Hypopituitarism
... WHAT DOES IT DO? The pituitary gland is a pea-sized gland found at the base of your brain. It is called the “master gland” because it affects the action of many other important glands that produce their own hormones. The pituitary gland affects almost all parts of your body. ...
... WHAT DOES IT DO? The pituitary gland is a pea-sized gland found at the base of your brain. It is called the “master gland” because it affects the action of many other important glands that produce their own hormones. The pituitary gland affects almost all parts of your body. ...
Document
... A hormone is a chemical that is secreted into extracellular fluid and carried by the blood -Can therefore act at a distance from source -Only targets with receptor can respond Paracrine regulators do not travel in blood -Allow cells of organ to regulate each other Pheromones are chemicals released i ...
... A hormone is a chemical that is secreted into extracellular fluid and carried by the blood -Can therefore act at a distance from source -Only targets with receptor can respond Paracrine regulators do not travel in blood -Allow cells of organ to regulate each other Pheromones are chemicals released i ...
The Endocrine System
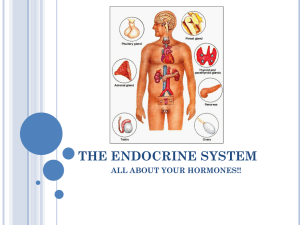
... The endocrine glands include the hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, thymus, and pancreas. ...
... The endocrine glands include the hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, thymus, and pancreas. ...
H1 Hormones - TASIS IB Biology
... Peptide and protein hormones • Soluble in plasma but cannot cross the lipid membrane • Act on cell surface receptors • Binding with the receptor leads to activtion of a ‘second messenger’ cascade ...
... Peptide and protein hormones • Soluble in plasma but cannot cross the lipid membrane • Act on cell surface receptors • Binding with the receptor leads to activtion of a ‘second messenger’ cascade ...
Chapter 13 Endocrine System
... Pituitary Gland (pituit/o): The master gland that is located at the base of the brain. It consists of two lobes, the anterior and the posterior. This gland is referred to as the master gland because it secretes hormones that affect how the other endocrine glands function. ...
... Pituitary Gland (pituit/o): The master gland that is located at the base of the brain. It consists of two lobes, the anterior and the posterior. This gland is referred to as the master gland because it secretes hormones that affect how the other endocrine glands function. ...
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... There are a myriad of drugs that affect the body sharpshooters use beta blockers that slow the heartbeat (helps to steady ain and calm jangled ...
... There are a myriad of drugs that affect the body sharpshooters use beta blockers that slow the heartbeat (helps to steady ain and calm jangled ...
1 2 - UMSONPatho
... Regulation of Cortisol Synthesis and Secretion Description • Pharmacologic steroids produce a negative feedback effect on the hypothalamus and pituitary. – CRH and ACTH are decreased to zero – Over time, the adrenal gland becomes less able to produce cortisol. ...
... Regulation of Cortisol Synthesis and Secretion Description • Pharmacologic steroids produce a negative feedback effect on the hypothalamus and pituitary. – CRH and ACTH are decreased to zero – Over time, the adrenal gland becomes less able to produce cortisol. ...
Endocrine System Study Questions with answers
... 17. Discuss the adrenal glands. How are they structured? What hormones do they secrete? The adrenal glands are two organs (the adrenal medulla and adrenal cortex) which sit on top of the kidneys. The adrenal cortex functions as a gland. It produces three groups of steroid hormones: mineralocorticoi ...
... 17. Discuss the adrenal glands. How are they structured? What hormones do they secrete? The adrenal glands are two organs (the adrenal medulla and adrenal cortex) which sit on top of the kidneys. The adrenal cortex functions as a gland. It produces three groups of steroid hormones: mineralocorticoi ...
Chapter 13 Endocrine
... i. Name the two hormones secreted from the follicular cells of the thyroid gland. What chemical element is essential for the production of these hormones? What condition arises in an adult from the lack of this element? ii. What is the storage form of these hormones called? Where is this substance s ...
... i. Name the two hormones secreted from the follicular cells of the thyroid gland. What chemical element is essential for the production of these hormones? What condition arises in an adult from the lack of this element? ii. What is the storage form of these hormones called? Where is this substance s ...
Surgical Anatomy of Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands and Basic
... in case of an unprofessional “en masse” lygating the artery. Behind the lower pole or the border between the middle and lower third, approximately 1cm far from the thyroid lobe, the inferior thyroid artery is divided into three ultimate branches: inferior, posterior (upward) and internal (middle). T ...
... in case of an unprofessional “en masse” lygating the artery. Behind the lower pole or the border between the middle and lower third, approximately 1cm far from the thyroid lobe, the inferior thyroid artery is divided into three ultimate branches: inferior, posterior (upward) and internal (middle). T ...
Endocrine PP - Laura Banks
... 1. Oxytocin (OT) :common in women, stimulates contractions during labor, sex, and also causes milk ejection 2. Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) Kidneys reduce water excretion (inhibits urine production) ...
... 1. Oxytocin (OT) :common in women, stimulates contractions during labor, sex, and also causes milk ejection 2. Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) Kidneys reduce water excretion (inhibits urine production) ...
The Endocrine System
... two thyroid hormones, T4 and T3. T4, also called thyroxine or tetraiodothyronine, is the inactive form, while T3, triiodothyronine, is the active hormone. T4 has four iodine atoms while T3 has three. Thyronine is the name given to a dimer of the amino acid tyrosine. T4 is produced in about 20 times ...
... two thyroid hormones, T4 and T3. T4, also called thyroxine or tetraiodothyronine, is the inactive form, while T3, triiodothyronine, is the active hormone. T4 has four iodine atoms while T3 has three. Thyronine is the name given to a dimer of the amino acid tyrosine. T4 is produced in about 20 times ...
Chapter 20 - mwsu-wiki
... 3. increase in TH synthesis 4. increase in the synthesis and secretion of protaglandins by the thyroid Synthesis of Thyroid Hormone - Thyroid Hormone Synthesis 1. Uniodinated thyroglobulin is produced by endoplasmic reticulum of follicular cells 2. Tyrosine is incorporated into the thyroglobulin as ...
... 3. increase in TH synthesis 4. increase in the synthesis and secretion of protaglandins by the thyroid Synthesis of Thyroid Hormone - Thyroid Hormone Synthesis 1. Uniodinated thyroglobulin is produced by endoplasmic reticulum of follicular cells 2. Tyrosine is incorporated into the thyroglobulin as ...
Endocrine System
... two thyroid hormones, T4 and T3. T4, also called thyroxine or tetraiodothyronine, is the inactive form, while T3, triiodothyronine, is the active hormone. T4 has four iodine atoms while T3 has three. Thyronine is the name given to a dimer of the amino acid tyrosine. T4 is produced in about 20 times ...
... two thyroid hormones, T4 and T3. T4, also called thyroxine or tetraiodothyronine, is the inactive form, while T3, triiodothyronine, is the active hormone. T4 has four iodine atoms while T3 has three. Thyronine is the name given to a dimer of the amino acid tyrosine. T4 is produced in about 20 times ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... • Regulates the release of pancreatic digestive enzymes. This prevents the breakdown and absorption of carbohydrates from the small intestine if the blood sugar level is too high, and increases the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates if the blood sugar level is ...
... • Regulates the release of pancreatic digestive enzymes. This prevents the breakdown and absorption of carbohydrates from the small intestine if the blood sugar level is too high, and increases the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates if the blood sugar level is ...
endocrine glands
... The brain region keeps a check on internal organs and activities, such as the level of carbon dioxide or water in the blood. ...
... The brain region keeps a check on internal organs and activities, such as the level of carbon dioxide or water in the blood. ...
13 Unit 1 - Cloudfront.net
... thyroxin (T4) & triiodothyronine (T3) Stored in follicle calcitonin ...
... thyroxin (T4) & triiodothyronine (T3) Stored in follicle calcitonin ...
Pituitary Gland - inetTeacher.com
... What is the target organs for Vasopressin? What does Oxytocin hormone do? When is Oxytocin formed? ...
... What is the target organs for Vasopressin? What does Oxytocin hormone do? When is Oxytocin formed? ...
endocrine system - Sakshieducation.com
... These two systems co-ordinate and integrate functions of different parts of body in accordance with the changing needs of external and internal environments. Nervous system achieves functional coordination by transmitting information through nerve impulses. The Endocrine system achieves coordination ...
... These two systems co-ordinate and integrate functions of different parts of body in accordance with the changing needs of external and internal environments. Nervous system achieves functional coordination by transmitting information through nerve impulses. The Endocrine system achieves coordination ...
test review key - Hartland High School
... 1. The steroid hormone diffuses through the plasma membrane of their target cells 2. The hormone then enters the nucleus 3. The hormone binds to a specific receptor protein within the nucleus 4. the resulting hormone-receptor complex binds to specific sites on the cell’s DNA 5. this activates certai ...
... 1. The steroid hormone diffuses through the plasma membrane of their target cells 2. The hormone then enters the nucleus 3. The hormone binds to a specific receptor protein within the nucleus 4. the resulting hormone-receptor complex binds to specific sites on the cell’s DNA 5. this activates certai ...
Endocrine System and Stress
... generally understand the various factors that can cause hormone release understand how stress activates various body parts Important Concepts hormones as chemical signals target cells must have receptors hydrophobic hormones alter gene expression hydrophilic hormones act via second messe ...
... generally understand the various factors that can cause hormone release understand how stress activates various body parts Important Concepts hormones as chemical signals target cells must have receptors hydrophobic hormones alter gene expression hydrophilic hormones act via second messe ...
UNIT 5 Lecture 16 CONTROL SYSTEMS
... changes in the blood, and by other hormones. Most control is through negative feedback systems. Once hormones have had their effects on their target tissue, they are broken down by different systems in the body. Hormones are removed from the blood by the same mechanisms as any other substance: metab ...
... changes in the blood, and by other hormones. Most control is through negative feedback systems. Once hormones have had their effects on their target tissue, they are broken down by different systems in the body. Hormones are removed from the blood by the same mechanisms as any other substance: metab ...
Classification of Hormones Lecture 1
... 2. The hypothalamus secretes: • Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) which stimulates the release of ACTH from anterior pituitary. • Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) which stimulates the release of FSH and LH from anterior pituitary. • Growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) which stimulates t ...
... 2. The hypothalamus secretes: • Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) which stimulates the release of ACTH from anterior pituitary. • Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) which stimulates the release of FSH and LH from anterior pituitary. • Growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) which stimulates t ...
The Endocrine System
... Types of Hormones • Hormones can be grouped into two types based on their structure. Hormones can either be amino acid-based hormones or steroid hormones. – Amino acid based-hormones are made of amino acids, either a single modified amino acid or a protein made of 3-200 amino acids, and are water s ...
... Types of Hormones • Hormones can be grouped into two types based on their structure. Hormones can either be amino acid-based hormones or steroid hormones. – Amino acid based-hormones are made of amino acids, either a single modified amino acid or a protein made of 3-200 amino acids, and are water s ...
Thyroid

The thyroid gland, or simply the thyroid /ˈθaɪrɔɪd/, is one of the largest endocrine glands in the body, and consists of two connected lobes. It is found in the neck, below the laryngeal prominence (Adam's apple). The thyroid gland controls how quickly the body uses energy, makes proteins, and controls the body's sensitivity to other hormones. It participates in these processes by producing thyroid hormones, the principal ones being thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which is more active. These hormones regulate the growth and rate of function of many other systems in the body. T3 and T4 are synthesized from iodine and tyrosine. The thyroid also produces calcitonin, which plays a role in calcium homeostasis.Hormonal output from the thyroid is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) produced by the anterior pituitary, which itself is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) produced by the hypothalamus.The thyroid may be affected by some frequent thyroid diseases. Hyperthyroidism occurs when the gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones, the most common cause being Graves' disease—an autoimmune disorder. In contrast, hypothyroidism is a state of insufficient thyroid hormone production. Worldwide, the most common cause is iodine deficiency. Thyroid hormones are important for development, and hypothyroidism secondary to iodine deficiency remains the leading cause of preventable intellectual disability. In iodine-sufficient regions, the most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto's thyroiditis—also an autoimmune disease. In addition, the thyroid gland may also develop several types of nodules and cancer.