PowerPoint 演示文稿
... (1)stimulation of carbohydrate metabolism (2)stimulation of fat metabolism (3)increased requirement for vitamins. (4)increased basal metabolic rate (5)decreased body weight ...
... (1)stimulation of carbohydrate metabolism (2)stimulation of fat metabolism (3)increased requirement for vitamins. (4)increased basal metabolic rate (5)decreased body weight ...
Document
... • Production requires adequate iodine in the diet • Occurs in two forms, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) • Increases metabolism and heat production (calorigenic effect) • Required for normal development The Thyroid Gland The Thyroid Gland The Thyroid Gland C Cells of the Thyroid Gland • C c ...
... • Production requires adequate iodine in the diet • Occurs in two forms, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) • Increases metabolism and heat production (calorigenic effect) • Required for normal development The Thyroid Gland The Thyroid Gland The Thyroid Gland C Cells of the Thyroid Gland • C c ...
10_LectureOutline_DOC
... • Production requires adequate iodine in the diet • Occurs in two forms, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) • Increases metabolism and heat production (calorigenic effect) • Required for normal development The Thyroid Gland The Thyroid Gland The Thyroid Gland C Cells of the Thyroid Gland • C c ...
... • Production requires adequate iodine in the diet • Occurs in two forms, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) • Increases metabolism and heat production (calorigenic effect) • Required for normal development The Thyroid Gland The Thyroid Gland The Thyroid Gland C Cells of the Thyroid Gland • C c ...
Laboratory 11 Anatomy of the Endocrine System
... 3. Endocrine glands in the cervical and thoracic region: The thyroid gland, the largest of the endocrine glands, is located in the throat just inferior to the “Adam’s apple” (Figure 1). It is ...
... 3. Endocrine glands in the cervical and thoracic region: The thyroid gland, the largest of the endocrine glands, is located in the throat just inferior to the “Adam’s apple” (Figure 1). It is ...
Endocrine System
... response to many adverse conditions, such as malnutrition, injury, or illness (including infections, cancer, and liver, heart, and kidney diseases). The production of triiodothyronine is also inhibited by starvation and by several drugs, notably amiodarone, a drug used to treat patients with cardiac ...
... response to many adverse conditions, such as malnutrition, injury, or illness (including infections, cancer, and liver, heart, and kidney diseases). The production of triiodothyronine is also inhibited by starvation and by several drugs, notably amiodarone, a drug used to treat patients with cardiac ...
Endocrine Note Cards
... Thyroid is composed of spherical follicles Follicle cells: produce thyroglobulin, the precursor of thryoid hormone (thyroxin) Colloid lumen is of thyroglobulin Parafollicular “C” cells: produce calcitonin ...
... Thyroid is composed of spherical follicles Follicle cells: produce thyroglobulin, the precursor of thryoid hormone (thyroxin) Colloid lumen is of thyroglobulin Parafollicular “C” cells: produce calcitonin ...
Endocrine_System__part_1__Feb_28__studen
... • Hormone excess, hormone deficiency, or abnormal responsiveness of target tissue • Can be primary (last endocrine gland in a reflex) or secondary (further up, in gland producing trophic hormone) ...
... • Hormone excess, hormone deficiency, or abnormal responsiveness of target tissue • Can be primary (last endocrine gland in a reflex) or secondary (further up, in gland producing trophic hormone) ...
Larynx
... • The larynx is an organ that provides a protective sphincter at the inlet of the air passages. • It is also responsible for voice production ; beside that it is a respiratory organ. • It is situated below the tongue and hyoid bone • and between the great blood vessels of the neck • It lies at the l ...
... • The larynx is an organ that provides a protective sphincter at the inlet of the air passages. • It is also responsible for voice production ; beside that it is a respiratory organ. • It is situated below the tongue and hyoid bone • and between the great blood vessels of the neck • It lies at the l ...
The Endocrine System
... • Target cells contain molecules on their surface called receptors, to which hormones can bind. Target cells do their job when hormones are bound to their receptors. ...
... • Target cells contain molecules on their surface called receptors, to which hormones can bind. Target cells do their job when hormones are bound to their receptors. ...
13 Physiologicoanatomical peculiarities of endocrine system in
... ("pharmacologic") doses are required to produce significant acceleration of growth in these conditions, producing blood levels well above physiologic. ...
... ("pharmacologic") doses are required to produce significant acceleration of growth in these conditions, producing blood levels well above physiologic. ...
Endocrine System
... Thyroid is composed of spherical follicles Follicle cells: produce thyroglobulin, the precursor of thryoid hormone (thyroxin) Colloid lumen is of thyroglobulin Parafollicular “C” cells: produce calcitonin ...
... Thyroid is composed of spherical follicles Follicle cells: produce thyroglobulin, the precursor of thryoid hormone (thyroxin) Colloid lumen is of thyroglobulin Parafollicular “C” cells: produce calcitonin ...
thyroid hormone
... Thyroid is composed of spherical follicles Follicle cells: produce thyroglobulin, the precursor of thryoid hormone (thyroxin) Colloid lumen is of thyroglobulin Parafollicular “C” cells: produce calcitonin ...
... Thyroid is composed of spherical follicles Follicle cells: produce thyroglobulin, the precursor of thryoid hormone (thyroxin) Colloid lumen is of thyroglobulin Parafollicular “C” cells: produce calcitonin ...
Slide 1
... Thyroid is composed of spherical follicles Follicle cells: produce thyroglobulin, the precursor of thryoid hormone (thyroxin) Colloid lumen is of thyroglobulin Parafollicular “C” cells: produce calcitonin ...
... Thyroid is composed of spherical follicles Follicle cells: produce thyroglobulin, the precursor of thryoid hormone (thyroxin) Colloid lumen is of thyroglobulin Parafollicular “C” cells: produce calcitonin ...
thyroid releasing hormone
... Thyroid is composed of spherical follicles Follicle cells: produce thyroglobulin, the precursor of thryoid hormone (thyroxin) Colloid lumen is of thyroglobulin Parafollicular “C” cells: produce calcitonin ...
... Thyroid is composed of spherical follicles Follicle cells: produce thyroglobulin, the precursor of thryoid hormone (thyroxin) Colloid lumen is of thyroglobulin Parafollicular “C” cells: produce calcitonin ...
The Endocrine System
... Thyroid is composed of spherical follicles Follicle cells: produce thyroglobulin, the precursor of thryoid hormone (thyroxin) Colloid lumen is of thyroglobulin Parafollicular “C” cells: produce calcitonin ...
... Thyroid is composed of spherical follicles Follicle cells: produce thyroglobulin, the precursor of thryoid hormone (thyroxin) Colloid lumen is of thyroglobulin Parafollicular “C” cells: produce calcitonin ...
adrenal & thyroid
... multinodular goitre thyroid adenoma subacute thyroiditis ingestion of TH (OD / factitial / food) anterior pituitary disease ...
... multinodular goitre thyroid adenoma subacute thyroiditis ingestion of TH (OD / factitial / food) anterior pituitary disease ...
Endocrine Physiology - e-safe
... The follicles comprise a single layer of epithelial cells forming a cavity that contains colloid where the thyroid hormones are stores as thyroglobulin. C-cells, which secrete calcitonin, are found outside the follicles. Synthesis and transport of thyroid hormones Dietary iodide is concentrated by t ...
... The follicles comprise a single layer of epithelial cells forming a cavity that contains colloid where the thyroid hormones are stores as thyroglobulin. C-cells, which secrete calcitonin, are found outside the follicles. Synthesis and transport of thyroid hormones Dietary iodide is concentrated by t ...
The Endocrine System Chapter 47 1
... – Shaped like a shield and lies just below the Adam’s apple in the front of the neck. Thyroxine helps set basal metabolic rate by stimulating the rate of cell respiration. In children, thyroid hormones also promote growth and stimulate maturation of the central nervous system. unique function ...
... – Shaped like a shield and lies just below the Adam’s apple in the front of the neck. Thyroxine helps set basal metabolic rate by stimulating the rate of cell respiration. In children, thyroid hormones also promote growth and stimulate maturation of the central nervous system. unique function ...
thyroid releasing hormone
... • TSH from anterior pituitary • Thyroxine from the thyroid (TSH has caused cleavage of thryroglobulin into thyroxine) ...
... • TSH from anterior pituitary • Thyroxine from the thyroid (TSH has caused cleavage of thryroglobulin into thyroxine) ...
Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 10: Endocrine System
... b. The anterior pituitary gland is indirectly connected to the hypothalamus by means of a venous portal system. By "portal," we mean that the veins carry substances from the capillaries at one point to the capillaries at another point (hypothalamus to the anterior pituitary gland). c. In the hypotha ...
... b. The anterior pituitary gland is indirectly connected to the hypothalamus by means of a venous portal system. By "portal," we mean that the veins carry substances from the capillaries at one point to the capillaries at another point (hypothalamus to the anterior pituitary gland). c. In the hypotha ...
branchial anomalies
... Low in neck (anterior to SCM) -> Deep to common carotid -> Loops around aortic arch on the left (subclavian on the right) -> Deep to superior laryngeal nerve -> Superficial to recurrent laryngeal nerve -> ...
... Low in neck (anterior to SCM) -> Deep to common carotid -> Loops around aortic arch on the left (subclavian on the right) -> Deep to superior laryngeal nerve -> Superficial to recurrent laryngeal nerve -> ...
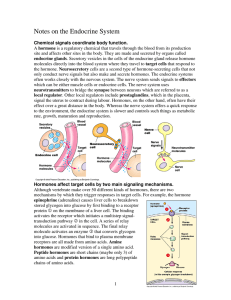
Notes on the Endocrine System
... As part of the brain, the hypothalamus receives information from nerves about the external and internal environment. It can respond to those conditions by sending out either nervous or hormonal signals. It is directly connected to the pituitary gland which also secretes hormones that influence numer ...
... As part of the brain, the hypothalamus receives information from nerves about the external and internal environment. It can respond to those conditions by sending out either nervous or hormonal signals. It is directly connected to the pituitary gland which also secretes hormones that influence numer ...
Hormones - SITH ITB
... – estrogens, which maintain the female reproductive system and promote the development of female characteristics, – progestins, such as progesterone, which prepare and maintain the uterus to support a developing embryo, and – androgens, such as testosterone, which stimulate the development and ma ...
... – estrogens, which maintain the female reproductive system and promote the development of female characteristics, – progestins, such as progesterone, which prepare and maintain the uterus to support a developing embryo, and – androgens, such as testosterone, which stimulate the development and ma ...
Chapter 7: Introduction to the Endocrine System
... Graves disease (Running Problem) ► Gigantism in child (acromegaly in ...
... Graves disease (Running Problem) ► Gigantism in child (acromegaly in ...
Thyroid

The thyroid gland, or simply the thyroid /ˈθaɪrɔɪd/, is one of the largest endocrine glands in the body, and consists of two connected lobes. It is found in the neck, below the laryngeal prominence (Adam's apple). The thyroid gland controls how quickly the body uses energy, makes proteins, and controls the body's sensitivity to other hormones. It participates in these processes by producing thyroid hormones, the principal ones being thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which is more active. These hormones regulate the growth and rate of function of many other systems in the body. T3 and T4 are synthesized from iodine and tyrosine. The thyroid also produces calcitonin, which plays a role in calcium homeostasis.Hormonal output from the thyroid is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) produced by the anterior pituitary, which itself is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) produced by the hypothalamus.The thyroid may be affected by some frequent thyroid diseases. Hyperthyroidism occurs when the gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones, the most common cause being Graves' disease—an autoimmune disorder. In contrast, hypothyroidism is a state of insufficient thyroid hormone production. Worldwide, the most common cause is iodine deficiency. Thyroid hormones are important for development, and hypothyroidism secondary to iodine deficiency remains the leading cause of preventable intellectual disability. In iodine-sufficient regions, the most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto's thyroiditis—also an autoimmune disease. In addition, the thyroid gland may also develop several types of nodules and cancer.