Questions for Anatomy Exam
... c. The parietal pleura does not adhere to the thoracic wall. d. The visceral pleura is directly adherent to the thoracic wall. 10. Which of the following statements are true: A. The prognosis from cancer is determined in large part from the number of adjacent lymph nodes that have tumor B. Axillary ...
... c. The parietal pleura does not adhere to the thoracic wall. d. The visceral pleura is directly adherent to the thoracic wall. 10. Which of the following statements are true: A. The prognosis from cancer is determined in large part from the number of adjacent lymph nodes that have tumor B. Axillary ...
Right
... membrane that line the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities and cover the organs within these cavities Parietal peritoneum -lines the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities Visceral peritoneum -covers the organs Peritoneal cavity -the potential space between the parietal and visceral layer ...
... membrane that line the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities and cover the organs within these cavities Parietal peritoneum -lines the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities Visceral peritoneum -covers the organs Peritoneal cavity -the potential space between the parietal and visceral layer ...
Human Anatomy & Physiology II
... Neutralize stomach acid and dilutes chyme Proteases: chymotrypsinogen, trypsinogen, et. al. Activated by entreokinase from intestine Starch digesting- pancreatic amylase Pancreatic lipase Nucleotidases – RNAase & DNAase ...
... Neutralize stomach acid and dilutes chyme Proteases: chymotrypsinogen, trypsinogen, et. al. Activated by entreokinase from intestine Starch digesting- pancreatic amylase Pancreatic lipase Nucleotidases – RNAase & DNAase ...
37 Motor function of digestion
... intestine as soon as they acquire a fluid or semifluid consistency); 2) their osmotic pressure (hypertonic solutions inhibit evacuation and leave the stomach only after they have been diluted by gastric juice to an isotonic concentration); 3) how full the duodenum is (distention of the duodenum also ...
... intestine as soon as they acquire a fluid or semifluid consistency); 2) their osmotic pressure (hypertonic solutions inhibit evacuation and leave the stomach only after they have been diluted by gastric juice to an isotonic concentration); 3) how full the duodenum is (distention of the duodenum also ...
The Hormone Connection KEY
... While the nervous system communicates using electrical signals, the body’s endocrine system uses chemical signals, called hormones, to regulate body functioning. Hormones are proteins involved in maintaining the body’s homeostasis. These chemical messengers carry signals from one cell to another and ...
... While the nervous system communicates using electrical signals, the body’s endocrine system uses chemical signals, called hormones, to regulate body functioning. Hormones are proteins involved in maintaining the body’s homeostasis. These chemical messengers carry signals from one cell to another and ...
Chapter 23,24,25
... At the time of diagnosis, distant metastases are present in about __________% of patients. Lung cancer is _____ to ______times more common in smokers than in nonsmokers. Secondhand smoke (is? Is not?) known to lead to lung cancer deaths. The most common form of lung cancer, known as ____________ car ...
... At the time of diagnosis, distant metastases are present in about __________% of patients. Lung cancer is _____ to ______times more common in smokers than in nonsmokers. Secondhand smoke (is? Is not?) known to lead to lung cancer deaths. The most common form of lung cancer, known as ____________ car ...
Food and Nutrition Food & Energy
... Food mixed with saliva becomes a soft mass and is moved to the back of your mouth by your tongue. It is swallowed and passes into your esophagus. Food moving into the esophagus passes over the epiglottis ...
... Food mixed with saliva becomes a soft mass and is moved to the back of your mouth by your tongue. It is swallowed and passes into your esophagus. Food moving into the esophagus passes over the epiglottis ...
THE HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM.
... identify and locate the major parts of the digestive system including the mouth, oesophagus, stomach,liver, pancreas, small intestine and large intestine, and know their functions ...
... identify and locate the major parts of the digestive system including the mouth, oesophagus, stomach,liver, pancreas, small intestine and large intestine, and know their functions ...
The Digestive and Excretory Systems
... system? List at least 5 items. Write 2 questions about digestive system that you don’t know the answer to, but like to learn about it. ...
... system? List at least 5 items. Write 2 questions about digestive system that you don’t know the answer to, but like to learn about it. ...
Lab 8
... • Peristaltic waves move toward the pylorus at the rate of 3 per minute • This basic electrical rhythm (BER) is initiated by pacemaker cells (cells of Cajal) • Most vigorous peristalsis and mixing occurs near the pylorus • Chyme is either: – Delivered in small amounts to the duodenum or – Forced bac ...
... • Peristaltic waves move toward the pylorus at the rate of 3 per minute • This basic electrical rhythm (BER) is initiated by pacemaker cells (cells of Cajal) • Most vigorous peristalsis and mixing occurs near the pylorus • Chyme is either: – Delivered in small amounts to the duodenum or – Forced bac ...
molecular physiology
... Pancreas is a situated near the duodenum. It has both endocrine and exocrine functions: Exocrine function of pancreas is carried out by secretory acini and duct cells, which secrete pancreatic juice. The enzymes are stored in the form of zymogen granules, which are present in apices of acinar cells ...
... Pancreas is a situated near the duodenum. It has both endocrine and exocrine functions: Exocrine function of pancreas is carried out by secretory acini and duct cells, which secrete pancreatic juice. The enzymes are stored in the form of zymogen granules, which are present in apices of acinar cells ...
The Digestive and Excretory Systems
... about the digestive system that you don’t know the answer to, but want to learn about it. ...
... about the digestive system that you don’t know the answer to, but want to learn about it. ...
Respiratory System Cardiovascular System
... stomach and small intestines; makes juices which flow to small intestine to neutralize acid ...
... stomach and small intestines; makes juices which flow to small intestine to neutralize acid ...
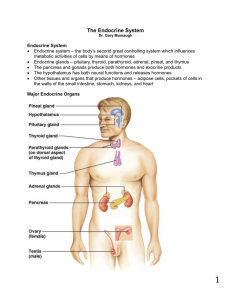
The Endocrine System
... A triangular gland, which has both exocrine and endocrine cells, located behind the stomach Cells produce an enzyme-rich juice used for digestion (exocrine product) Pancreatic islets (islets of Langerhans) produce hormones (endocrine products) Glucagon Its major target is the liver, where it ...
... A triangular gland, which has both exocrine and endocrine cells, located behind the stomach Cells produce an enzyme-rich juice used for digestion (exocrine product) Pancreatic islets (islets of Langerhans) produce hormones (endocrine products) Glucagon Its major target is the liver, where it ...
Chapter 13 The Endocrine System • Endocrine System Produces
... – Most of its growth-promoting effects occur during childhood and adolescence ...
... – Most of its growth-promoting effects occur during childhood and adolescence ...
ACP Level 2 Lesson Seven
... of food will take longer to process than others. Soup, for instance will be allowed to pass through far more quickly than a piece of steak! An average meal will usually stay in the system for about 4 hours. At the closed end of the caecum is the vermiform appendix. This measures around 7.5 cm or 3 i ...
... of food will take longer to process than others. Soup, for instance will be allowed to pass through far more quickly than a piece of steak! An average meal will usually stay in the system for about 4 hours. At the closed end of the caecum is the vermiform appendix. This measures around 7.5 cm or 3 i ...
Endocrine System - Seattle Central College
... glands that communicate with each other & all body cells via hormones. • Endocrine glands: secrete chemical messages onto extracellular surface – Pituitary, adrenal, testes, etc. ...
... glands that communicate with each other & all body cells via hormones. • Endocrine glands: secrete chemical messages onto extracellular surface – Pituitary, adrenal, testes, etc. ...
INTRODUCTION TO THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
... Two basic types of digestive motility are superimposed on the ongoing tonic activity: ...
... Two basic types of digestive motility are superimposed on the ongoing tonic activity: ...
File
... the stomach. The food remains in the mouth only a short time, so probably not more than 5 percent of all the starches will have become hydrolyzed by the time the food is swallowed. Starch digestion sometimes continues in the body and fundus of the stomach for as long as 1 hour before the food become ...
... the stomach. The food remains in the mouth only a short time, so probably not more than 5 percent of all the starches will have become hydrolyzed by the time the food is swallowed. Starch digestion sometimes continues in the body and fundus of the stomach for as long as 1 hour before the food become ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.