10/8/08 SI A ECL 365 The______ is the largest gland in the
... b. Carnivorous – food easier to breakdown, shorter c. Herbivores have longer intestines (cellulose breakdown) 12. Describe the cecum. a. Present in almost every animal, reservoir for intestinal bacteria in humans. b. Divides small and large intestine in birds and mammals. 13. What function does the ...
... b. Carnivorous – food easier to breakdown, shorter c. Herbivores have longer intestines (cellulose breakdown) 12. Describe the cecum. a. Present in almost every animal, reservoir for intestinal bacteria in humans. b. Divides small and large intestine in birds and mammals. 13. What function does the ...
Mechanical Digestion
... HCL kills bacteria, denatures protein pepsin begins digestion of proteins intrinsic factor aids absorption of vitamin B12 gastric lipase aids digestion of triglycerides 4. secretes gastrin (digestive hormone) into the blood ...
... HCL kills bacteria, denatures protein pepsin begins digestion of proteins intrinsic factor aids absorption of vitamin B12 gastric lipase aids digestion of triglycerides 4. secretes gastrin (digestive hormone) into the blood ...
Mechanical Digestion
... in diameter than the small intestine (about 3” vs. 1”). Responsible for absorbing water from undigested food. Material ...
... in diameter than the small intestine (about 3” vs. 1”). Responsible for absorbing water from undigested food. Material ...
Get Notes - Mindset Learn
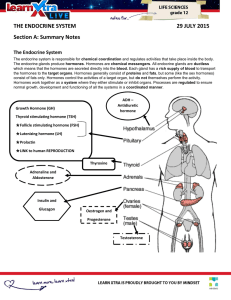
... The endocrine system is responsible for chemical coordination and regulates activities that take place inside the body. The endocrine glands produce hormones. Hormones are chemical messengers. All endocrine glands are ductless which means that the hormones are secreted directly into the blood. Each ...
... The endocrine system is responsible for chemical coordination and regulates activities that take place inside the body. The endocrine glands produce hormones. Hormones are chemical messengers. All endocrine glands are ductless which means that the hormones are secreted directly into the blood. Each ...
Human Digestive System
... 2- Extracellular Digestion: Animals take the food into a body cavity that is continuous with the outside environment, into which they secrete digestive enzymes. Enzymes act on food, reducing it to nutrient molecules that can be absorbed by the cells lining the cavity. e.g: all vertebrates, some pro ...
... 2- Extracellular Digestion: Animals take the food into a body cavity that is continuous with the outside environment, into which they secrete digestive enzymes. Enzymes act on food, reducing it to nutrient molecules that can be absorbed by the cells lining the cavity. e.g: all vertebrates, some pro ...
Midterm Review Packet
... 11. The three types of muscle fibers are (1) Muscular, heart and rough (2) Smooth, cardiac, skeletal (3) Heart, quadriceps, sternoclydomastoid (4) Smooth, rough, tumor 12. An example of a ball and socket joint is (1) Shoulder (2) Knee (3) Elbow (4) Ankle ...
... 11. The three types of muscle fibers are (1) Muscular, heart and rough (2) Smooth, cardiac, skeletal (3) Heart, quadriceps, sternoclydomastoid (4) Smooth, rough, tumor 12. An example of a ball and socket joint is (1) Shoulder (2) Knee (3) Elbow (4) Ankle ...
Basics of Digestion Review ?`s
... 9. What is reflux? Why does it have a “burning” sensation? 10. What is the name of the hormone that stimulates digestion in the stomach? 11. What are the five basic taste categories and their location in the mouth/tongue? 12. What part of the brain signals us that you are hungry and should eat? 13. ...
... 9. What is reflux? Why does it have a “burning” sensation? 10. What is the name of the hormone that stimulates digestion in the stomach? 11. What are the five basic taste categories and their location in the mouth/tongue? 12. What part of the brain signals us that you are hungry and should eat? 13. ...
Physiology of Digestive System I - كلية طب الاسنان
... Second: bicarbonate ions are secreted by the ductal epithelium into the lumen of the duct. This is at least partly caused by passive exchange of bicarbonate for chloride ions, but it may also result partly from an active secretory process. The result of these transport processes is that: Under resti ...
... Second: bicarbonate ions are secreted by the ductal epithelium into the lumen of the duct. This is at least partly caused by passive exchange of bicarbonate for chloride ions, but it may also result partly from an active secretory process. The result of these transport processes is that: Under resti ...
This assessment is worth 95 points.
... Glucagon is produced by endocrine cells. Bicarbonate ions are produced by exocrine cells. Chymotrypsinogen is produced by exocrine cells. Amylase is produced by exocrine cells. All of these are produced by the pancreas. ...
... Glucagon is produced by endocrine cells. Bicarbonate ions are produced by exocrine cells. Chymotrypsinogen is produced by exocrine cells. Amylase is produced by exocrine cells. All of these are produced by the pancreas. ...
Revision Sheet G (8)
... 13.Which of the following organs is NOT part of the digestive tract? a. stomach b. pharynx c. large intestine d. kidneys 14.What are the two main kinds of digestion? a. mechanical and chemical b. mechanical and liquid c. mechanical and solid d. mechanical and heat 15.Which of the following is NOT a ...
... 13.Which of the following organs is NOT part of the digestive tract? a. stomach b. pharynx c. large intestine d. kidneys 14.What are the two main kinds of digestion? a. mechanical and chemical b. mechanical and liquid c. mechanical and solid d. mechanical and heat 15.Which of the following is NOT a ...
Bio Digestion 30.3 9
... Enzymes: What and Where • Another important digestive fluid is called bile. • Bile is produced by the liver, and separates fats so lipase can break it down. ...
... Enzymes: What and Where • Another important digestive fluid is called bile. • Bile is produced by the liver, and separates fats so lipase can break it down. ...
Ch. 14 The Digestive System and Body Metabolism
... (2) Helps to form a food bolus (3) Contains salivary amylase to begin starch digestion (4) Dissolves chemicals so they can be tasted Pancreas a. Found posterior to the parietal peritoneum b. Extends across the abdomen from spleen to duodenum ...
... (2) Helps to form a food bolus (3) Contains salivary amylase to begin starch digestion (4) Dissolves chemicals so they can be tasted Pancreas a. Found posterior to the parietal peritoneum b. Extends across the abdomen from spleen to duodenum ...
Digestion - Net Start Class
... • Pouch structure located near the liver which concentrates and stores bile • Bile duct – a long tube that carries BILE. The top half of the common bile duct is associated with the liver, while the bottom half of the common bile duct is associated with the pancreas, through which it passes on its wa ...
... • Pouch structure located near the liver which concentrates and stores bile • Bile duct – a long tube that carries BILE. The top half of the common bile duct is associated with the liver, while the bottom half of the common bile duct is associated with the pancreas, through which it passes on its wa ...
Human Digestion
... • Bile duct – a long tube that carries BILE. The top half of the common bile duct is associated with the liver, while the bottom half of the common bile duct is associated with the pancreas, through which it passes on its way to the intestine. ...
... • Bile duct – a long tube that carries BILE. The top half of the common bile duct is associated with the liver, while the bottom half of the common bile duct is associated with the pancreas, through which it passes on its way to the intestine. ...
Endocrine System
... body cells where it can be used for energy which leads to increased hunger. ...
... body cells where it can be used for energy which leads to increased hunger. ...
CASE 28
... at acid-secreting (parietal) and pepsin-secreting (chief) cells in the body of the stomach, and at enzyme-secreting (acinar) cells of the pancreas. Vagal neural pathways also initiate the release from antral G cells of the hormone gastrin, which reaches parietal cells through the circulation. Thus, ...
... at acid-secreting (parietal) and pepsin-secreting (chief) cells in the body of the stomach, and at enzyme-secreting (acinar) cells of the pancreas. Vagal neural pathways also initiate the release from antral G cells of the hormone gastrin, which reaches parietal cells through the circulation. Thus, ...
12 The Digestive and Excretory Systems
... – The lining of the stomach contains millions of microscopic gastric glands that release a number of substances into the stomach • Mucus that lubricates and protects the stomach wall • Hydrochloric acid which makes the contents of the stomach very acidic – Activates pepsin, an enzyme that begins ...
... – The lining of the stomach contains millions of microscopic gastric glands that release a number of substances into the stomach • Mucus that lubricates and protects the stomach wall • Hydrochloric acid which makes the contents of the stomach very acidic – Activates pepsin, an enzyme that begins ...
Topic D.2 Digestion - Cougar science rocks!
... Excretory products, like bilirubin from breakdown of red blood cells A lot of water from saliva, stomach and small intestine, reabsorbed by large intestine ...
... Excretory products, like bilirubin from breakdown of red blood cells A lot of water from saliva, stomach and small intestine, reabsorbed by large intestine ...
Digestion after the Stomach
... The small intestine is a long tube that is only about __________ in diameter and approximately 7 m long. Whereas the large intestine is around 7.6cm in diameter and ___________ in length. Lipids, carbohydrates, and remaining proteins are digested in the small intestine. It is made up of 3 sections: ...
... The small intestine is a long tube that is only about __________ in diameter and approximately 7 m long. Whereas the large intestine is around 7.6cm in diameter and ___________ in length. Lipids, carbohydrates, and remaining proteins are digested in the small intestine. It is made up of 3 sections: ...
ch24 outline
... The mucosa of the gallbladder is simple columnar epithelium arranged in rugae. There is no submucosa. The smooth muscle of the muscularis ejects bile into the cystic duct. The outer layer is the visceral peritoneum. Functions of the gallbladder are to store and concentrate bile until it is needed in ...
... The mucosa of the gallbladder is simple columnar epithelium arranged in rugae. There is no submucosa. The smooth muscle of the muscularis ejects bile into the cystic duct. The outer layer is the visceral peritoneum. Functions of the gallbladder are to store and concentrate bile until it is needed in ...
lab 7 digestive system 1 - Dr. Justo Lopez Website
... It receives the pancreas and liver secretions that mix with the chyme ...
... It receives the pancreas and liver secretions that mix with the chyme ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.