L 2 parathyroid and calcium homeostasis 25th september 2012
... • Especially diets formulated primarily on grain products • Chronically low intake of dietary Ca - stimulates increased secretion of PTH to keep blood Ca level for nerve and muscle function. • Ca is removed from bone matrix - bone decalcification - bone deformities - osteoporosis • k/s - Nutritional ...
... • Especially diets formulated primarily on grain products • Chronically low intake of dietary Ca - stimulates increased secretion of PTH to keep blood Ca level for nerve and muscle function. • Ca is removed from bone matrix - bone decalcification - bone deformities - osteoporosis • k/s - Nutritional ...
21-endocrine - life.illinois.edu
... –! May involve the same or another hormone –! As hormone levels rise, further secretion is inhibited ...
... –! May involve the same or another hormone –! As hormone levels rise, further secretion is inhibited ...
Chapter 13 Notes - Biology at the Rural
... 5)Luteinizing Hormone (LH)- releases eggs in ovaries and stimulates production of sex hormones in both males and females 6)Prolactin- protein type hormone which stimulates milk production in female after birth and the development of mammary gland tissue Posterior Lobe of Pituitary Hormones: 1) Antid ...
... 5)Luteinizing Hormone (LH)- releases eggs in ovaries and stimulates production of sex hormones in both males and females 6)Prolactin- protein type hormone which stimulates milk production in female after birth and the development of mammary gland tissue Posterior Lobe of Pituitary Hormones: 1) Antid ...
Hormonal Regula on of Homeostasis
... kidneys more permeable to water (more water retained by the body) ...
... kidneys more permeable to water (more water retained by the body) ...
Chapter 11 Endocrine System
... nervous system. The hormones secreted are the same as neurotransmitters of this system but are called hormones because they are secreted into the _______________________. Epinephrine and norepinephrine: What affect do these have on the body? What are they secreted in response to? ...
... nervous system. The hormones secreted are the same as neurotransmitters of this system but are called hormones because they are secreted into the _______________________. Epinephrine and norepinephrine: What affect do these have on the body? What are they secreted in response to? ...
HumanEndocrineSystem
... muscles of the uterus during birth. Thyroid gland The thyroid gland lies against the pharynx at the base of the neck. It consists of two lateral lobes connected by an isthmus. The gland produces thyroxine, a hormone that regulates the rate of metabolism in the body. It also produces a second hormone ...
... muscles of the uterus during birth. Thyroid gland The thyroid gland lies against the pharynx at the base of the neck. It consists of two lateral lobes connected by an isthmus. The gland produces thyroxine, a hormone that regulates the rate of metabolism in the body. It also produces a second hormone ...
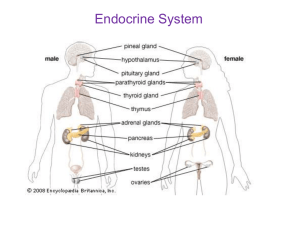
Endocrine System
... Amino acid derivatives – water-soluble molecules derived from amino acids • Epinephrine, insulin, growth hormone. • These hormones are stored in endocrine cells until needed. • They act by binding to protein receptors on the outside surface of the cell. The binding alerts a second messenger molecule ...
... Amino acid derivatives – water-soluble molecules derived from amino acids • Epinephrine, insulin, growth hormone. • These hormones are stored in endocrine cells until needed. • They act by binding to protein receptors on the outside surface of the cell. The binding alerts a second messenger molecule ...
The Endocrine System - Part 1
... What is the Function of the Endocrine System? The endocrine system is in charge of body systems that happen slowly, such as cell growth. The foundations of the endocrine system are glands and hormones. Hormones transfer information and instructions from one set of cells to another. Glands produce an ...
... What is the Function of the Endocrine System? The endocrine system is in charge of body systems that happen slowly, such as cell growth. The foundations of the endocrine system are glands and hormones. Hormones transfer information and instructions from one set of cells to another. Glands produce an ...
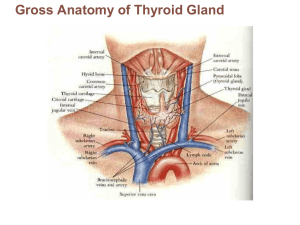
Clinical Anatomy of Thyroid Gland
... develop thyroid carcinoma in the early and middle adult years. In contrast, cases presenting in childhood and late adult life are distributed equally among males and females. • Most thyroid carcinomas (except medullary carcinomas) are derived from the thyroid follicular epithelium • There are 4 type ...
... develop thyroid carcinoma in the early and middle adult years. In contrast, cases presenting in childhood and late adult life are distributed equally among males and females. • Most thyroid carcinomas (except medullary carcinomas) are derived from the thyroid follicular epithelium • There are 4 type ...
The Endocrine System
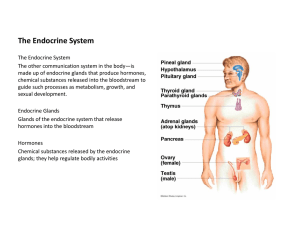
... chemical substances released into the bloodstream to guide such processes as metabolism, growth, and sexual development. Endocrine Glands Glands of the endocrine system that release hormones into the bloodstream Hormones Chemical substances released by the endocrine glands; they help regulate bodily ...
... chemical substances released into the bloodstream to guide such processes as metabolism, growth, and sexual development. Endocrine Glands Glands of the endocrine system that release hormones into the bloodstream Hormones Chemical substances released by the endocrine glands; they help regulate bodily ...
HPAT AXIS - DaVinci Labs
... of the brain which ‘regulates memory and emotions, and plays a role in various emotional disorders’ and whose size and functionality has been known to affected under extended periods of acute stress’. Long-term, chronic stress, however, also resulted in a potentially damaging overproduction of the m ...
... of the brain which ‘regulates memory and emotions, and plays a role in various emotional disorders’ and whose size and functionality has been known to affected under extended periods of acute stress’. Long-term, chronic stress, however, also resulted in a potentially damaging overproduction of the m ...
ANSWERS TO CHAPTER 10
... the thymus gland. Erythropoietin is secreted by the kidneys in response to reduced oxygen levels in the blood. Human chorionic gonadotropin is produced by the placenta; its function is similar to LH. Melatonin is produced by the pineal body, and is thought to play a role in the onset of puberty. Pro ...
... the thymus gland. Erythropoietin is secreted by the kidneys in response to reduced oxygen levels in the blood. Human chorionic gonadotropin is produced by the placenta; its function is similar to LH. Melatonin is produced by the pineal body, and is thought to play a role in the onset of puberty. Pro ...
Laryngocoele, laryngocele - Vula
... component of the cyst. It arises from the ganglion nodosum of the vagus nerve, descends alongside the pharynx, passes behind the internal carotid artery, and divides into external and internal branches. The internal branch crosses the thyrohyoid membrane and pierces it, accompanied by the superior l ...
... component of the cyst. It arises from the ganglion nodosum of the vagus nerve, descends alongside the pharynx, passes behind the internal carotid artery, and divides into external and internal branches. The internal branch crosses the thyrohyoid membrane and pierces it, accompanied by the superior l ...
Chapter 17
... – The neuronal system – has clear pathways which are connected with neurons. Thus it is reasonably clear for each neuron where it starts and where it ends. (reflex --- cerebral cortex ---- targets) – At the end knob, neurotransmitters are released. – Its complexity makes it possible to stimulate mor ...
... – The neuronal system – has clear pathways which are connected with neurons. Thus it is reasonably clear for each neuron where it starts and where it ends. (reflex --- cerebral cortex ---- targets) – At the end knob, neurotransmitters are released. – Its complexity makes it possible to stimulate mor ...
Comparative Vertebrate Physiology
... from ER Ca++ activates channels on plasma membrane or binds to calmodulin which activates metabolism ...
... from ER Ca++ activates channels on plasma membrane or binds to calmodulin which activates metabolism ...
Endocrine System
... thyroglobulin protein • Thyroid hormones synthesized by follicle cells and stored in combination with thyroglobulin ...
... thyroglobulin protein • Thyroid hormones synthesized by follicle cells and stored in combination with thyroglobulin ...
the endocrine system - The Liberty Common School
... · Know the difference between duct and ductless glands? · Define the following vocabulary as pertaining to only its job in the endocrine system: hormones, glands, endocrine glands, exocrine glands, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, pancreas gland, adrenal gland, ovaries, testes? · I ...
... · Know the difference between duct and ductless glands? · Define the following vocabulary as pertaining to only its job in the endocrine system: hormones, glands, endocrine glands, exocrine glands, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, pancreas gland, adrenal gland, ovaries, testes? · I ...
Thyroid Hormone
... Transport and Regulation of TH • Negative feedback regulation of TH release – Rising TH levels provide negative feedback inhibition on release of TSH – Hypothalamic thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) can overcome negative feedback during pregnancy or exposure to cold ...
... Transport and Regulation of TH • Negative feedback regulation of TH release – Rising TH levels provide negative feedback inhibition on release of TSH – Hypothalamic thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) can overcome negative feedback during pregnancy or exposure to cold ...
Slide 1
... • T3 or triiodothyronine: increases oxygen consumption and metabolism of all cells; regulates energy levels • T4 or thyroxine: regulates metabolism for the production of heat and energy in body tissue by controlling rate at which glucose is oxidized • Calcitonin or thyrocalcitonin: active in calcium ...
... • T3 or triiodothyronine: increases oxygen consumption and metabolism of all cells; regulates energy levels • T4 or thyroxine: regulates metabolism for the production of heat and energy in body tissue by controlling rate at which glucose is oxidized • Calcitonin or thyrocalcitonin: active in calcium ...
hormone notes
... H. Pituitary – found in sella turcia pea-size, master gland. The Anterior pituitary has hormone production glandular portion. The Posterior pituitary neural portion & extension of hypothalamus. Ex. GH (bone & muscle) & TSH (growth of thyroid) I. Thyroid-Found in anterior throat overlying inferior bo ...
... H. Pituitary – found in sella turcia pea-size, master gland. The Anterior pituitary has hormone production glandular portion. The Posterior pituitary neural portion & extension of hypothalamus. Ex. GH (bone & muscle) & TSH (growth of thyroid) I. Thyroid-Found in anterior throat overlying inferior bo ...
Genetics Information Sheet
... The thyroid gland is found in the middle of the neck, just under the Adam’s apple. Normally it makes the hormone thyroxine which regulates the metabolic rate. Thyroxine levels are not affected by Medullary Thyroid Cancer (MTC) in MEN2. The thyroid gland also makes the hormone calcitonin which has a ...
... The thyroid gland is found in the middle of the neck, just under the Adam’s apple. Normally it makes the hormone thyroxine which regulates the metabolic rate. Thyroxine levels are not affected by Medullary Thyroid Cancer (MTC) in MEN2. The thyroid gland also makes the hormone calcitonin which has a ...
Thyroid

The thyroid gland, or simply the thyroid /ˈθaɪrɔɪd/, is one of the largest endocrine glands in the body, and consists of two connected lobes. It is found in the neck, below the laryngeal prominence (Adam's apple). The thyroid gland controls how quickly the body uses energy, makes proteins, and controls the body's sensitivity to other hormones. It participates in these processes by producing thyroid hormones, the principal ones being thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which is more active. These hormones regulate the growth and rate of function of many other systems in the body. T3 and T4 are synthesized from iodine and tyrosine. The thyroid also produces calcitonin, which plays a role in calcium homeostasis.Hormonal output from the thyroid is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) produced by the anterior pituitary, which itself is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) produced by the hypothalamus.The thyroid may be affected by some frequent thyroid diseases. Hyperthyroidism occurs when the gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones, the most common cause being Graves' disease—an autoimmune disorder. In contrast, hypothyroidism is a state of insufficient thyroid hormone production. Worldwide, the most common cause is iodine deficiency. Thyroid hormones are important for development, and hypothyroidism secondary to iodine deficiency remains the leading cause of preventable intellectual disability. In iodine-sufficient regions, the most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto's thyroiditis—also an autoimmune disease. In addition, the thyroid gland may also develop several types of nodules and cancer.