 • Calcitonin ...
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... It is an organ that develops a secretion which performs specific functions. ...
... It is an organ that develops a secretion which performs specific functions. ...
Podcast summary chapter 15
... The adrenal glands secrete glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids and androgens in response to ACTH released from the anterior pituitary gland. ACTH is adrenocorticotropic hormone. The pancreas performs both endocrine and exocrine functions. The islets of Langerhans secrete insulin and glucagons, the h ...
... The adrenal glands secrete glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids and androgens in response to ACTH released from the anterior pituitary gland. ACTH is adrenocorticotropic hormone. The pancreas performs both endocrine and exocrine functions. The islets of Langerhans secrete insulin and glucagons, the h ...
1. Endocrine Glands of the Body
... Thyroid gland disorders – Clinical App ONLINE A. Hyperthyroidism = excessive thyroid hormones Causes: - thyroid tumor - Graves disease = autoimmune attack, over-stimulates thyroid receptors. Clinical presentation: - High metabolism & anxiety - Intolerant to heat (sweating) - Tachycardia - Hypertensi ...
... Thyroid gland disorders – Clinical App ONLINE A. Hyperthyroidism = excessive thyroid hormones Causes: - thyroid tumor - Graves disease = autoimmune attack, over-stimulates thyroid receptors. Clinical presentation: - High metabolism & anxiety - Intolerant to heat (sweating) - Tachycardia - Hypertensi ...
Bio Endocrine System Art
... overweight. Some kids and teens can control their blood sugar level with dietary changes, exercise, and oral medications, but many will need to take insulin injections like people with type 1 diabetes. Growth hormone problems. Too much growth hormone in kids an ...
... overweight. Some kids and teens can control their blood sugar level with dietary changes, exercise, and oral medications, but many will need to take insulin injections like people with type 1 diabetes. Growth hormone problems. Too much growth hormone in kids an ...
Chapter 13 The Endocrine System • Endocrine System Produces
... – enhance function of sympathetic nervous system (fight-or-flight response) ...
... – enhance function of sympathetic nervous system (fight-or-flight response) ...
Chapter 37: The Endocrine System
... The islets of Langerhans are clusters of endocrine cells found in the pancreas; they stain lighter than surrounding cells. (credit: modification of work by Muhammad T. Tabiin, Christopher P. White, Grant Morahan, and Bernard E. Tuch; scale-bar data from ...
... The islets of Langerhans are clusters of endocrine cells found in the pancreas; they stain lighter than surrounding cells. (credit: modification of work by Muhammad T. Tabiin, Christopher P. White, Grant Morahan, and Bernard E. Tuch; scale-bar data from ...
NECK AND MEDIASTINUM
... The deep cervical fascia forms cleavage planes that 1) limits spread of infection 2) Invests/support structures (can be manipulated); and 3) Conveys the ability for structures to slide/glide across one another ...
... The deep cervical fascia forms cleavage planes that 1) limits spread of infection 2) Invests/support structures (can be manipulated); and 3) Conveys the ability for structures to slide/glide across one another ...
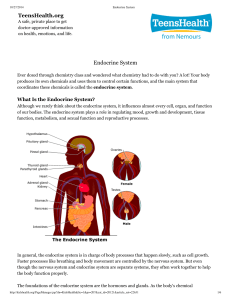
Endocrine System
... Rapidly metabolized so circulating levels are very low Produced in a tissue and diffuse a short distance to other cells in the tissue ...
... Rapidly metabolized so circulating levels are very low Produced in a tissue and diffuse a short distance to other cells in the tissue ...
Adrenal Glands
... • In males, after puberty the hormone testosterone is secreted in much larger quantities so DHEA has virtually no effect. • In females, DHEA and other adrenal androgens play a major role in promoting libido and are converted to estrogens. • In menopausal women, all female estrogens come from adrenal ...
... • In males, after puberty the hormone testosterone is secreted in much larger quantities so DHEA has virtually no effect. • In females, DHEA and other adrenal androgens play a major role in promoting libido and are converted to estrogens. • In menopausal women, all female estrogens come from adrenal ...
Indezine Template
... ENDOCRINE SYSTEM • Key role to secrete hormones • Hormones: are natural chemicals that exert their effects on specific tissues known as target tissues. • Endocrine Glands are ductless and must use the blood system to transport secreted hormones to target tissues ...
... ENDOCRINE SYSTEM • Key role to secrete hormones • Hormones: are natural chemicals that exert their effects on specific tissues known as target tissues. • Endocrine Glands are ductless and must use the blood system to transport secreted hormones to target tissues ...
Chapter 1 Goals
... Pituitary Gland Location & Structure The pituitary gland is a small pea-sized gland located at the base of the brain in a small pocketlike depression of the skull call the sella turcica. It is a well-protected gland, with the entire mass of the brain above it & the nasal cavity below. It consists ...
... Pituitary Gland Location & Structure The pituitary gland is a small pea-sized gland located at the base of the brain in a small pocketlike depression of the skull call the sella turcica. It is a well-protected gland, with the entire mass of the brain above it & the nasal cavity below. It consists ...
[ PDF ] - journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences
... (musculus levator glandulae thyroidea) sometimes descends from the hyoid body to the isthmus or apex of pyramidal lobe. EMBRYOLOGICAL BASIS: It is the first endocrine gland which appears and begins to function at approximately by the end of 3rd month, at which time the first follicles containing col ...
... (musculus levator glandulae thyroidea) sometimes descends from the hyoid body to the isthmus or apex of pyramidal lobe. EMBRYOLOGICAL BASIS: It is the first endocrine gland which appears and begins to function at approximately by the end of 3rd month, at which time the first follicles containing col ...
File - Patricia Schwandt Courses
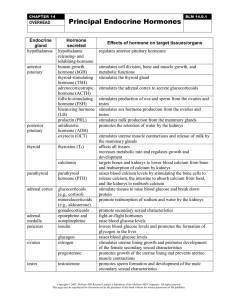
... Hormone secreted hypothalamic releasing- and inhibiting-hormone human growth hormone (hGH) thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) luteinizing hormone (LH) prolactin (PRL) antidiuretic hormone (ADH) oxytocin (OCT) ...
... Hormone secreted hypothalamic releasing- and inhibiting-hormone human growth hormone (hGH) thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) luteinizing hormone (LH) prolactin (PRL) antidiuretic hormone (ADH) oxytocin (OCT) ...
Thyroid

The thyroid gland, or simply the thyroid /ˈθaɪrɔɪd/, is one of the largest endocrine glands in the body, and consists of two connected lobes. It is found in the neck, below the laryngeal prominence (Adam's apple). The thyroid gland controls how quickly the body uses energy, makes proteins, and controls the body's sensitivity to other hormones. It participates in these processes by producing thyroid hormones, the principal ones being thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which is more active. These hormones regulate the growth and rate of function of many other systems in the body. T3 and T4 are synthesized from iodine and tyrosine. The thyroid also produces calcitonin, which plays a role in calcium homeostasis.Hormonal output from the thyroid is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) produced by the anterior pituitary, which itself is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) produced by the hypothalamus.The thyroid may be affected by some frequent thyroid diseases. Hyperthyroidism occurs when the gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones, the most common cause being Graves' disease—an autoimmune disorder. In contrast, hypothyroidism is a state of insufficient thyroid hormone production. Worldwide, the most common cause is iodine deficiency. Thyroid hormones are important for development, and hypothyroidism secondary to iodine deficiency remains the leading cause of preventable intellectual disability. In iodine-sufficient regions, the most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto's thyroiditis—also an autoimmune disease. In addition, the thyroid gland may also develop several types of nodules and cancer.



















![[ PDF ] - journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007955894_2-e1c257efa5596d9bcec4f688fb06dda4-300x300.png)