Chapter 13 Endocrine System
... of sugars. When there is not enough insulin being produced you develop a condition called diabetes mellitus. ...
... of sugars. When there is not enough insulin being produced you develop a condition called diabetes mellitus. ...
Clomid PDF
... About Clomid (Clomiphene Citrate) Clomid is the most commonly used fertility drug. Clomid increased the body’s own production of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). These two hormones drive the ovaries to produce a healthier oocyte (egg) or extra oocytes. This results in ...
... About Clomid (Clomiphene Citrate) Clomid is the most commonly used fertility drug. Clomid increased the body’s own production of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). These two hormones drive the ovaries to produce a healthier oocyte (egg) or extra oocytes. This results in ...
Anatomy of the pituitary gland
... The pituitary gland is sometimes called the "master" gland of the endocrine system, because it controls the functions of the other endocrine glands. The pituitary gland is no larger than a pea, and is located at the base of the brain. The gland is attached to the hypothalumus (a part of the brain th ...
... The pituitary gland is sometimes called the "master" gland of the endocrine system, because it controls the functions of the other endocrine glands. The pituitary gland is no larger than a pea, and is located at the base of the brain. The gland is attached to the hypothalumus (a part of the brain th ...
Trauma: The Mind/Body Connection.1998
... yields unusual results. In normal subjects, dexamethasone will suppress the adrenal release of cortisol. The brain reacts to a high adrenal steroid level (from a pill) and turns off the hypothalamic-pituitary stimulation of the adrenal cortex. This test has been used in the study of depression, in w ...
... yields unusual results. In normal subjects, dexamethasone will suppress the adrenal release of cortisol. The brain reacts to a high adrenal steroid level (from a pill) and turns off the hypothalamic-pituitary stimulation of the adrenal cortex. This test has been used in the study of depression, in w ...
PoWeR Handout -- 12-page document give out at lectures
... tests, like SGOT and SGPT, when looking for potential liver problems related to anabolic steroids.11 12 Of course, it is prudent to respond to all aberrant liver function tests when pharmacology is complicated with compounds like the standard AIDS medications. 4. Virilizing means masculinizing. This ...
... tests, like SGOT and SGPT, when looking for potential liver problems related to anabolic steroids.11 12 Of course, it is prudent to respond to all aberrant liver function tests when pharmacology is complicated with compounds like the standard AIDS medications. 4. Virilizing means masculinizing. This ...
Current perspectives on testosterone therapy for women
... be due to decreased blood flow to the sexual organs. Androgen receptors identified in the vagina may play a role in vaginal health. Testosterone appears to exert vasomotor effects in the vagina, enhancing vaginal blood flow and lubrication.10,11 ...
... be due to decreased blood flow to the sexual organs. Androgen receptors identified in the vagina may play a role in vaginal health. Testosterone appears to exert vasomotor effects in the vagina, enhancing vaginal blood flow and lubrication.10,11 ...
PITUITARY FUNCTION TESTS: An Overview
... (2.2mmol/L or lower blood glucose level) was not achieved during the test; In apparently healthy individuals, Hypoglycemia causes: • Increase in Plasma [HGH] to more than 20m U/L; • Plasma [Cortisol] increases to maximum (about 425nmol/L) in 60 to 90 minutes; In patient with Partial Pituitary Fail ...
... (2.2mmol/L or lower blood glucose level) was not achieved during the test; In apparently healthy individuals, Hypoglycemia causes: • Increase in Plasma [HGH] to more than 20m U/L; • Plasma [Cortisol] increases to maximum (about 425nmol/L) in 60 to 90 minutes; In patient with Partial Pituitary Fail ...
Study Guide
... Be able to compare and contrast endocrine and exocrine glands Distinguish between and be able to describe the different types of secretory cells o Describe their roles in chemical signaling within the body Explain the actions of hormones in general terms from their release to reception on target cel ...
... Be able to compare and contrast endocrine and exocrine glands Distinguish between and be able to describe the different types of secretory cells o Describe their roles in chemical signaling within the body Explain the actions of hormones in general terms from their release to reception on target cel ...
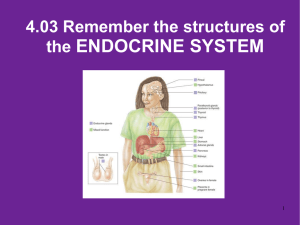
4.03 Remember Structures of the endocrine system What are the
... What is the chemical that is secreted by the endocrine glands? TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) is secreted by the pituitary and acts on what gland? Which gland is divided into anterior and posterior lobes? Which gland is butterfly shaped and is located in the neck? Which endocrine gland is located ...
... What is the chemical that is secreted by the endocrine glands? TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) is secreted by the pituitary and acts on what gland? Which gland is divided into anterior and posterior lobes? Which gland is butterfly shaped and is located in the neck? Which endocrine gland is located ...
AMEND AMEND - Association for Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia
... and abdominal area. If a growth is diagnosed, it may require surgical removal by itself or possibly with the entire affected gland. ...
... and abdominal area. If a growth is diagnosed, it may require surgical removal by itself or possibly with the entire affected gland. ...
Endocrine Vs Exocrine glands
... 2. Exocrine gland -- Secretes chemical substances into a duct. a. salivary glands that secrete saliva into the mouth b. bile-producing glands of the liver c. prostate gland d. the portion of the pancreas that secretes pancreatic fluid into the duodenum. (The pancreas is also an endocrine gland - its ...
... 2. Exocrine gland -- Secretes chemical substances into a duct. a. salivary glands that secrete saliva into the mouth b. bile-producing glands of the liver c. prostate gland d. the portion of the pancreas that secretes pancreatic fluid into the duodenum. (The pancreas is also an endocrine gland - its ...
HPAT AXIS - DaVinci Labs
... The hypothalamus’ relationship to thyroid hormones is incredibly relevant to the the body’s ability to maintain hormone balance. The hypothalamus senses low circulating levels of thyroid hormones T3 and T4, and responds by releasing thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH). The release of TRH tells the ...
... The hypothalamus’ relationship to thyroid hormones is incredibly relevant to the the body’s ability to maintain hormone balance. The hypothalamus senses low circulating levels of thyroid hormones T3 and T4, and responds by releasing thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH). The release of TRH tells the ...
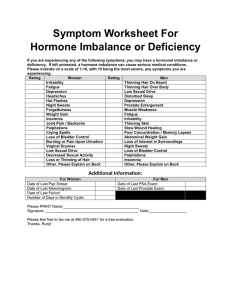
Symptom Worksheet For Hormone Imbalance or
... ii. In this case, we recommend that you continue to increase the T3 dose on the prescribed schedule. If symptoms are not relieved at that point, it is generally recommended that you decrease your dosage by 7.5 mcg each day until this symptom is alleviated. iii. After this you may be asked to cycle d ...
... ii. In this case, we recommend that you continue to increase the T3 dose on the prescribed schedule. If symptoms are not relieved at that point, it is generally recommended that you decrease your dosage by 7.5 mcg each day until this symptom is alleviated. iii. After this you may be asked to cycle d ...
What is Endocrine Surgery?
... The adrenal glands are small glands that sit on top of the kidneys. The gland has an inner core called the medulla and an outer layer named the cortex. The medulla makes epinephrine and norepinephrine. The cortex makes hormones that help regulate the heart, kidneys, GI tract, bones, genitalia, and i ...
... The adrenal glands are small glands that sit on top of the kidneys. The gland has an inner core called the medulla and an outer layer named the cortex. The medulla makes epinephrine and norepinephrine. The cortex makes hormones that help regulate the heart, kidneys, GI tract, bones, genitalia, and i ...
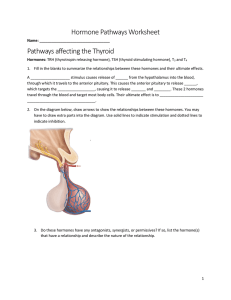
Hormone Pathways worksheet
... 15. Fill in the blanks to summarize the relationships between these hormones and their ultimate effects. When blood is too concentrated, it generally indicates that blood volume is low and there is not enough water in the blood. In this situation, blood pressure tends to be ________. Osmoreceptors i ...
... 15. Fill in the blanks to summarize the relationships between these hormones and their ultimate effects. When blood is too concentrated, it generally indicates that blood volume is low and there is not enough water in the blood. In this situation, blood pressure tends to be ________. Osmoreceptors i ...
Virtual Rat Endocrine Lab
... tubules of the testes. The Leydig cells release testosterone, which is responsible for the male sex drive and secondary sex characteristics, such as increased body hair and a deeper voice. An excess of testosterone can cause an increase (anabolic) in muscle mass. Negative effects of testosterone ar ...
... tubules of the testes. The Leydig cells release testosterone, which is responsible for the male sex drive and secondary sex characteristics, such as increased body hair and a deeper voice. An excess of testosterone can cause an increase (anabolic) in muscle mass. Negative effects of testosterone ar ...
Provocative Tests of the Hypothalamic-Anterior Pituitary
... MEASUREMENT OF HORMONES IN BIOLOGICAL FLUID When hormones circulate in relatively high concentrations, they are measured biochemically, e.g. the fluorometric assay for plasma cortisol. However, most hormones, particularly the polypeptides, circulate at nanogram (10'· g) or picogram (lO-"g) levels an ...
... MEASUREMENT OF HORMONES IN BIOLOGICAL FLUID When hormones circulate in relatively high concentrations, they are measured biochemically, e.g. the fluorometric assay for plasma cortisol. However, most hormones, particularly the polypeptides, circulate at nanogram (10'· g) or picogram (lO-"g) levels an ...
Chapter 16
... and releases glucose to blood and norepinephrine) 4. Dilation of bronchioles 5. Changes in blood flow patterns leading to decreased digestive system activity and reduced ...
... and releases glucose to blood and norepinephrine) 4. Dilation of bronchioles 5. Changes in blood flow patterns leading to decreased digestive system activity and reduced ...
Primary Endocrine Organs, Tissues and Cells
... They promote the development of female secondary sexual characteristics, such as breasts, and are also involved in the thickening of the endometrium and other aspects of regulating the menstrual cycle. ...
... They promote the development of female secondary sexual characteristics, such as breasts, and are also involved in the thickening of the endometrium and other aspects of regulating the menstrual cycle. ...
Hormonal Control
... The posterior lobe of the pituitary does not synthesize hormones, but it does store and release ADH. The main function of ADH is to decrease urinary output and maintain water levels. In the absence of ADH, normal urine output of 1-2 L would increase to 25 L per day. ADH is also released if there is ...
... The posterior lobe of the pituitary does not synthesize hormones, but it does store and release ADH. The main function of ADH is to decrease urinary output and maintain water levels. In the absence of ADH, normal urine output of 1-2 L would increase to 25 L per day. ADH is also released if there is ...
ADRENAL GLAND ADRENAL INSUFFICIENCY Adrenal
... weakness, muscle cramping, paresthesias, headaches, palpitations, polyuria, and polydipsia. Screening the hypertensive patient for aldosteronism is best accomplished by measuring morning plasma aldosterone and plasma renin activity. Aldosterone is autonomously produced, and expanded intravascular vo ...
... weakness, muscle cramping, paresthesias, headaches, palpitations, polyuria, and polydipsia. Screening the hypertensive patient for aldosteronism is best accomplished by measuring morning plasma aldosterone and plasma renin activity. Aldosterone is autonomously produced, and expanded intravascular vo ...
The stress–hypothyroid connection
... Because both of these endocrine loops trace back to the pituitary and hypothalamus in the brain, and the hormones produced along these two axes interact, chances of dysregulation are higher along one axis when the other loop is overactive- or underactive. ...
... Because both of these endocrine loops trace back to the pituitary and hypothalamus in the brain, and the hormones produced along these two axes interact, chances of dysregulation are higher along one axis when the other loop is overactive- or underactive. ...