Digestive Physiology A. Motility = Mechanical Movement of Materials
... a. release of bile from liver & gall bladder b. release of pancreatic secretions c. release of duodenal secretions a. Bile contains no enzymes main constituents of bile are: bile salts made from cholesterol help emulsify (solubilizing) dietary lipids b. Pancreatic Juices pancreas is an endocrine gla ...
... a. release of bile from liver & gall bladder b. release of pancreatic secretions c. release of duodenal secretions a. Bile contains no enzymes main constituents of bile are: bile salts made from cholesterol help emulsify (solubilizing) dietary lipids b. Pancreatic Juices pancreas is an endocrine gla ...
Endocrine System
... Pancreas The pancreas also has an exocrine function. Where are these products released? Describe the overlapping homeostatic mechanisms involving insulin and glucagon. ...
... Pancreas The pancreas also has an exocrine function. Where are these products released? Describe the overlapping homeostatic mechanisms involving insulin and glucagon. ...
Human Endocrine System
... Stimulates the release of sugar from the liver and into the blood Therefore: insulin lowers sugar level in blood glucagon raises sugar level in blood ...
... Stimulates the release of sugar from the liver and into the blood Therefore: insulin lowers sugar level in blood glucagon raises sugar level in blood ...
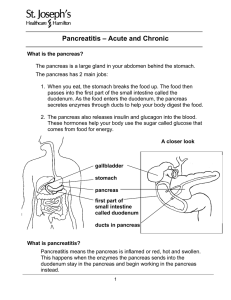
Pancreatitis - Acute and Chronic
... The doctor takes a full medical history and does a complete medical exam. Blood tests show an increase in 2 enzymes called amylase and lipase made by the pancreas. Blood tests often show changes in other things such as white blood cells, glucose, sodium, calcium and potassium. These tests are also d ...
... The doctor takes a full medical history and does a complete medical exam. Blood tests show an increase in 2 enzymes called amylase and lipase made by the pancreas. Blood tests often show changes in other things such as white blood cells, glucose, sodium, calcium and potassium. These tests are also d ...
The Digestive System
... abdominal cavity and covering abdominal organs 1. The parietal layer of peritoneum lines abdominal cavity 2. Viscreal layer of peritoneum covers abdominal organs 3. Peritoneal space lies between parietal and visceral layers ...
... abdominal cavity and covering abdominal organs 1. The parietal layer of peritoneum lines abdominal cavity 2. Viscreal layer of peritoneum covers abdominal organs 3. Peritoneal space lies between parietal and visceral layers ...
About The Digestive System
... occur. Its main function is to absorb water from the indigestible parts of food so the body can use the water. The time it takes to digest food depends on its composition- a fatty meal takes longer to digest than one rich in sugars or proteins. On average, digestion takes about 55 hours in men and 7 ...
... occur. Its main function is to absorb water from the indigestible parts of food so the body can use the water. The time it takes to digest food depends on its composition- a fatty meal takes longer to digest than one rich in sugars or proteins. On average, digestion takes about 55 hours in men and 7 ...
Digestion and Absorption of Nutrients
... Bile emulsifies fatsoluble vitamins and aids in their absorption with ...
... Bile emulsifies fatsoluble vitamins and aids in their absorption with ...
Respiratory Physiology
... Composition of Pancreatic Juice Water solution of enzymes and electrolytes (primarily HCO3–) Neutralizes acid chyme Provides optimal environment for pancreatic enzymes Enzymes are released in inactive form and activated in the duodenum Examples include: Trypsinogen is activated to trypsin Procarboxy ...
... Composition of Pancreatic Juice Water solution of enzymes and electrolytes (primarily HCO3–) Neutralizes acid chyme Provides optimal environment for pancreatic enzymes Enzymes are released in inactive form and activated in the duodenum Examples include: Trypsinogen is activated to trypsin Procarboxy ...
Small bowel physiology
... hand, remain bound to the apical membranes of brush border cells, anchored by transmembrane protein “stalks”. Brush border enzymes are stationary and will not be swept out of the small intestine along with the chyme as it is propelled forward. The brush border enzymes include peptidases, disaccharid ...
... hand, remain bound to the apical membranes of brush border cells, anchored by transmembrane protein “stalks”. Brush border enzymes are stationary and will not be swept out of the small intestine along with the chyme as it is propelled forward. The brush border enzymes include peptidases, disaccharid ...
Biology 12 - The Digestive System
... • NaHCO3 makes the juice highly alkaline (pH ~ 8.5). It neutralizes the acid chyme and make the small intestine pH basic • pancreatic juice contains hydrolytic enzymes including pancreatic amylase (digests starch to maltose), trypsin (digests protein to peptides), and lipase (digests fat droplets to ...
... • NaHCO3 makes the juice highly alkaline (pH ~ 8.5). It neutralizes the acid chyme and make the small intestine pH basic • pancreatic juice contains hydrolytic enzymes including pancreatic amylase (digests starch to maltose), trypsin (digests protein to peptides), and lipase (digests fat droplets to ...
Introduction - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... Consists of two main lobes connected by the isthmus Controls metabolism Thyroxine (T4) Triiodothyronine (T3) ...
... Consists of two main lobes connected by the isthmus Controls metabolism Thyroxine (T4) Triiodothyronine (T3) ...
PowerPoint Presentation - The Human Digestive System
... Not part of the path of food, but play a critical role. ...
... Not part of the path of food, but play a critical role. ...
Figure from: Martini, Anatomy & Physiology
... for absorption in the small intestine Form a ‘brush border’ on the intestine Digestive enzymes are embedded in the membrane of microvilli ...
... for absorption in the small intestine Form a ‘brush border’ on the intestine Digestive enzymes are embedded in the membrane of microvilli ...
Digestion2
... The lining of the small intestine is not smooth: • Circular folds in the submucosa slow the passage of food and increase the area. They are covered with... • Villi, millions of microscopic fingerlike projections which are, in turn, covered with... • Microvilli, tiny cytoplasmic projections from the ...
... The lining of the small intestine is not smooth: • Circular folds in the submucosa slow the passage of food and increase the area. They are covered with... • Villi, millions of microscopic fingerlike projections which are, in turn, covered with... • Microvilli, tiny cytoplasmic projections from the ...
Digestive
... The small intestine is divided into the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. The duodenum has mucous glands in the submucosa; the jejunum has numerous, long villi; and the ileum has a large number of goblet cells. Cells in the small intestine produce peptidase, which act on proteins; maltase, sucrose, and ...
... The small intestine is divided into the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. The duodenum has mucous glands in the submucosa; the jejunum has numerous, long villi; and the ileum has a large number of goblet cells. Cells in the small intestine produce peptidase, which act on proteins; maltase, sucrose, and ...
Anatomy
... and nerves. The pulp is surrounded by a layer of dentin, which is then surrounded by a layer of cementum. The cementum is attached to the alveolar bone by periodontal ligaments, forming the gomphosis/dental-alveolar joint, which is a peg and socket joint. The root canal is the extension of the pu ...
... and nerves. The pulp is surrounded by a layer of dentin, which is then surrounded by a layer of cementum. The cementum is attached to the alveolar bone by periodontal ligaments, forming the gomphosis/dental-alveolar joint, which is a peg and socket joint. The root canal is the extension of the pu ...
Digestive enzymes - Univerzita Karlova v Praze
... Secretion of electrolytes, acid, or base to provide an appropriate environment for enzyme digestion Secretion of bile acids to solubilize lipids Hydrolysis of oligomers by intestinal surface enzymes Transport of nutrient molecules and of electrolytes from the intestinal lumen across the epithelial c ...
... Secretion of electrolytes, acid, or base to provide an appropriate environment for enzyme digestion Secretion of bile acids to solubilize lipids Hydrolysis of oligomers by intestinal surface enzymes Transport of nutrient molecules and of electrolytes from the intestinal lumen across the epithelial c ...
GI 32
... Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Oral Cavity and Pharynx- mechanical digestion begins ...
... Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Oral Cavity and Pharynx- mechanical digestion begins ...
The Digestive System
... The middle segment of the small intestine is called the: Jejunum What feather shaped organ secreted enzymes to digest food? Pancreas A small muscular sac that secretes bile and is located in the right upper quadrant of the ...
... The middle segment of the small intestine is called the: Jejunum What feather shaped organ secreted enzymes to digest food? Pancreas A small muscular sac that secretes bile and is located in the right upper quadrant of the ...
Ch 24: Digestive, urinary and nervous system study guide
... 1. Digestive System: Consists of the organs that break down food so that it can be used by the body. 2. Digestion begins in the mouth. 3. The two types of digestion are: chemical and mechanical 4. The breaking, crushing, and mashing of food is mechanical digestion. 5. Large molecules being broken do ...
... 1. Digestive System: Consists of the organs that break down food so that it can be used by the body. 2. Digestion begins in the mouth. 3. The two types of digestion are: chemical and mechanical 4. The breaking, crushing, and mashing of food is mechanical digestion. 5. Large molecules being broken do ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.