The Digestive System
... world with his book on a “diet revolution” that placed extreme emphasis on protein and fat, and discouraged eating vegetables or carbohydrates. When a revised version of the diet was published in 1992, the book became an instant best-seller. Dieters waxed rhapsodic about the quick and persistent wei ...
... world with his book on a “diet revolution” that placed extreme emphasis on protein and fat, and discouraged eating vegetables or carbohydrates. When a revised version of the diet was published in 1992, the book became an instant best-seller. Dieters waxed rhapsodic about the quick and persistent wei ...
English
... The rumen is the largest section of the stomach. The rumen contains bacteria and other microbes that promote fermentation. The rumen is the first compartment of the stomach that food enters. The polygastric system is designed for food to be ingested, eructated (belched up), chewed, and swallowed ...
... The rumen is the largest section of the stomach. The rumen contains bacteria and other microbes that promote fermentation. The rumen is the first compartment of the stomach that food enters. The polygastric system is designed for food to be ingested, eructated (belched up), chewed, and swallowed ...
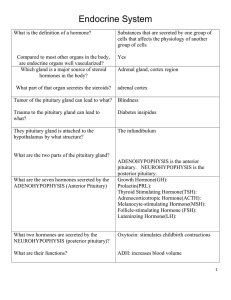
7 Endocrine Anat and Physio flashcards
... and the definition of a hormone is one that does not secrete into a duct; it secretes into the blood, where it is transported elsewhere in the body and has its effect there. a series of glands that release a hormone into the plasma, where it is dissolved and ...
... and the definition of a hormone is one that does not secrete into a duct; it secretes into the blood, where it is transported elsewhere in the body and has its effect there. a series of glands that release a hormone into the plasma, where it is dissolved and ...
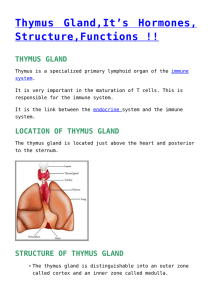
thymus gland - Biology Notes Help
... These axons release peptide hormones into the capillaries of the hypophyseal circulation. 3. The gland is connected to a region of the brain called hypothalamus by the pituitary stalk. Directly above the pituitary gland and in front of the pituitary stalk are the crossing fibers of the optic nerve, ...
... These axons release peptide hormones into the capillaries of the hypophyseal circulation. 3. The gland is connected to a region of the brain called hypothalamus by the pituitary stalk. Directly above the pituitary gland and in front of the pituitary stalk are the crossing fibers of the optic nerve, ...
Cardiovascular System part II
... large amounts of nutrients and ensures that the liver processes these nutrients before entering systemic circulation. Inferior mesentric vein: drains part of the large intestine and drains into the … Splenic vein: drains the spleen, pancreas and left side of the stomach ...
... large amounts of nutrients and ensures that the liver processes these nutrients before entering systemic circulation. Inferior mesentric vein: drains part of the large intestine and drains into the … Splenic vein: drains the spleen, pancreas and left side of the stomach ...
Chapter 14 Assignments, Study Guide, Word List, Pronunciation
... a constriction or narrow passage connecting two larger parts of an organ or other anatomical structure. a high level of this substance in the blood occurs in diabetes mellitus as the body metabolizes fat instead of glucose a subdivision of a body organ or part bounded by fissures, connective tissu ...
... a constriction or narrow passage connecting two larger parts of an organ or other anatomical structure. a high level of this substance in the blood occurs in diabetes mellitus as the body metabolizes fat instead of glucose a subdivision of a body organ or part bounded by fissures, connective tissu ...
dnt 200 nutrition for health sciences
... The Absorptive System Release of Absorbed Nutrients • Once inside the intestinal cells, the products of digestion must be released for transport to the rest of the body • Water soluble nutrients are released directly into the bloodstream via the capillaries • Larger fats and fat soluble vitamins – A ...
... The Absorptive System Release of Absorbed Nutrients • Once inside the intestinal cells, the products of digestion must be released for transport to the rest of the body • Water soluble nutrients are released directly into the bloodstream via the capillaries • Larger fats and fat soluble vitamins – A ...
File
... longer, and more horizontal than right. It passes to left below arch of aorta & in front of esophagus. On entering hilum of left lung, principal bronchus divides into a superior & an inferior lobar bronchus ...
... longer, and more horizontal than right. It passes to left below arch of aorta & in front of esophagus. On entering hilum of left lung, principal bronchus divides into a superior & an inferior lobar bronchus ...
exam 4
... 48) Which of the following INCORRECTLY describes the root of the lung? A) it is where visceral and parietal pleura are continuous with one another B) it is the diaphragmatic surface C) it enters the hilum on the mediastinal surface D) it consists of the primary bronchus and pulmonary artery and vein ...
... 48) Which of the following INCORRECTLY describes the root of the lung? A) it is where visceral and parietal pleura are continuous with one another B) it is the diaphragmatic surface C) it enters the hilum on the mediastinal surface D) it consists of the primary bronchus and pulmonary artery and vein ...
Ehrlich_8e_ppt__chapter_13 Endocrine System
... The pancreatic islets (pan-kree-AT-ick EYE-lets) are those parts of the pancreas that have endocrine functions. An islet is a small isolated mass, or island, of one type of tissue within a larger mass of a different type. The endocrine functions of these islets are the control of blood sugar levels ...
... The pancreatic islets (pan-kree-AT-ick EYE-lets) are those parts of the pancreas that have endocrine functions. An islet is a small isolated mass, or island, of one type of tissue within a larger mass of a different type. The endocrine functions of these islets are the control of blood sugar levels ...
stomach and pH NOTES
... •_________________________: surface is columnar epithelial cells (goblet cells) which: produce mucous to protect stomach lining from acid. Below the surface are gastric glands also lined with columnar epithelial cells, but are 2 specialized types: 1.______________________: make pepsinogen- an inacti ...
... •_________________________: surface is columnar epithelial cells (goblet cells) which: produce mucous to protect stomach lining from acid. Below the surface are gastric glands also lined with columnar epithelial cells, but are 2 specialized types: 1.______________________: make pepsinogen- an inacti ...
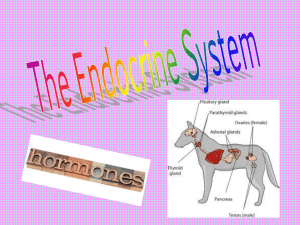
Endocrine System - Killingly Public Schools
... • Comprised of glands and other tissues that produce hormones ...
... • Comprised of glands and other tissues that produce hormones ...
The peritoneum 腹膜
... Position: lies between the liver and duodenum, behind the lesser omentum and infront of the inferior vena cava The omental bursa (lesser sac) communicates with the greater sac through the omental foramen. ...
... Position: lies between the liver and duodenum, behind the lesser omentum and infront of the inferior vena cava The omental bursa (lesser sac) communicates with the greater sac through the omental foramen. ...
PowerPoint Lecture 10
... the ventral opening of the yolk sac. Initially, this means that the angiogenetic cell clusters (and the blood vessel that forms from them) have the pattern of a "horseshoe" if viewed from a dorsal or ventral perspective. ...
... the ventral opening of the yolk sac. Initially, this means that the angiogenetic cell clusters (and the blood vessel that forms from them) have the pattern of a "horseshoe" if viewed from a dorsal or ventral perspective. ...
Thyroid Gland
... Increasing rate of calcium excretion by kidneys Reducing calcium absorption in intestines ...
... Increasing rate of calcium excretion by kidneys Reducing calcium absorption in intestines ...
Chapter 16 - apsubiology.org
... Bind to cytoplasmic receptors inside the cell Hormone-receptor (h-r) complex enters the nucleus, binds to a DNA receptor protein This causes transcription of certain genes, and thus produces specific proteins This direct gene activation is a slower process, but with longer lasting effects ...
... Bind to cytoplasmic receptors inside the cell Hormone-receptor (h-r) complex enters the nucleus, binds to a DNA receptor protein This causes transcription of certain genes, and thus produces specific proteins This direct gene activation is a slower process, but with longer lasting effects ...
Blood/Vessels - Austin Community College
... supply a region of the body, the blood circulates in the following order: arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, and veins. The distribution of arteries and veins on the left and right sides of the body are usually identical, except near the heart where large vessels connect to the atria or ven ...
... supply a region of the body, the blood circulates in the following order: arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, and veins. The distribution of arteries and veins on the left and right sides of the body are usually identical, except near the heart where large vessels connect to the atria or ven ...
Gi Embryology 3
... at about the sixth week as a small conical dilation of the caudal limb of the primary intestinal loop, is the last part of the gut to reenter the abdominal cavity. • Temporarily it lies in the right ...
... at about the sixth week as a small conical dilation of the caudal limb of the primary intestinal loop, is the last part of the gut to reenter the abdominal cavity. • Temporarily it lies in the right ...
study guide unit 3
... What is the foramen ovale called in adults? Fossa ovalis What is the connection between the pulmonary artery and the aorta? Ductus arteriosus What is the name for the venous vessel leading to the liver? Hepatic portal vein (not hepatic vein!) A portal system is a ________ system within the ________s ...
... What is the foramen ovale called in adults? Fossa ovalis What is the connection between the pulmonary artery and the aorta? Ductus arteriosus What is the name for the venous vessel leading to the liver? Hepatic portal vein (not hepatic vein!) A portal system is a ________ system within the ________s ...
Dr. AASHISH H. PANCHAL (M.PHARM., Ph.D.) GSEB, CBSE, ICSE
... CHAPTER-2 Endocrine System Marks:40 ...
... CHAPTER-2 Endocrine System Marks:40 ...
Digestive Tract
... • Become more fluid • pH approaches 2.0 • Pepsin activity increases • Protein disassembly begins • Although digestion occurs in the stomach, nutrients are not absorbed there ...
... • Become more fluid • pH approaches 2.0 • Pepsin activity increases • Protein disassembly begins • Although digestion occurs in the stomach, nutrients are not absorbed there ...
Document
... Free hormone released in blood Bound to thyroxine binding globulin (TBG) Which slowly releases the hormone to target ...
... Free hormone released in blood Bound to thyroxine binding globulin (TBG) Which slowly releases the hormone to target ...
I. Introduction and
... gland to release its hormones. 11. The secretion of TSH is controlled by TRH. 12. The actions of adrenocorticotropic hormone are to control secretion of certain hormone from the adrenal cortex. 13. The secretion of ACTH is controlled by CRH. 14. Gonadotropins are LH and FSH. 15. The actions of folli ...
... gland to release its hormones. 11. The secretion of TSH is controlled by TRH. 12. The actions of adrenocorticotropic hormone are to control secretion of certain hormone from the adrenal cortex. 13. The secretion of ACTH is controlled by CRH. 14. Gonadotropins are LH and FSH. 15. The actions of folli ...
Anatomy Lab – Exam 2
... Celiac Trunk → Common hepatic artery → proper hepatic artery (in hepatoduodenal ligament) → ○ Right gastric artery – to lesser curvature of stomach ○ Right, left hepatic arteries ○ Cystic artery – goes to gallbladder, is a branch of the right hepatic artery Celiac Trunk → Common hepatic artery → ...
... Celiac Trunk → Common hepatic artery → proper hepatic artery (in hepatoduodenal ligament) → ○ Right gastric artery – to lesser curvature of stomach ○ Right, left hepatic arteries ○ Cystic artery – goes to gallbladder, is a branch of the right hepatic artery Celiac Trunk → Common hepatic artery → ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.