The Endocrine System - Palm Beach State College
... amino acid tryptophan Other monoamines come from the amino acid tyrosine Thyroid hormone is composed of two tyrosines – Follicular cells absorb iodide (I−) ions from blood and oxidize them to a reactive form – The cells also synthesize the large protein thyroglobulin (Tg) and store it in follicle lu ...
... amino acid tryptophan Other monoamines come from the amino acid tyrosine Thyroid hormone is composed of two tyrosines – Follicular cells absorb iodide (I−) ions from blood and oxidize them to a reactive form – The cells also synthesize the large protein thyroglobulin (Tg) and store it in follicle lu ...
Chapter 13
... • Two small glands on top of kidneys • Each gland has two parts that act as separate glands ...
... • Two small glands on top of kidneys • Each gland has two parts that act as separate glands ...
Chapter 25 - Austin Community College
... Hypothalamic releasing hormones Release of anterior pituitary hormones is directed by specific releasing hormones (factors) from the hypothalamic nuclei. All of these are polypeptide molecules. TRH – thyrotropin releasing hormone → (TSH and PRL) GHRH – growth hormone releasing hormone → (GH) Somato ...
... Hypothalamic releasing hormones Release of anterior pituitary hormones is directed by specific releasing hormones (factors) from the hypothalamic nuclei. All of these are polypeptide molecules. TRH – thyrotropin releasing hormone → (TSH and PRL) GHRH – growth hormone releasing hormone → (GH) Somato ...
VISCERA OF NECK Cervical viscera (3 layers) Endocrine layer
... aryepiglottic, thyroepiglottic muscles Posterior supplies posterior cricoarytenoid, transverse and oblique arytenoid muscles Inferior is primary motor nerve of larynx, as well as sensory fibers to mucosa of infraglottic cavity ...
... aryepiglottic, thyroepiglottic muscles Posterior supplies posterior cricoarytenoid, transverse and oblique arytenoid muscles Inferior is primary motor nerve of larynx, as well as sensory fibers to mucosa of infraglottic cavity ...
20 Endocrine System - Orange Coast College
... Distinctive “butterfly” shape due to its left and right lobes, which are connected at the anterior midline by a narrow isthmus. Both lobes of the thyroid gland are highly vascularized, giving it an intense reddish coloration. Regulation of thyroid hormone secretion depends upon a complex thyroid gla ...
... Distinctive “butterfly” shape due to its left and right lobes, which are connected at the anterior midline by a narrow isthmus. Both lobes of the thyroid gland are highly vascularized, giving it an intense reddish coloration. Regulation of thyroid hormone secretion depends upon a complex thyroid gla ...
Chapter 15-B Endocrine Glands
... • Iodides (I–) are actively taken into the cell, oxidized to iodine (I2), and released into the lumen • Iodine attaches to tyrosine (part of thyroglobulin), mediated by peroxidase enzymes, forming T1 (monoiodotyrosine, or MIT), and T2 (diiodotyrosine, or DIT) ...
... • Iodides (I–) are actively taken into the cell, oxidized to iodine (I2), and released into the lumen • Iodine attaches to tyrosine (part of thyroglobulin), mediated by peroxidase enzymes, forming T1 (monoiodotyrosine, or MIT), and T2 (diiodotyrosine, or DIT) ...
CRYDERS-Endocrine System
... taken into the cell, oxidized to iodine (I2), and released into the lumen Iodine attaches to tyrosine (part of thyroglobulin), mediated by peroxidase enzymes, forming T1 (monoiodotyrosine, or MIT), and T2 (diiodotyrosine, or DIT) ...
... taken into the cell, oxidized to iodine (I2), and released into the lumen Iodine attaches to tyrosine (part of thyroglobulin), mediated by peroxidase enzymes, forming T1 (monoiodotyrosine, or MIT), and T2 (diiodotyrosine, or DIT) ...
III Semester Botany MODULE 7 ENDOCRINOLOGY
... up of endocrine tissues that produce specific hormones, for example the endocrine pancreas, gonads (ovaries and testes), and hypothalamus. Also, the walls of the small intestine, stomach, kidneys, and heart contain small pockets of endocrine cells. Chemistry of Hormones Most hormones belong to one o ...
... up of endocrine tissues that produce specific hormones, for example the endocrine pancreas, gonads (ovaries and testes), and hypothalamus. Also, the walls of the small intestine, stomach, kidneys, and heart contain small pockets of endocrine cells. Chemistry of Hormones Most hormones belong to one o ...
Hyperthyroidism in Cats - PetCare Veterinary Hospital
... Some of the risk factors for hyperthyroidism have been defined above. A specific cause for hyperthyroidism has not been identified. The possible role of dietary iodine continues to be investigated as a dietary influence on development of hyperthyroidism. ...
... Some of the risk factors for hyperthyroidism have been defined above. A specific cause for hyperthyroidism has not been identified. The possible role of dietary iodine continues to be investigated as a dietary influence on development of hyperthyroidism. ...
Chapter 41 Animal Hormones
... Thyroid Gland In humans/other mammals, thyroid gland consists of 2 lobes located on ventral side of trachea Produces 2 very similar hormones from tyrosine Triiodothyronine (T3) and Tetraiodothyronine (T4)/thyroxine ...
... Thyroid Gland In humans/other mammals, thyroid gland consists of 2 lobes located on ventral side of trachea Produces 2 very similar hormones from tyrosine Triiodothyronine (T3) and Tetraiodothyronine (T4)/thyroxine ...
4.03-4.04 Endocrine System PPP
... Hormones-Target cells & negative feedback https://youtu.be/tN78hYn3ehc ...
... Hormones-Target cells & negative feedback https://youtu.be/tN78hYn3ehc ...
Hormone
... Hormones • Structurally consists of nerve fibers and neuroglia v. glandular epithelial cells of the anterior pituitary gland • The nerve fibers originate in the hypothalamus • Two hormones are produced: • Antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) • Oxytocin ...
... Hormones • Structurally consists of nerve fibers and neuroglia v. glandular epithelial cells of the anterior pituitary gland • The nerve fibers originate in the hypothalamus • Two hormones are produced: • Antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) • Oxytocin ...
The Endocrine System The Endocrine System The endocrine
... The hypothalamus is connected to the pituitary gland, and partners in the process of hormone secretion and production. The hormones released from the posterior pituitary glands, antidiuretic hormone, and oxytocin are produced in the hypothalamus and travel to the posterior pituitary gland for relea ...
... The hypothalamus is connected to the pituitary gland, and partners in the process of hormone secretion and production. The hormones released from the posterior pituitary glands, antidiuretic hormone, and oxytocin are produced in the hypothalamus and travel to the posterior pituitary gland for relea ...
The endocrine system
... • 3 – Gland stimulates more hormone. • 4 – When blood levels of hormone increase, the brain hormone stops. Nervous Control ...
... • 3 – Gland stimulates more hormone. • 4 – When blood levels of hormone increase, the brain hormone stops. Nervous Control ...
Chapter 13: The Endocrine System
... Over production of thyroid hormones leads to a sped-up metabolic state Common type is Grave’s disease o Increased heart rate o Increase in peristalsis resulting in diarrhea o Elevation in body temperature o Hyperactivity o Weight loss o Wide emotional swings o Bulging eyes called exophthalmia du ...
... Over production of thyroid hormones leads to a sped-up metabolic state Common type is Grave’s disease o Increased heart rate o Increase in peristalsis resulting in diarrhea o Elevation in body temperature o Hyperactivity o Weight loss o Wide emotional swings o Bulging eyes called exophthalmia du ...
Endocrine Review Sheet
... mechanisms involved in maintaining the appropriate level of calcium in the blood and interstitial fluid. Please be sure to include what hormones are involved, where they are produced, what stimulates the production and release of these hormones, what the target cells are and what happens as a result ...
... mechanisms involved in maintaining the appropriate level of calcium in the blood and interstitial fluid. Please be sure to include what hormones are involved, where they are produced, what stimulates the production and release of these hormones, what the target cells are and what happens as a result ...
Endocrine System
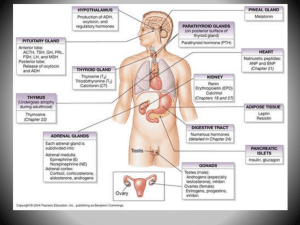
... • Hypothalamus – The Hypothalamus is a collection of specialized cells that is located in the lower central part of the brain. It has a small, cone shaped structure which projects downward ending in the pituitary stalk. • Pituitary Glands: The pituitary gland is a little bigger than a pea and is nes ...
... • Hypothalamus – The Hypothalamus is a collection of specialized cells that is located in the lower central part of the brain. It has a small, cone shaped structure which projects downward ending in the pituitary stalk. • Pituitary Glands: The pituitary gland is a little bigger than a pea and is nes ...
Biology 251 Fall 2015 1 TOPIC 9: THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM I
... In these discussions of the endocrine system, we will focus on some general principles and on a few select systems. Throughout the remainder of the course, as we discuss the different body systems, we will refer to the general principles you learn in these two topics to provide an understanding of h ...
... In these discussions of the endocrine system, we will focus on some general principles and on a few select systems. Throughout the remainder of the course, as we discuss the different body systems, we will refer to the general principles you learn in these two topics to provide an understanding of h ...
Endocrine Overview - Solon City Schools
... Paracrines: affect local and other cells Eicosanoids: local hormones involved in inflammation ...
... Paracrines: affect local and other cells Eicosanoids: local hormones involved in inflammation ...
Chapter 18 - Endocrine
... Hypothalamic releasing hormones Release of anterior pituitary hormones is directed by specific releasing hormones (factors) from the hypothalamic nuclei. All of these are polypeptide molecules. TRH – thyrotropin releasing hormone → (TSH and PRL) GHRH – growth hormone releasing hormone → (GH) CRH – ...
... Hypothalamic releasing hormones Release of anterior pituitary hormones is directed by specific releasing hormones (factors) from the hypothalamic nuclei. All of these are polypeptide molecules. TRH – thyrotropin releasing hormone → (TSH and PRL) GHRH – growth hormone releasing hormone → (GH) CRH – ...
handout
... cecum of tongue; tissue migrates ant. hyoid bone in midline of neck to below cricoid cartilage Normally posterior to thyroid gland or embedded in it; develop from branchial pouches 3 and 4 Inferior parathyroid pouch 3 Superior parathyroid pouch 4 ...
... cecum of tongue; tissue migrates ant. hyoid bone in midline of neck to below cricoid cartilage Normally posterior to thyroid gland or embedded in it; develop from branchial pouches 3 and 4 Inferior parathyroid pouch 3 Superior parathyroid pouch 4 ...
Thyroiditis
... may be confused with surrounding fat. A distinct hilar vessel is also present that can be seen if the surrounding fat does not obscure the glands' hila. The superior parathyroid glands are most commonly located in the posterolateral aspect of the superior pole of the thyroid gland at the cricothyroi ...
... may be confused with surrounding fat. A distinct hilar vessel is also present that can be seen if the surrounding fat does not obscure the glands' hila. The superior parathyroid glands are most commonly located in the posterolateral aspect of the superior pole of the thyroid gland at the cricothyroi ...
Thyroid

The thyroid gland, or simply the thyroid /ˈθaɪrɔɪd/, is one of the largest endocrine glands in the body, and consists of two connected lobes. It is found in the neck, below the laryngeal prominence (Adam's apple). The thyroid gland controls how quickly the body uses energy, makes proteins, and controls the body's sensitivity to other hormones. It participates in these processes by producing thyroid hormones, the principal ones being thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which is more active. These hormones regulate the growth and rate of function of many other systems in the body. T3 and T4 are synthesized from iodine and tyrosine. The thyroid also produces calcitonin, which plays a role in calcium homeostasis.Hormonal output from the thyroid is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) produced by the anterior pituitary, which itself is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) produced by the hypothalamus.The thyroid may be affected by some frequent thyroid diseases. Hyperthyroidism occurs when the gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones, the most common cause being Graves' disease—an autoimmune disorder. In contrast, hypothyroidism is a state of insufficient thyroid hormone production. Worldwide, the most common cause is iodine deficiency. Thyroid hormones are important for development, and hypothyroidism secondary to iodine deficiency remains the leading cause of preventable intellectual disability. In iodine-sufficient regions, the most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto's thyroiditis—also an autoimmune disease. In addition, the thyroid gland may also develop several types of nodules and cancer.