Endocrine System
... • Endocrine glands: secrete hormones in small amounts directly into the bloodstream. • Specific hormones effect specific body parts. • They travel through the bloodstream until they reach their target cells (they cell that the hormone acts on) • Hormones do NOT affect other cells other than the targ ...
... • Endocrine glands: secrete hormones in small amounts directly into the bloodstream. • Specific hormones effect specific body parts. • They travel through the bloodstream until they reach their target cells (they cell that the hormone acts on) • Hormones do NOT affect other cells other than the targ ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... 3. What prevents a hormone from affecting all body cells equally? A hormone exerts a physiological effect only on target cells that have specific receptors for the hormone. 4. Many dairy operators inject their cows with bovine growth hormone to stimulate milk production. Cite two reasons that bovin ...
... 3. What prevents a hormone from affecting all body cells equally? A hormone exerts a physiological effect only on target cells that have specific receptors for the hormone. 4. Many dairy operators inject their cows with bovine growth hormone to stimulate milk production. Cite two reasons that bovin ...
Outline 14
... It stimulates the development of the eggs in the ____________ that contain them It stimulates secretion of ovarian hormones In the testes, it stimulates the production of sperm o Luteinizing Hormone In females, it stimulates ovulation (the release of the egg) It’s named for the fact that a ...
... It stimulates the development of the eggs in the ____________ that contain them It stimulates secretion of ovarian hormones In the testes, it stimulates the production of sperm o Luteinizing Hormone In females, it stimulates ovulation (the release of the egg) It’s named for the fact that a ...
Endocrine System - UNT's College of Education
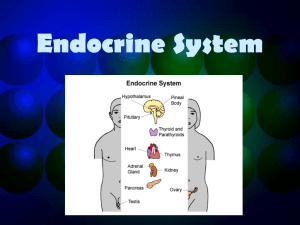
... pituitary gland. In addition, it makes hormones that are stored in the pituitary gland. Pituitary gland The pituitary gland produces hormones that regulate many of the other endocrine glands. Parathyroid glands These four glands release parathyroid hormone, which regulate the level of calcium in the ...
... pituitary gland. In addition, it makes hormones that are stored in the pituitary gland. Pituitary gland The pituitary gland produces hormones that regulate many of the other endocrine glands. Parathyroid glands These four glands release parathyroid hormone, which regulate the level of calcium in the ...
The Endocrine System
... It stimulates the development of the eggs in the follicles that contain them It stimulates secretion of ovarian hormones In the testes, it stimulates the production of sperm o Luteinizing Hormone In females, it stimulates ovulation (the release of the egg) It’s named for the fact that afte ...
... It stimulates the development of the eggs in the follicles that contain them It stimulates secretion of ovarian hormones In the testes, it stimulates the production of sperm o Luteinizing Hormone In females, it stimulates ovulation (the release of the egg) It’s named for the fact that afte ...
Prevalence of Laryngeal Cartilage Calcifications in Mangalore
... usually symmetrical.. Similar studies7,8 done in the past have reported that ossifications are first seen in the thyroid, followed by cricoid and the arytenoids. In both males and females, the ossification began at the age of 18 to 20 years in the posterior part of the thyroid cartilage, same as our ...
... usually symmetrical.. Similar studies7,8 done in the past have reported that ossifications are first seen in the thyroid, followed by cricoid and the arytenoids. In both males and females, the ossification began at the age of 18 to 20 years in the posterior part of the thyroid cartilage, same as our ...
BSC 2086 Class Notes Chapter 16 – Part 1 Summer 2010
... Parafollicular cells produce the hormone ...
... Parafollicular cells produce the hormone ...
Endocrine System
... pituitary gland. In addition, it makes hormones that are stored in the pituitary gland. Pituitary gland The pituitary gland produces hormones that regulate many of the other endocrine glands. Parathyroid glands These four glands release parathyroid hormone, which regulate the level of calcium in the ...
... pituitary gland. In addition, it makes hormones that are stored in the pituitary gland. Pituitary gland The pituitary gland produces hormones that regulate many of the other endocrine glands. Parathyroid glands These four glands release parathyroid hormone, which regulate the level of calcium in the ...
13. Name the hormones and their functions that are secreted from
... (similar and different from each other) 3. All of the following are chemical signals. What is the difference between them? a. pheromones b. neurotransmitters c. hormones d. local chemical messengers/hormones ...
... (similar and different from each other) 3. All of the following are chemical signals. What is the difference between them? a. pheromones b. neurotransmitters c. hormones d. local chemical messengers/hormones ...
The Endocrine System
... • The endocrine system releases chemical hormones into the blood • This system is slower in producing its effect than the nervous system, however, the effect lasts longer • It helps to maintain homeostasis by monitoring changes in organs or tissues of the body. ...
... • The endocrine system releases chemical hormones into the blood • This system is slower in producing its effect than the nervous system, however, the effect lasts longer • It helps to maintain homeostasis by monitoring changes in organs or tissues of the body. ...
Endocrine Pathology and Reproductive Pathology
... • Excess GH leads to acromegaly if hypersecretion occurs after body growth has stopped. – Elongation of long bones not possible so there is over growth of cancellous bones– protruding jaw, thickening of phalanges, and over growth of visceral organs ...
... • Excess GH leads to acromegaly if hypersecretion occurs after body growth has stopped. – Elongation of long bones not possible so there is over growth of cancellous bones– protruding jaw, thickening of phalanges, and over growth of visceral organs ...
The Endocrine System
... exposure to radiation as part of treatment for cancer of the thyroid or adjacent tissues. The thyroid may also be damaged in an autoimmune disorder that results in the production of antibodies that attack and destroy normal follicle cells. ...
... exposure to radiation as part of treatment for cancer of the thyroid or adjacent tissues. The thyroid may also be damaged in an autoimmune disorder that results in the production of antibodies that attack and destroy normal follicle cells. ...
Hormones - NeuroScience, Inc.
... the 3 members of the estrogen family: estradiol, estrone, and estriol. Estradiol, also known as “E2”, is the primary estrogen in the body. Estrone, also known as “E1”, is a weaker form of estradiol. Estriol, also known as “E3”, is the weakest of the estrogens and is produced in significant amounts d ...
... the 3 members of the estrogen family: estradiol, estrone, and estriol. Estradiol, also known as “E2”, is the primary estrogen in the body. Estrone, also known as “E1”, is a weaker form of estradiol. Estriol, also known as “E3”, is the weakest of the estrogens and is produced in significant amounts d ...
Chapter 20: Endocrine System
... Giants result from too much growth hormone during childhood. If growth hormone is overproduced in an adult, it causes acromegaly. ...
... Giants result from too much growth hormone during childhood. If growth hormone is overproduced in an adult, it causes acromegaly. ...
Practice Exam 3 10/31/10 1) The site of ovulation in mares. A
... 17) Which of the following is released from the posterior pituitary gland? A) growth hormone B) prolactin C) antidiuretic hormone D) follicle stimulating hormone 18) The hormone that causes the CL to regress. A) Estrogen B) Progesterone C) Prostaglandin- F₂α D) Prolactin 19) Pituitary hypersecretion ...
... 17) Which of the following is released from the posterior pituitary gland? A) growth hormone B) prolactin C) antidiuretic hormone D) follicle stimulating hormone 18) The hormone that causes the CL to regress. A) Estrogen B) Progesterone C) Prostaglandin- F₂α D) Prolactin 19) Pituitary hypersecretion ...
Surgical Anatomy of the Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands
... clinically relevant.2 Alternatively, the tissue may be sublingual or prelaryngeal in location, and often may be mistaken for a thyroglossal duct cyst. It is essential to determine the presence or absence of functional thyroid tissue at this ectopic location before removal. About 70% of patients with ...
... clinically relevant.2 Alternatively, the tissue may be sublingual or prelaryngeal in location, and often may be mistaken for a thyroglossal duct cyst. It is essential to determine the presence or absence of functional thyroid tissue at this ectopic location before removal. About 70% of patients with ...
Power Point - Science Olympiad
... Parathyroid These four little glands are embedded in the thyroid gland They secrete parathyroid hormone which regulates the amount of calcium in the blood and its absorption by bones ...
... Parathyroid These four little glands are embedded in the thyroid gland They secrete parathyroid hormone which regulates the amount of calcium in the blood and its absorption by bones ...
hormone - Daniela Sartori
... of microscopic thyroid follicles Outer layer is follicle cells that synthesize T4 Interior filled with colloid, a protein-rich fluid ...
... of microscopic thyroid follicles Outer layer is follicle cells that synthesize T4 Interior filled with colloid, a protein-rich fluid ...
EFFICACY OF PHENOBARBITONE - International Journal of Plant
... administration of these controversial barbiturate drugs. As barbiturates are known to inhibit the secretion and release of pituitary gonadotrophins, reduce the adreno-cortical secretion, and alter the metabolism of steroids during sedation (Harwood and Mason, 1957, Purshottom et al., 1961, Meyer et ...
... administration of these controversial barbiturate drugs. As barbiturates are known to inhibit the secretion and release of pituitary gonadotrophins, reduce the adreno-cortical secretion, and alter the metabolism of steroids during sedation (Harwood and Mason, 1957, Purshottom et al., 1961, Meyer et ...
Topic: The Endocrine System
... brain • Major link between nervous and endocrine systems • Produces hormones that help turn all other endocrine glands on or off ...
... brain • Major link between nervous and endocrine systems • Produces hormones that help turn all other endocrine glands on or off ...
SChapter9
... Hormone-Most hormones can be classified as either amino acid based or steroid bases. -Others, prostaglandins, are derived from lipids. Mechanisms of Hormone Action -Target cells/organs-Specific receptors must be found on the target cells to react to the specific hormones. -Precise changes in a cell ...
... Hormone-Most hormones can be classified as either amino acid based or steroid bases. -Others, prostaglandins, are derived from lipids. Mechanisms of Hormone Action -Target cells/organs-Specific receptors must be found on the target cells to react to the specific hormones. -Precise changes in a cell ...
Unit P: Endocrine System
... OXYTOCIN – released during childbirth causing contractions of the uterus ...
... OXYTOCIN – released during childbirth causing contractions of the uterus ...
Chemical Signals in Animals: Endocrine System and Hormonal
... Thyroid is on the ventral side of the trachea. plays a major role in vertebrate development: participates in embryonic development ...
... Thyroid is on the ventral side of the trachea. plays a major role in vertebrate development: participates in embryonic development ...
Thyroid

The thyroid gland, or simply the thyroid /ˈθaɪrɔɪd/, is one of the largest endocrine glands in the body, and consists of two connected lobes. It is found in the neck, below the laryngeal prominence (Adam's apple). The thyroid gland controls how quickly the body uses energy, makes proteins, and controls the body's sensitivity to other hormones. It participates in these processes by producing thyroid hormones, the principal ones being thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which is more active. These hormones regulate the growth and rate of function of many other systems in the body. T3 and T4 are synthesized from iodine and tyrosine. The thyroid also produces calcitonin, which plays a role in calcium homeostasis.Hormonal output from the thyroid is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) produced by the anterior pituitary, which itself is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) produced by the hypothalamus.The thyroid may be affected by some frequent thyroid diseases. Hyperthyroidism occurs when the gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones, the most common cause being Graves' disease—an autoimmune disorder. In contrast, hypothyroidism is a state of insufficient thyroid hormone production. Worldwide, the most common cause is iodine deficiency. Thyroid hormones are important for development, and hypothyroidism secondary to iodine deficiency remains the leading cause of preventable intellectual disability. In iodine-sufficient regions, the most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto's thyroiditis—also an autoimmune disease. In addition, the thyroid gland may also develop several types of nodules and cancer.