Nutrient Absorption
... to the esophagus = a muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach – Food moves through the esophagus by peristalsis = a series of involuntary smooth muscle contraction along the walls of the digestive tract ...
... to the esophagus = a muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach – Food moves through the esophagus by peristalsis = a series of involuntary smooth muscle contraction along the walls of the digestive tract ...
The Digestive System
... • Only through the process of absorption do the nutrients in food enter into and nourish the body’s “inner space.” ...
... • Only through the process of absorption do the nutrients in food enter into and nourish the body’s “inner space.” ...
Biology Mid-Term Study Guide 8: Nutrition Food and Energy Energy
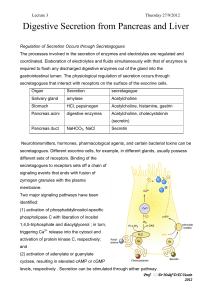
... a. Duodenum is the first part of the small intestine to get the chyme b. Small intestine is where most of the chemical digestion occurs c. Chyme mixes with enzymes and digestive fluids in the duodenum d. Pancreas glands i. Produce hormones that regulate blood sugar levels ii. Produces enzymes that b ...
... a. Duodenum is the first part of the small intestine to get the chyme b. Small intestine is where most of the chemical digestion occurs c. Chyme mixes with enzymes and digestive fluids in the duodenum d. Pancreas glands i. Produce hormones that regulate blood sugar levels ii. Produces enzymes that b ...
Osmoregulation and excretion (kidney function): Two basic ideas: 1
... -ADH (anti-diuretic-hormone) is produced in the hypothalamus and stored in pituitary. The hypothalamus monitors salt concentration of blood. - If salt concentration rises, then more water is needed in the body. So ADH is released. ADH increases the permeability of the collecting duct and so more wat ...
... -ADH (anti-diuretic-hormone) is produced in the hypothalamus and stored in pituitary. The hypothalamus monitors salt concentration of blood. - If salt concentration rises, then more water is needed in the body. So ADH is released. ADH increases the permeability of the collecting duct and so more wat ...
Chapter 41
... 3. Insulin stimulates cells to take up glucose and liver and muscle cells to store glucose as glycogen. 4. Glucose level drops below certain point. 5. The pancreas secretes glucagon. 6. Glucagon promotes the breakdown of glycogen and the release of glucose into the blood. 7. Glucose level increases ...
... 3. Insulin stimulates cells to take up glucose and liver and muscle cells to store glucose as glycogen. 4. Glucose level drops below certain point. 5. The pancreas secretes glucagon. 6. Glucagon promotes the breakdown of glycogen and the release of glucose into the blood. 7. Glucose level increases ...
Model Building - Digestive System Organs
... C. What is the position of the stomach in a. short, obese people: b. tall, thin people: D. ~ 10 inches long on ____________________ side of abdomen E. can hold _______________________ L of food F. _____________________ – large longitudinal folds that help mix food in stomach H. __________________ sp ...
... C. What is the position of the stomach in a. short, obese people: b. tall, thin people: D. ~ 10 inches long on ____________________ side of abdomen E. can hold _______________________ L of food F. _____________________ – large longitudinal folds that help mix food in stomach H. __________________ sp ...
lecture 13 gastrointestinal pathophysiology
... Although the liver has remarkable regenerative capability, chronic hepatitis can cause irreversible liver damage. In this case, normal functional liver cells are replaced by connective scar tissue, which performs none of the normal liver functions. This development of scar tissue in the liver is ter ...
... Although the liver has remarkable regenerative capability, chronic hepatitis can cause irreversible liver damage. In this case, normal functional liver cells are replaced by connective scar tissue, which performs none of the normal liver functions. This development of scar tissue in the liver is ter ...
Digestive System - Mercer Island School District
... Pathway of Food Step 1) Mouth/Pharynx- Mechanical breakdown of food by chewing and chemical breakdown through saliva Step 2) Esophagus- Food moves towards the stomach by peristaltic movements Step 3) Small intestines- Where the food is broken down and also the digestion of starches and salt ...
... Pathway of Food Step 1) Mouth/Pharynx- Mechanical breakdown of food by chewing and chemical breakdown through saliva Step 2) Esophagus- Food moves towards the stomach by peristaltic movements Step 3) Small intestines- Where the food is broken down and also the digestion of starches and salt ...
Digestive System
... cavity produced by three pairs of glands 1. Parotid glands are just below the ears 2. Submandibular are posterior to the mandible 3. Sublingual are on the floor of the mouth Each gland has at least one duct to take saliva to the oral cavity ...
... cavity produced by three pairs of glands 1. Parotid glands are just below the ears 2. Submandibular are posterior to the mandible 3. Sublingual are on the floor of the mouth Each gland has at least one duct to take saliva to the oral cavity ...
The Pancreas
... • Chymotrypsin: Cuts on the C-terminal side of tyrosine, phenylalanine, and tryptophan residues (the same bonds as pepsin, whose action ceases when the NaHCOs raises the pH of the intestinal contents). Once trypsinogen and chymotrypsinogen are released into the lumen of the small intestine, they mus ...
... • Chymotrypsin: Cuts on the C-terminal side of tyrosine, phenylalanine, and tryptophan residues (the same bonds as pepsin, whose action ceases when the NaHCOs raises the pH of the intestinal contents). Once trypsinogen and chymotrypsinogen are released into the lumen of the small intestine, they mus ...
Chapter 23 - Digestive System, Part 1
... Microvilli – sub-microscopic size, projections on simple columnar cells Function of all three? ...
... Microvilli – sub-microscopic size, projections on simple columnar cells Function of all three? ...
Hormone - ScienceToGo
... Endocrine signals (hormones) are secreted into extracellular fluids and travel via the bloodstream ...
... Endocrine signals (hormones) are secreted into extracellular fluids and travel via the bloodstream ...
List of Hormones to Know ANSWERS
... of women participate in monthly menstrual cycle participate in pregnancy prepares endometrium for possible pregnancy secretion is maintained if pregnancy occurs prevents deterioration of corpus luteum after fourth week and allows pregnancy to continue commonly tested for in pregnancy tests develops ...
... of women participate in monthly menstrual cycle participate in pregnancy prepares endometrium for possible pregnancy secretion is maintained if pregnancy occurs prevents deterioration of corpus luteum after fourth week and allows pregnancy to continue commonly tested for in pregnancy tests develops ...
15. corn into milk lab
... Our food and drink must be changed into smaller molecules of nutrients before they can be absorbed into the blood and carried to cells throughout the body. Digestion is the process by which food and drink are broken down into their smallest parts so that the body can use them to build and nourish ce ...
... Our food and drink must be changed into smaller molecules of nutrients before they can be absorbed into the blood and carried to cells throughout the body. Digestion is the process by which food and drink are broken down into their smallest parts so that the body can use them to build and nourish ce ...
File
... Stomach /Pancreas / Small intestine Where will you find epithelial tissue? What are some of its functions? Lining body surfaces – protection or exchange ...
... Stomach /Pancreas / Small intestine Where will you find epithelial tissue? What are some of its functions? Lining body surfaces – protection or exchange ...
Slide 1
... Stomach /Pancreas / Small intestine Where will you find epithelial tissue? What are some of its functions? Lining body surfaces – protection or exchange ...
... Stomach /Pancreas / Small intestine Where will you find epithelial tissue? What are some of its functions? Lining body surfaces – protection or exchange ...
Enzymes & Digestion
... A substance called bile (produced in the stomach and stored in the gall bladder) neutralises the acid to provide the alkaline conditions needed in the small intestine (as well as breaking down fat) ...
... A substance called bile (produced in the stomach and stored in the gall bladder) neutralises the acid to provide the alkaline conditions needed in the small intestine (as well as breaking down fat) ...
Digestion Exercise 42 (2013)
... • Bile duct • Hepatic artery – supplies oxygen-rich blood to the liver • Hepatic portal vein – carries venous blood with nutrients from digestive viscera ...
... • Bile duct • Hepatic artery – supplies oxygen-rich blood to the liver • Hepatic portal vein – carries venous blood with nutrients from digestive viscera ...
File
... receptors in the cytoplasm or nucleus • Protein-receptor complexes then act as transcription factors in the nucleus, regulating transcription of specific genes ...
... receptors in the cytoplasm or nucleus • Protein-receptor complexes then act as transcription factors in the nucleus, regulating transcription of specific genes ...
Vertebrate Endocrine Systems
... stimulate the b cells to release insulin. • Insulin stimulates cells to use glucose and to convert it to glycogen and fat. • When blood glucose levels fall, the pancreas stops releasing insulin, and cells switch to using glycogen and fat for energy. • If blood glucose falls too low, the cells releas ...
... stimulate the b cells to release insulin. • Insulin stimulates cells to use glucose and to convert it to glycogen and fat. • When blood glucose levels fall, the pancreas stops releasing insulin, and cells switch to using glycogen and fat for energy. • If blood glucose falls too low, the cells releas ...
The Digestive System
... Colon Cancer: Cancer starts in the inner layer and can grow through some or all of the other layers. Knowing a little about these layers is helpful because the stage (extent of spread) of a cancer depends to a great degree on which of these layers it affects. Cancer that starts in the different area ...
... Colon Cancer: Cancer starts in the inner layer and can grow through some or all of the other layers. Knowing a little about these layers is helpful because the stage (extent of spread) of a cancer depends to a great degree on which of these layers it affects. Cancer that starts in the different area ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.