Review
... 3. The “gatekeeper” of the small intestine that regulates food movement into it is the: 4. The primary function of the small intestine is: 5. Amylase is an enzyme that digests what? 6. Pancreatic enzymes for digestion are secreted into which section of the SI? 7. Swallowing & peristalsis both assist ...
... 3. The “gatekeeper” of the small intestine that regulates food movement into it is the: 4. The primary function of the small intestine is: 5. Amylase is an enzyme that digests what? 6. Pancreatic enzymes for digestion are secreted into which section of the SI? 7. Swallowing & peristalsis both assist ...
Digestive system1
... • Segment I is caudate lobe of liver • Lie in RT hypochondrium • Produce bile, leave liver through RT, LT hepatic ducts, join cystic duct to form bile duct ...
... • Segment I is caudate lobe of liver • Lie in RT hypochondrium • Produce bile, leave liver through RT, LT hepatic ducts, join cystic duct to form bile duct ...
Bio 242 Unit 1 Study Guide
... Gallbladder in bile storage and modification (Bile salts, Bilirubin, Cholesterol, Emulsification, Enterohepatic circulation) 9. Understand the functions of the liver in carbohydrate, lipid, and protein metabolism, hormone and drug removal, storage, phagocytosis, and activation of vitamin D. (Glycoge ...
... Gallbladder in bile storage and modification (Bile salts, Bilirubin, Cholesterol, Emulsification, Enterohepatic circulation) 9. Understand the functions of the liver in carbohydrate, lipid, and protein metabolism, hormone and drug removal, storage, phagocytosis, and activation of vitamin D. (Glycoge ...
Chapter 25: Digestive System
... Gallbladder in bile storage and modification (Bile salts, Bilirubin, Cholesterol, Emulsification, Enterohepatic circulation) 9. Understand the functions of the liver in carbohydrate, lipid, and protein metabolism, hormone and drug removal, storage, phagocytosis, and activation of vitamin D. (Glycoge ...
... Gallbladder in bile storage and modification (Bile salts, Bilirubin, Cholesterol, Emulsification, Enterohepatic circulation) 9. Understand the functions of the liver in carbohydrate, lipid, and protein metabolism, hormone and drug removal, storage, phagocytosis, and activation of vitamin D. (Glycoge ...
INDIVIDUAL ANIMAL SUBMISSION FORM (A)
... Please print and complete this form and forward/fax to MDS. We will contact you for a detailed quotation. ...
... Please print and complete this form and forward/fax to MDS. We will contact you for a detailed quotation. ...
The Digestive System
... *Liquid food as it leaves the stomach is called CHYME *Forcible explusion of upper GI contents = vomiting ...
... *Liquid food as it leaves the stomach is called CHYME *Forcible explusion of upper GI contents = vomiting ...
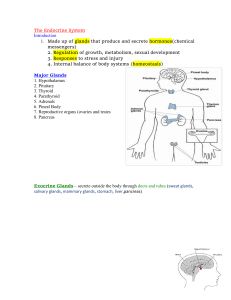
Endocrine System
... gland selects and removes materials from the blood, processes them, and secretes the finished chemical product for use somewhere in the body. ...
... gland selects and removes materials from the blood, processes them, and secretes the finished chemical product for use somewhere in the body. ...
Digestion
... bacteria. Our body provides nutrients, water, and a warm environment. The bacteria synthesize vitamin K. ...
... bacteria. Our body provides nutrients, water, and a warm environment. The bacteria synthesize vitamin K. ...
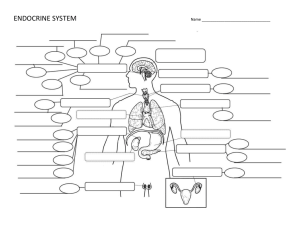
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Name 1. Gland in the brain that is the control
... 1. Gland in the brain that is the control center for all regulatory activities of the body: ____________________________ 2. Condition in which levels of thyroid hormones in the blood are very low: _________________________ __ 3. Helps regulate when you sleep at night and when you wake in the mornin ...
... 1. Gland in the brain that is the control center for all regulatory activities of the body: ____________________________ 2. Condition in which levels of thyroid hormones in the blood are very low: _________________________ __ 3. Helps regulate when you sleep at night and when you wake in the mornin ...
Digestive System - Miss Gleason`s Science
... – with small openings called gastric pits, containing gastric glands Gastric Juice- pepsin Chyme –broken down food molecules from gastric juices/movement of stomach ◦ released from the pyloric sphincter valve into the first portion of the small intestine – duodenum ...
... – with small openings called gastric pits, containing gastric glands Gastric Juice- pepsin Chyme –broken down food molecules from gastric juices/movement of stomach ◦ released from the pyloric sphincter valve into the first portion of the small intestine – duodenum ...
10. Digestive System
... Additional organs and glands run along this tube to aid in digestion. Below is a list of the organs in the digestive system with their functions. Peritoneum: lines the abdominal wall and consists of epithelium supported by connective tissue. Mesenteries: Double-layered sheets of peritoneum, called, ...
... Additional organs and glands run along this tube to aid in digestion. Below is a list of the organs in the digestive system with their functions. Peritoneum: lines the abdominal wall and consists of epithelium supported by connective tissue. Mesenteries: Double-layered sheets of peritoneum, called, ...
The Endocrine System
... Contains islands of cells called the Islets of Langerhans which secrete glucagon and insulin Glucagon – stimulates the liver to break down glycogen, raises blood sugar concentration Insulin – decreases blood sugar concentrations, affects the uptake of glucose by cells Disorders Related to the Pancre ...
... Contains islands of cells called the Islets of Langerhans which secrete glucagon and insulin Glucagon – stimulates the liver to break down glycogen, raises blood sugar concentration Insulin – decreases blood sugar concentrations, affects the uptake of glucose by cells Disorders Related to the Pancre ...
Pancreatic Surgery: Procedures, Complications
... tail of the pancreas lies adjacent to the spleen toward the left side, and the body of the pancreas comprises the midportion between the head and tail. The bile duct passes through the head of the pancreas as it courses from the liver to the duodenum, and may be obstructed by processes affecting the ...
... tail of the pancreas lies adjacent to the spleen toward the left side, and the body of the pancreas comprises the midportion between the head and tail. The bile duct passes through the head of the pancreas as it courses from the liver to the duodenum, and may be obstructed by processes affecting the ...
CARBOHYDRATE DIGESTION MMHS SCIENCE DEPT.
... As bacteria metabolize more food, they produce more gas resulting in symptoms like constipation, cramping, and diarrhea. ...
... As bacteria metabolize more food, they produce more gas resulting in symptoms like constipation, cramping, and diarrhea. ...
Digestive System
... 1. Starts in stomach by pepsin 2. Trypsin, chemotrypsin, carboxypeptidase and elastase breaks down proteins into peptides ...
... 1. Starts in stomach by pepsin 2. Trypsin, chemotrypsin, carboxypeptidase and elastase breaks down proteins into peptides ...
Multiple Choice Set 6
... D. all of the above are correct E. none of the above are correct 19. All of the following are functions of the liver EXCEPT A. detoxification of blood-borne compounds B. storage of fat-soluble vitamins C. bile storage D. processing of nutrients from the bloodstream E. processing of alcohol to acetic ...
... D. all of the above are correct E. none of the above are correct 19. All of the following are functions of the liver EXCEPT A. detoxification of blood-borne compounds B. storage of fat-soluble vitamins C. bile storage D. processing of nutrients from the bloodstream E. processing of alcohol to acetic ...
Outline 19
... The large intestine is about 6 feet long and 2.5 inches in __________________ (it’s larger in diameter than the small intestine) Regions: o ___________________ Blind pouch at the beginning of the large intestine that connects to the ileum (at the ileocecal valve) Attached to the cecum is the ...
... The large intestine is about 6 feet long and 2.5 inches in __________________ (it’s larger in diameter than the small intestine) Regions: o ___________________ Blind pouch at the beginning of the large intestine that connects to the ileum (at the ileocecal valve) Attached to the cecum is the ...
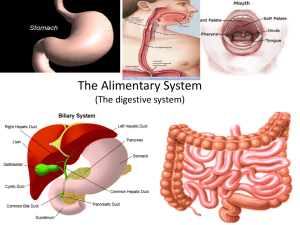
The Alimentary System (The digestive system)
... • The gall bladder stores and secretes bile only. The liver produces it. • When bile is stored in the gall bladder, water is continually being reabsorbed from the bile. • When water is reabsorbed, bile become more concentrated. • Sometimes when this occurs, too much cholesterol can crystallize formi ...
... • The gall bladder stores and secretes bile only. The liver produces it. • When bile is stored in the gall bladder, water is continually being reabsorbed from the bile. • When water is reabsorbed, bile become more concentrated. • Sometimes when this occurs, too much cholesterol can crystallize formi ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.