Head, Neck, and Regional Lymphatics
... The neck is supported and made mobile by vertebral processes and the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles . The hyoid bone, superior to the larynx, is the only bone in the body that does not directly articulate with another bone. It serves as a movable base for the tongue, and an attachment for ...
... The neck is supported and made mobile by vertebral processes and the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles . The hyoid bone, superior to the larynx, is the only bone in the body that does not directly articulate with another bone. It serves as a movable base for the tongue, and an attachment for ...
Slide 1
... Functions of Prostaglandins • Immune system: promote inflammation • Reproductive system: aid ovulation • Digestive system: inhibit secretion; stimulate propulsion and absorption • Respiratory system: aid bronchoconstriction and dilation ...
... Functions of Prostaglandins • Immune system: promote inflammation • Reproductive system: aid ovulation • Digestive system: inhibit secretion; stimulate propulsion and absorption • Respiratory system: aid bronchoconstriction and dilation ...
Chemical coordina Answer 1: (a) Exocrine gland
... behaviour. These hormones also produce synthetic effects on protein and carbohydrate metabolism. (e) Estrogens: It produce wide ranging actions such as stimulation of growth and activities of female secondary sex organs, development of growing ovarian follicles, appearance of female secondary sex ch ...
... behaviour. These hormones also produce synthetic effects on protein and carbohydrate metabolism. (e) Estrogens: It produce wide ranging actions such as stimulation of growth and activities of female secondary sex organs, development of growing ovarian follicles, appearance of female secondary sex ch ...
Chapter 45. - RMC Science Home
... are specialized neurons – they can synthesize hormones, release hormones and they can conduct nerve impulses ...
... are specialized neurons – they can synthesize hormones, release hormones and they can conduct nerve impulses ...
The endocrine system
... 2. Thyroid gland con’t --functions to maintain body metabolism --produces the hormone THYROXIN which is mostly iodine based (controls the rate of metabolism and is responsible for normal physical and mental development.) ...
... 2. Thyroid gland con’t --functions to maintain body metabolism --produces the hormone THYROXIN which is mostly iodine based (controls the rate of metabolism and is responsible for normal physical and mental development.) ...
The Endocrine System - APBIOSTUDENTS
... thyroid hormone secretion. When iodine level in blood declines the hypothalamus secretes a releasing hormone (TRH or Thyroid Releasing Hormone) to the anterior pituitary. The releaser causes the pituitary to secrete thyroidstimulating hormone (TSH). TSH thus goes to the thyroid gland and induces sec ...
... thyroid hormone secretion. When iodine level in blood declines the hypothalamus secretes a releasing hormone (TRH or Thyroid Releasing Hormone) to the anterior pituitary. The releaser causes the pituitary to secrete thyroidstimulating hormone (TSH). TSH thus goes to the thyroid gland and induces sec ...
Chapter 18
... circulatory system bound with thyroxin-binding globulin (TBG) The binding helps the half-life of the hormones to increase to 1 week in the circulatory system. During this period thyroxin (T4) may convert to T3, which is the more active form ...
... circulatory system bound with thyroxin-binding globulin (TBG) The binding helps the half-life of the hormones to increase to 1 week in the circulatory system. During this period thyroxin (T4) may convert to T3, which is the more active form ...
Document
... What is sensitivity? What are endocrine glands? What are exocrine glands? What is the nervous system? Give the main differences between the nervous and endocrine systems. ...
... What is sensitivity? What are endocrine glands? What are exocrine glands? What is the nervous system? Give the main differences between the nervous and endocrine systems. ...
PPT
... is responsible for growth of male sex organs and is necessary for sperm maturation. It also influences the development of secondary sex characteristics. ...
... is responsible for growth of male sex organs and is necessary for sperm maturation. It also influences the development of secondary sex characteristics. ...
The Endocrine System (Chapter 16)
... synthesis and secretion of T3 and T4 from follicular cells. Explain what thyroxine is and which thyroid hormone is the active form circulating in the blood. Explain the physiological basis for the endocrine abnormalities seen in hyperthyroidism due to Grave’s disease and in hypothyroidism due to iod ...
... synthesis and secretion of T3 and T4 from follicular cells. Explain what thyroxine is and which thyroid hormone is the active form circulating in the blood. Explain the physiological basis for the endocrine abnormalities seen in hyperthyroidism due to Grave’s disease and in hypothyroidism due to iod ...
Endocrine System Disorders
... Thyroid gland – Thyroxine (regulates the rate of metabolism) Adrenal gland - corticosteroids and catecholamines including cortisol and adrenaline and small amounts of testosterone (regulates stress levels) Pancreas – peptides (regulates the production of shorter active ...
... Thyroid gland – Thyroxine (regulates the rate of metabolism) Adrenal gland - corticosteroids and catecholamines including cortisol and adrenaline and small amounts of testosterone (regulates stress levels) Pancreas – peptides (regulates the production of shorter active ...
Chp.18 Endocrine Glands
... – GHRH. Growth hormone-releasing hormone. Causes the anterior pituitary to release growth hormone. – TRH. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone. Causes the anterior pituitary to release thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). – CRH. Corticotropin-releasing hormone. Causes anterior pituitary to produce adrenocort ...
... – GHRH. Growth hormone-releasing hormone. Causes the anterior pituitary to release growth hormone. – TRH. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone. Causes the anterior pituitary to release thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). – CRH. Corticotropin-releasing hormone. Causes anterior pituitary to produce adrenocort ...
Slide 1
... – Thyroxine (T4) & triiodothyronine (T3) tyrosine-based hormones produced by thyroid – Involved in regulation of metabolism act on nearly all cells of body; increase basal metabolic rate, protein synthesis; long bone growth; increase body’s sensitivity to catecholamines; regulate protein, fat & ...
... – Thyroxine (T4) & triiodothyronine (T3) tyrosine-based hormones produced by thyroid – Involved in regulation of metabolism act on nearly all cells of body; increase basal metabolic rate, protein synthesis; long bone growth; increase body’s sensitivity to catecholamines; regulate protein, fat & ...
The Endocrine System
... the thyroid hormones: – thyroxine (T4) – triiodothyronine (T3) • When stimulated (by TSH or by cold), these are released into the circulatory system and the metabolic rate. – “C” cells within the thyroid produce the ...
... the thyroid hormones: – thyroxine (T4) – triiodothyronine (T3) • When stimulated (by TSH or by cold), these are released into the circulatory system and the metabolic rate. – “C” cells within the thyroid produce the ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿 - Shandong University
... Major communication systems in the body Integrate stimuli and responses to changes in external and internal environment Both are crucial to coordinated functions of highly differentiated cells, tissues and ...
... Major communication systems in the body Integrate stimuli and responses to changes in external and internal environment Both are crucial to coordinated functions of highly differentiated cells, tissues and ...
Endocrine System
... Pancreas: Located near the stomach. Its hormones include insulin and glucagon. These two hormones work together to control the level of glucose in the blood. Pineal Glands: A tiny gland located at the base of the brain. It secretes the hormone melatonin. This hormone controls sleepwake cycles and se ...
... Pancreas: Located near the stomach. Its hormones include insulin and glucagon. These two hormones work together to control the level of glucose in the blood. Pineal Glands: A tiny gland located at the base of the brain. It secretes the hormone melatonin. This hormone controls sleepwake cycles and se ...
Chapter 15 - Los Angeles City College
... Paired organs that cap the kidneys. Each gland consists of an outer cortex and inner ...
... Paired organs that cap the kidneys. Each gland consists of an outer cortex and inner ...
Endocrine System: http://science.nhmccd.edu/biol/ap1int.htm
... hormones control your metabolism, which is the body's ability to break down food and store it as energy and the ability to break down food into waste products with a release of energy in the process. The thyroid produces two hormones, T3 (called tri-iodothyronine) and T4 (called thyroxine). Thyroid ...
... hormones control your metabolism, which is the body's ability to break down food and store it as energy and the ability to break down food into waste products with a release of energy in the process. The thyroid produces two hormones, T3 (called tri-iodothyronine) and T4 (called thyroxine). Thyroid ...
Endocrine System Not..
... •PRL – ( secreted by lactotropes ) •Female, milk synthesis after delivery •Male, increase sensitivity lo LH, thus increase testosterone secretion •GH ( Somatotropin ) – ( secreted by somatotropes) •Promotes tissue growth GROWTH HORMONE •PROMOTES TISSUE GROWTH •Directly affects mitosis and cellular ...
... •PRL – ( secreted by lactotropes ) •Female, milk synthesis after delivery •Male, increase sensitivity lo LH, thus increase testosterone secretion •GH ( Somatotropin ) – ( secreted by somatotropes) •Promotes tissue growth GROWTH HORMONE •PROMOTES TISSUE GROWTH •Directly affects mitosis and cellular ...
Biology 218 – Human Anatomy - RIDDELL
... drain into the capillary plexus of the infundibular process; from this plexus, hormones pass into the posterior hypophyseal veins for delivery to target cells in other tissues. iv. Table 23.3 provides a summary of posterior pituitary gland hormones and their actions. E. Thyroid Gland (p. 711) 1. The ...
... drain into the capillary plexus of the infundibular process; from this plexus, hormones pass into the posterior hypophyseal veins for delivery to target cells in other tissues. iv. Table 23.3 provides a summary of posterior pituitary gland hormones and their actions. E. Thyroid Gland (p. 711) 1. The ...
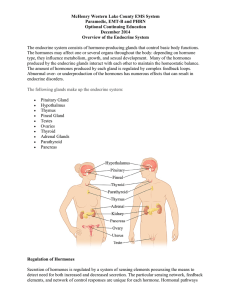
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT
... production and breastfeeding. In a normal pregnancy, hCG stimulates the ovary to produce estrogens and progestins and helps stimulate normal development of the fetal genitals. The estrogens in the placenta stimulate breast development, promote normal labor, and help produce a steady rise in prolacti ...
... production and breastfeeding. In a normal pregnancy, hCG stimulates the ovary to produce estrogens and progestins and helps stimulate normal development of the fetal genitals. The estrogens in the placenta stimulate breast development, promote normal labor, and help produce a steady rise in prolacti ...
Endocrine System
... The release of oxytocin from the posterior pituitary is controlled by negative feedback mechanisms. ...
... The release of oxytocin from the posterior pituitary is controlled by negative feedback mechanisms. ...
Thyroid

The thyroid gland, or simply the thyroid /ˈθaɪrɔɪd/, is one of the largest endocrine glands in the body, and consists of two connected lobes. It is found in the neck, below the laryngeal prominence (Adam's apple). The thyroid gland controls how quickly the body uses energy, makes proteins, and controls the body's sensitivity to other hormones. It participates in these processes by producing thyroid hormones, the principal ones being thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which is more active. These hormones regulate the growth and rate of function of many other systems in the body. T3 and T4 are synthesized from iodine and tyrosine. The thyroid also produces calcitonin, which plays a role in calcium homeostasis.Hormonal output from the thyroid is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) produced by the anterior pituitary, which itself is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) produced by the hypothalamus.The thyroid may be affected by some frequent thyroid diseases. Hyperthyroidism occurs when the gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones, the most common cause being Graves' disease—an autoimmune disorder. In contrast, hypothyroidism is a state of insufficient thyroid hormone production. Worldwide, the most common cause is iodine deficiency. Thyroid hormones are important for development, and hypothyroidism secondary to iodine deficiency remains the leading cause of preventable intellectual disability. In iodine-sufficient regions, the most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto's thyroiditis—also an autoimmune disease. In addition, the thyroid gland may also develop several types of nodules and cancer.