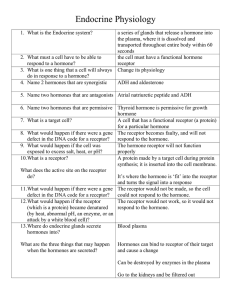
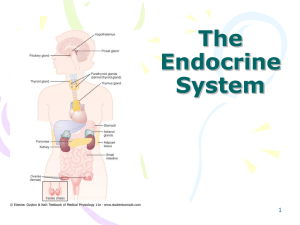
File - Mr. Downing Biology 30
... Elevated metabolic rate – increased heat production, excessive perspiration, weight loss, weakness attributed with muscle loss Bulging eyes – reason still unknown ...
... Elevated metabolic rate – increased heat production, excessive perspiration, weight loss, weakness attributed with muscle loss Bulging eyes – reason still unknown ...
Mader/Biology, 11/e – Chapter Outline
... the gland to the target cell. 4. Pheromones are environmental signals that act at a distance between individual organisms. 5. The Action of Peptide Hormones a. The term peptide hormone is used to include hormones that are peptides, proteins, glycoproteins, and modified amino acids. b. Epinephrine is ...
... the gland to the target cell. 4. Pheromones are environmental signals that act at a distance between individual organisms. 5. The Action of Peptide Hormones a. The term peptide hormone is used to include hormones that are peptides, proteins, glycoproteins, and modified amino acids. b. Epinephrine is ...
Endocrine System
... Found deep within the brain, directly controls the pituitary gland Coordinator of the endocrine system. May secrete body chemicals that either stimulate or suppress hormone secretions from the pituitary gland to affect the other glands The primary link between the endocrine and nervous systems. ...
... Found deep within the brain, directly controls the pituitary gland Coordinator of the endocrine system. May secrete body chemicals that either stimulate or suppress hormone secretions from the pituitary gland to affect the other glands The primary link between the endocrine and nervous systems. ...
Chemical Signaling in Animals
... activities - called signal transduction cascade because process amplified as it continues down path. ...
... activities - called signal transduction cascade because process amplified as it continues down path. ...
CHAPTER 45
... activities - called signal transduction cascade because process amplified as it continues down path. ...
... activities - called signal transduction cascade because process amplified as it continues down path. ...
Endocrine System - Mr. Ford`s Class
... • Most hormone will use this • Activates protein kinase A, which causes phosphorylation that can turn on or turn off target enzymes • Phosphorylation attaches a phosphate group to a protein or other organic molecule ...
... • Most hormone will use this • Activates protein kinase A, which causes phosphorylation that can turn on or turn off target enzymes • Phosphorylation attaches a phosphate group to a protein or other organic molecule ...
Ch. 45 - Ltcconline.net
... C. Hypothalamus and pituitary have multiple endocrine functions 1. hypothalamus exerts master control over endocrine system, serves as feedback center 2. uses pituitary to relay directives to other glands 3. neurosecretory cells 4. these cells synthesize hormones Hormones and homeostasis A. Thyroid ...
... C. Hypothalamus and pituitary have multiple endocrine functions 1. hypothalamus exerts master control over endocrine system, serves as feedback center 2. uses pituitary to relay directives to other glands 3. neurosecretory cells 4. these cells synthesize hormones Hormones and homeostasis A. Thyroid ...
Ch 18 Notes: Endocrine System 2014
... Has right and left lateral lobes, located below larynx. Histology: (thyroid follicles) 1. Follicular cells = secrete thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) 2. Parafollicular cells = secrete calcitonin (CT) which lowers calcium ion level in blood FX = regulate: 1. rate of metabolism 2. growth and d ...
... Has right and left lateral lobes, located below larynx. Histology: (thyroid follicles) 1. Follicular cells = secrete thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) 2. Parafollicular cells = secrete calcitonin (CT) which lowers calcium ion level in blood FX = regulate: 1. rate of metabolism 2. growth and d ...
Chapter 9 Endocrine System
... located in the neck pituitary gland controls the release of thyroid hormones ...
... located in the neck pituitary gland controls the release of thyroid hormones ...
Endocrine Notes
... o Activated gene produces an enzyme (protein) that initiates a chemical reaction within the cell. 2. Non-Steroid Hormones – Hormones composed of proteins, peptides or amino acids. These hormones are NOT fat soluble. They are unable to enter cells because they are not solube in the cell membrane. ...
... o Activated gene produces an enzyme (protein) that initiates a chemical reaction within the cell. 2. Non-Steroid Hormones – Hormones composed of proteins, peptides or amino acids. These hormones are NOT fat soluble. They are unable to enter cells because they are not solube in the cell membrane. ...
Chapter Two Line Title Here and Chapter Title Here and Here
... 4. Hormones are a. chemical signals, b. produced by endocrine glands, c. usually carried in the blood, and d. responsible for specific changes in target cells. 5. Hormones may also be released from specialized nerve cells called neurosecretory cells. B. 26.2 Hormones affect target cells using two ma ...
... 4. Hormones are a. chemical signals, b. produced by endocrine glands, c. usually carried in the blood, and d. responsible for specific changes in target cells. 5. Hormones may also be released from specialized nerve cells called neurosecretory cells. B. 26.2 Hormones affect target cells using two ma ...
Chapter 9: The Endocrine System
... • 1. thyroid hormone: a metabolic hormone made of two chemicals (thyroxin T4 and triiodothyronine T3) • Thyroid sends out mainly T4 to target tissues where it is converted to the ...
... • 1. thyroid hormone: a metabolic hormone made of two chemicals (thyroxin T4 and triiodothyronine T3) • Thyroid sends out mainly T4 to target tissues where it is converted to the ...
Endocrine System
... Growth hormones -chemicals causing bones, muscles and other organs to grow. Hormones-chemicals that tell your body when/how to function. Insulin- hormone that controls how your body uses sugar. Mammary Glands-found in woman’s breast, makes milk for ...
... Growth hormones -chemicals causing bones, muscles and other organs to grow. Hormones-chemicals that tell your body when/how to function. Insulin- hormone that controls how your body uses sugar. Mammary Glands-found in woman’s breast, makes milk for ...
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction (p. 293) A. The
... 11.2 General Characteristics of the Endocrine System (p. 293; Fig. 11.1) A. Endocrine glands and their hormones regulate a number of metabolic processes within cells, as well as reproduction, development, and growth. B. Endocrine glands include the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, ...
... 11.2 General Characteristics of the Endocrine System (p. 293; Fig. 11.1) A. Endocrine glands and their hormones regulate a number of metabolic processes within cells, as well as reproduction, development, and growth. B. Endocrine glands include the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, ...
Pancreas and blood glucose regulation
... between the thyroid follicles. C cells are very difficult to identify. ...
... between the thyroid follicles. C cells are very difficult to identify. ...
doc Lectures 1
... Endocrine means 'the internal secretion of a biologically active substance'. The system is hierarchical, some glands control other glands. Hormone Definitions A chemical messenger effective in minute quantities. Synthesised in ductless glands. Secreted into and transported by blood. Acts on receptor ...
... Endocrine means 'the internal secretion of a biologically active substance'. The system is hierarchical, some glands control other glands. Hormone Definitions A chemical messenger effective in minute quantities. Synthesised in ductless glands. Secreted into and transported by blood. Acts on receptor ...
2 Communication Systems
... using chemical signals • Neurons release neurotransmitters into a synapse affecting postsynaptic cells • Endocrine glands release hormones into the bloodstream to specific target cell receptors Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... using chemical signals • Neurons release neurotransmitters into a synapse affecting postsynaptic cells • Endocrine glands release hormones into the bloodstream to specific target cell receptors Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
Endocrine PPT
... rate slows, gains weight again. They set off Geiger counters for months afterwards. Then start on artificial thyroxin, need to figure out what their set point is for normal. • The other way (not so good) is to have the thyroid gland surgically removed. However, the parathyroid glands are often damag ...
... rate slows, gains weight again. They set off Geiger counters for months afterwards. Then start on artificial thyroxin, need to figure out what their set point is for normal. • The other way (not so good) is to have the thyroid gland surgically removed. However, the parathyroid glands are often damag ...
Title: The Endocrine System
... 2- Exocrine glands – Secrete their products into ducts that carry into body cavities, into the lumen of an organ or onto the skin surface (sweat glands, oil glands, mucus glands) 3- Hormone Receptors – As a rule the 50 (or so) hormones in the body only affect a few types of cells. These are called t ...
... 2- Exocrine glands – Secrete their products into ducts that carry into body cavities, into the lumen of an organ or onto the skin surface (sweat glands, oil glands, mucus glands) 3- Hormone Receptors – As a rule the 50 (or so) hormones in the body only affect a few types of cells. These are called t ...
chapter 16-the endocrine system
... 2) What is diabetes insipidus and what causes this problem? B. The Thyroid Gland-located in the neck, just below the larynx on either side of the trachea. The two lobes of the thyroid gland are connected by a mass of tissue known as the isthmus. 1. Internally, the thyroid gland is composed of hollow ...
... 2) What is diabetes insipidus and what causes this problem? B. The Thyroid Gland-located in the neck, just below the larynx on either side of the trachea. The two lobes of the thyroid gland are connected by a mass of tissue known as the isthmus. 1. Internally, the thyroid gland is composed of hollow ...
Thyroid

The thyroid gland, or simply the thyroid /ˈθaɪrɔɪd/, is one of the largest endocrine glands in the body, and consists of two connected lobes. It is found in the neck, below the laryngeal prominence (Adam's apple). The thyroid gland controls how quickly the body uses energy, makes proteins, and controls the body's sensitivity to other hormones. It participates in these processes by producing thyroid hormones, the principal ones being thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which is more active. These hormones regulate the growth and rate of function of many other systems in the body. T3 and T4 are synthesized from iodine and tyrosine. The thyroid also produces calcitonin, which plays a role in calcium homeostasis.Hormonal output from the thyroid is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) produced by the anterior pituitary, which itself is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) produced by the hypothalamus.The thyroid may be affected by some frequent thyroid diseases. Hyperthyroidism occurs when the gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones, the most common cause being Graves' disease—an autoimmune disorder. In contrast, hypothyroidism is a state of insufficient thyroid hormone production. Worldwide, the most common cause is iodine deficiency. Thyroid hormones are important for development, and hypothyroidism secondary to iodine deficiency remains the leading cause of preventable intellectual disability. In iodine-sufficient regions, the most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto's thyroiditis—also an autoimmune disease. In addition, the thyroid gland may also develop several types of nodules and cancer.