
Anatomy Lab – Exam 2
... Celiac Trunk → Common hepatic artery → proper hepatic artery (in hepatoduodenal ligament) → ○ Right gastric artery – to lesser curvature of stomach ○ Right, left hepatic arteries ○ Cystic artery – goes to gallbladder, is a branch of the right hepatic artery Celiac Trunk → Common hepatic artery → ...
... Celiac Trunk → Common hepatic artery → proper hepatic artery (in hepatoduodenal ligament) → ○ Right gastric artery – to lesser curvature of stomach ○ Right, left hepatic arteries ○ Cystic artery – goes to gallbladder, is a branch of the right hepatic artery Celiac Trunk → Common hepatic artery → ...
Anatomy Lab – Exam 2
... Celiac Trunk → Common hepatic artery → proper hepatic artery (in hepatoduodenal ligament) → ○ Right gastric artery – to lesser curvature of stomach ○ Right, left hepatic arteries ○ Cystic artery – goes to gallbladder, is a branch of the right hepatic artery Celiac Trunk → Common hepatic artery → ...
... Celiac Trunk → Common hepatic artery → proper hepatic artery (in hepatoduodenal ligament) → ○ Right gastric artery – to lesser curvature of stomach ○ Right, left hepatic arteries ○ Cystic artery – goes to gallbladder, is a branch of the right hepatic artery Celiac Trunk → Common hepatic artery → ...
Glencoe Health Lesson 3 The Digestive System
... As food is digested in the stomach, it is converted to chyme, a creamy, fluid mixture of food and gastric juices, which is moved into the small intestine. ...
... As food is digested in the stomach, it is converted to chyme, a creamy, fluid mixture of food and gastric juices, which is moved into the small intestine. ...
How the Body Uses Food: Digestion and Absorption
... and transport absorbed nutrients toward the major branches of the lymphatic and circulatory systems. The breakdown products of fat digestion are largely absorbed into lymph vessels, whereas carbohydrate and protein breakdown products enter the blood vessels. The nutrient-rich contents of the lymphat ...
... and transport absorbed nutrients toward the major branches of the lymphatic and circulatory systems. The breakdown products of fat digestion are largely absorbed into lymph vessels, whereas carbohydrate and protein breakdown products enter the blood vessels. The nutrient-rich contents of the lymphat ...
D. hepatic artery
... on the medial thigh, superficial throughout its length, arises by a tendon from the lower one-half of the pubic symphysis and pubic arch, and inserts into the upper part of the medial surface of the tibia between the sartorius and semitendinosus A. B. C. D. E. ...
... on the medial thigh, superficial throughout its length, arises by a tendon from the lower one-half of the pubic symphysis and pubic arch, and inserts into the upper part of the medial surface of the tibia between the sartorius and semitendinosus A. B. C. D. E. ...
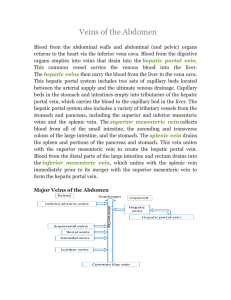
Veins of the Abdomen
... The hepatic veins then carry the blood from the liver to the vena cava. This hepatic portal system includes two sets of capillary beds located between the arterial supply and the ultimate venous drainage. Capillary beds in the stomach and intestines empty into tributaries of the hepatic portal vein, ...
... The hepatic veins then carry the blood from the liver to the vena cava. This hepatic portal system includes two sets of capillary beds located between the arterial supply and the ultimate venous drainage. Capillary beds in the stomach and intestines empty into tributaries of the hepatic portal vein, ...
D. hepatic artery
... on the medial thigh, superficial throughout its length, arises by a tendon from the lower one-half of the pubic symphysis and pubic arch, and inserts into the upper part of the medial surface of the tibia between the sartorius and semitendinosus A. B. C. D. E. ...
... on the medial thigh, superficial throughout its length, arises by a tendon from the lower one-half of the pubic symphysis and pubic arch, and inserts into the upper part of the medial surface of the tibia between the sartorius and semitendinosus A. B. C. D. E. ...
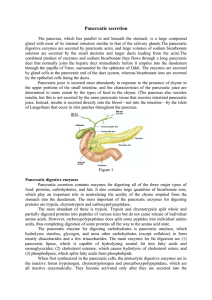
Pancreatic secretion
... but relatively small quantities of water and electrolytes to go with the enzymes. Without the water, most of the enzymes remain temporarily stored in the acini and ducts until more fluid secretion comes along to wash them into the duodenum. Secretin, in contrast to the first two basic stimuli, stimu ...
... but relatively small quantities of water and electrolytes to go with the enzymes. Without the water, most of the enzymes remain temporarily stored in the acini and ducts until more fluid secretion comes along to wash them into the duodenum. Secretin, in contrast to the first two basic stimuli, stimu ...
Digestive system - thephysicsteacher.ie
... 5. Write out the Human dental formula 6. Give the function of incisors, canines, pre molars and molars 7. Describe how food is mechanically broken down by (a) Teeth, (b) Contractions of the stomach wall, (c) Peristalsis 8. Explain the role of Bile Salts in Chemical digestion 9. Name one Amylase enzy ...
... 5. Write out the Human dental formula 6. Give the function of incisors, canines, pre molars and molars 7. Describe how food is mechanically broken down by (a) Teeth, (b) Contractions of the stomach wall, (c) Peristalsis 8. Explain the role of Bile Salts in Chemical digestion 9. Name one Amylase enzy ...
Slides - gserianne.com
... – Review of normal endocrine gland anatomy & physiology – Pancreatitis – Diabetes mellitus – Pancreatic neoplasms ...
... – Review of normal endocrine gland anatomy & physiology – Pancreatitis – Diabetes mellitus – Pancreatic neoplasms ...
introduction to digestive system anatomy
... emptying the contents of the stomach into the duodenum. Absorption of chemical compounds occurs principally in the small intestine. It is a 5- to 6-m-long tube. It is shorter in life, when tonus is present, than in the cadaver. It consists of the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. Peristalsis also occurs ...
... emptying the contents of the stomach into the duodenum. Absorption of chemical compounds occurs principally in the small intestine. It is a 5- to 6-m-long tube. It is shorter in life, when tonus is present, than in the cadaver. It consists of the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. Peristalsis also occurs ...
Digestive and Endocrine Systems
... glucose. Glucagon stimulates the release of glucose into the blood stream. Insulin deficiency causes diabetes mellitus: a condition of abnormally high blood glucose concentration. 2 types of diabetes: I and II. Type I diabetes is a severe childhood disorder in which insulin-producing cells die ...
... glucose. Glucagon stimulates the release of glucose into the blood stream. Insulin deficiency causes diabetes mellitus: a condition of abnormally high blood glucose concentration. 2 types of diabetes: I and II. Type I diabetes is a severe childhood disorder in which insulin-producing cells die ...
Quebec - Welcome to the WOW Lab at McGill University
... b. Digestive glands i) Names the main digestive glands (salivary glands, gastric glands, pancreas, liver, intestinal glands) ii) Describes the function of the main digestive glands (e.g. secretion of saliva, gastric enzymes, digestive juices, bile) Students will examine the digestive glands involve ...
... b. Digestive glands i) Names the main digestive glands (salivary glands, gastric glands, pancreas, liver, intestinal glands) ii) Describes the function of the main digestive glands (e.g. secretion of saliva, gastric enzymes, digestive juices, bile) Students will examine the digestive glands involve ...
test_1 - Homework Market
... 9) A long digestive system is usually found in animals that eat only Answer C) Plants or autotrophs The animals that eat plants are called herbivores (like cow, goat, sheep etc), which have a long and coiled type of digestive system. It is necessary to digest and observe highly complex carbohydrates ...
... 9) A long digestive system is usually found in animals that eat only Answer C) Plants or autotrophs The animals that eat plants are called herbivores (like cow, goat, sheep etc), which have a long and coiled type of digestive system. It is necessary to digest and observe highly complex carbohydrates ...
Potential Use of Left Renal Vein Graft in Pancreaticoduodenectomy
... a size disparity which requires some modification to be applied as a portal vein graft. Therefore, these veins cannot be used in the same way as the internal jugular vein and the others listed above. Furthermore, harvesting these autologous veins requires creating an additional wound and is associat ...
... a size disparity which requires some modification to be applied as a portal vein graft. Therefore, these veins cannot be used in the same way as the internal jugular vein and the others listed above. Furthermore, harvesting these autologous veins requires creating an additional wound and is associat ...
29.6 The Endocrine System and Hormones
... growth, development, and digestion. • It is a collection of physically disconnected organs • responds to environment May control: • Cell division • Cell death • Sexual development • Body temperature • Alertness • Salt levels… ...
... growth, development, and digestion. • It is a collection of physically disconnected organs • responds to environment May control: • Cell division • Cell death • Sexual development • Body temperature • Alertness • Salt levels… ...
26. Digestive System
... Ingestion (in-jes′chŭn; ingero = to carry in) is the introduction of solid and liquid materials into the oral cavity. It is the first step in the process of digesting and absorbing nutrients. Digestion is the breakdown of large food items into smaller structures and molecules. There are two aspects ...
... Ingestion (in-jes′chŭn; ingero = to carry in) is the introduction of solid and liquid materials into the oral cavity. It is the first step in the process of digesting and absorbing nutrients. Digestion is the breakdown of large food items into smaller structures and molecules. There are two aspects ...
Document
... • Exocrine function • Acini (clusters of secretory cells) secrete pancreatic juice • Zymogen granules of secretory cells contain digestive enzymes ...
... • Exocrine function • Acini (clusters of secretory cells) secrete pancreatic juice • Zymogen granules of secretory cells contain digestive enzymes ...
Digestive system and nutrition
... • Gastrin: stimulates release of gastric juice • Secretin: stimulates pancreas to secrete water and bicarbonate • Cholecystokinin (CCK): signals pancreas to secrete digestive enzymes Slide 14.15 ...
... • Gastrin: stimulates release of gastric juice • Secretin: stimulates pancreas to secrete water and bicarbonate • Cholecystokinin (CCK): signals pancreas to secrete digestive enzymes Slide 14.15 ...
Thyroid gland
... • It is formed by the ventral primary divisions of the first four cervical nerves. • Each nerve, except the first, divides into the superior branch and the inferior branch. • C1 joins the upper branch of C2 • the adjacent upper and lower branches of C2 and C3 fuse • Each nerve receives a gray ramus ...
... • It is formed by the ventral primary divisions of the first four cervical nerves. • Each nerve, except the first, divides into the superior branch and the inferior branch. • C1 joins the upper branch of C2 • the adjacent upper and lower branches of C2 and C3 fuse • Each nerve receives a gray ramus ...
Branches of axillary artery for PDF 13.5.11
... divides branches. (i)side clavicular, up over subclavius ; (ii) pectoral largesurface and runs into two, one goes toruns the side of the chest, the other to theisdeep of The axillary artery across thewith superior aspect ofanterior the axilla is marked by the latissimus down between with the runs th ...
... divides branches. (i)side clavicular, up over subclavius ; (ii) pectoral largesurface and runs into two, one goes toruns the side of the chest, the other to theisdeep of The axillary artery across thewith superior aspect ofanterior the axilla is marked by the latissimus down between with the runs th ...
the digestive system
... stomach, small intestine, and large intestine – Accessory digestive organs aid digestion physically and produce secretions that break down foodstuff in the GI tract; the organs involved are the teeth, tongue, gallbladder, salivary glands, liver, and pancreas ...
... stomach, small intestine, and large intestine – Accessory digestive organs aid digestion physically and produce secretions that break down foodstuff in the GI tract; the organs involved are the teeth, tongue, gallbladder, salivary glands, liver, and pancreas ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.




















![Chapter41 Hormones Notes [Compatibility Mode]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016605577_1-a7aad459db07937df65df4f3a411aef9-300x300.png)