ENDOCRINE GLANDS
... Endocrine glands secrete hormones into the bloodstream. Hormones are chemical messengers traveling through the bloodstream Target cells: Bodies response to hormones are slower and longer lasting Glands: (fig. 42-3) organ that produces a secretion and released from that cell Endocrine glands: Produce ...
... Endocrine glands secrete hormones into the bloodstream. Hormones are chemical messengers traveling through the bloodstream Target cells: Bodies response to hormones are slower and longer lasting Glands: (fig. 42-3) organ that produces a secretion and released from that cell Endocrine glands: Produce ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Name 1. Gland in the brain that is the control
... 1. Gland in the brain that is the control center for all regulatory activities of the body: ____________________________ 2. Condition in which levels of thyroid hormones in the blood are very low: _________________________ __ 3. Helps regulate when you sleep at night and when you wake in the mornin ...
... 1. Gland in the brain that is the control center for all regulatory activities of the body: ____________________________ 2. Condition in which levels of thyroid hormones in the blood are very low: _________________________ __ 3. Helps regulate when you sleep at night and when you wake in the mornin ...
ESSAY QUESTIONS WITH SAMPLE ANSWERS 1. Explain why the
... watched carefully because he may pass out. Coolie has high levels of serotonin. High serotonin is related to relaxation and emotional wellness. Coolie is probably in Dr. White’s care because he feels so little anxiety he may take great risks or be involved in illegal activity that would make most ...
... watched carefully because he may pass out. Coolie has high levels of serotonin. High serotonin is related to relaxation and emotional wellness. Coolie is probably in Dr. White’s care because he feels so little anxiety he may take great risks or be involved in illegal activity that would make most ...
Aim: How does the endocrine system work to maintain homeostasis?
... controls body activities • Controls body activities through messengers (hormones) • The endocrine system is made up of glands that release their hormones into the blood stream. ...
... controls body activities • Controls body activities through messengers (hormones) • The endocrine system is made up of glands that release their hormones into the blood stream. ...
Chapter 39 - Midway ISD
... Reproductive Glands Serve two functions: To produce gametes and also to secrete sex hormones. Ovaries – produce ova (eggs), secrete estrogen and progesterone (hormones) ...
... Reproductive Glands Serve two functions: To produce gametes and also to secrete sex hormones. Ovaries – produce ova (eggs), secrete estrogen and progesterone (hormones) ...
I-Introduction
... The immune system Virtually all cells in the body that use chemicals to communicate with one another ...
... The immune system Virtually all cells in the body that use chemicals to communicate with one another ...
The Endocrine System
... estrogen and progesterone which controls breast growth, the regulation of the menstrual cycle and to monitor pregnancy. The ovaries also contain the eggs used in reproduction. In men, the reproductive organs are the testes which are located in the scrotum. These secrete androgens such as testosteron ...
... estrogen and progesterone which controls breast growth, the regulation of the menstrual cycle and to monitor pregnancy. The ovaries also contain the eggs used in reproduction. In men, the reproductive organs are the testes which are located in the scrotum. These secrete androgens such as testosteron ...
Endocrine system notes
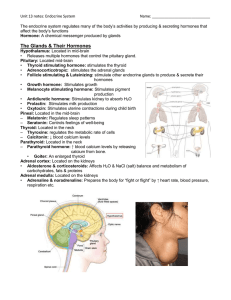
... The Glands & Their Hormones Hypothalamus: Located in mid-brain • Releases multiple hormones that control the pituitary gland. Pituitary: Located mid-brain • Thyroid stimulating hormone: stimulates the thyroid • Adrenocorticotropic: stimulates the adrenal glands • Follicle stimulating & Luteinizing: ...
... The Glands & Their Hormones Hypothalamus: Located in mid-brain • Releases multiple hormones that control the pituitary gland. Pituitary: Located mid-brain • Thyroid stimulating hormone: stimulates the thyroid • Adrenocorticotropic: stimulates the adrenal glands • Follicle stimulating & Luteinizing: ...
8.1 endocrine gland note
... _______________________rather than through a duct. e.g.: pituitary, pancreas, ovaries, testes, thyroid, adrenal Exocrine glands -secrete their products _________________________which lead directly into the external environment. e.g. sweat gland, salivary glands, mammary glands, stomach, liver, pancr ...
... _______________________rather than through a duct. e.g.: pituitary, pancreas, ovaries, testes, thyroid, adrenal Exocrine glands -secrete their products _________________________which lead directly into the external environment. e.g. sweat gland, salivary glands, mammary glands, stomach, liver, pancr ...
Chapter 18 Notes
... >>> Ductless – or tubeless – organs or groups of cells that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. ...
... >>> Ductless – or tubeless – organs or groups of cells that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. ...
I can File
... evaluate the use of hormone therapy in the treatment of humans (growth hormone and aging, anabolic steroids and human performance) explain that scientific knowledge and theories develop through hypotheses, the collection of evidence, investigation and the ability to provide explanations discus ...
... evaluate the use of hormone therapy in the treatment of humans (growth hormone and aging, anabolic steroids and human performance) explain that scientific knowledge and theories develop through hypotheses, the collection of evidence, investigation and the ability to provide explanations discus ...
Med Surg III/Endocrine power point/C. Mackey
... An adrenal gland is found on top of each kidney. Each adrenal gland has two regions that carry out separate functions! •The adrenal medulla •The adrenal cortex ...
... An adrenal gland is found on top of each kidney. Each adrenal gland has two regions that carry out separate functions! •The adrenal medulla •The adrenal cortex ...
The Endocrine System
... regulates the way cells release energy from nutrients. Too little thyroxine (hypothyroidism) causes tiredness, weight gain, constipation, and sensitivity to cold. Too much thyroxine (hyperthyroidism) causes weightloss, anxiety, diarrhea, and inability to tolerate ...
... regulates the way cells release energy from nutrients. Too little thyroxine (hypothyroidism) causes tiredness, weight gain, constipation, and sensitivity to cold. Too much thyroxine (hyperthyroidism) causes weightloss, anxiety, diarrhea, and inability to tolerate ...
Hormones Trigger Changes in Target Cells
... – Is a hormonal disease in which body cells are unable to absorb ...
... – Is a hormonal disease in which body cells are unable to absorb ...
Lesson 2.3: Chemical Communication Essential Questions
... from the blood, concentrates or alters them, and secretes them for further use in the body or for elimination from the body. A protein hormone that is produced especially by the pancreatic islets of Langerhans and that promotes an increase in the sugar content of the blood by increasing the rate of ...
... from the blood, concentrates or alters them, and secretes them for further use in the body or for elimination from the body. A protein hormone that is produced especially by the pancreatic islets of Langerhans and that promotes an increase in the sugar content of the blood by increasing the rate of ...
File
... Attached to posterior thyroid…. Produce PARATHORMONE which helps control blood calcium level, prevents hypocalcemia THYMUS…. Endocrine gland and lymphatic organ Located behind the ________, above and in front of the ______________ Begins to disappear at _________ ADRENAL GLANDS Located on to ...
... Attached to posterior thyroid…. Produce PARATHORMONE which helps control blood calcium level, prevents hypocalcemia THYMUS…. Endocrine gland and lymphatic organ Located behind the ________, above and in front of the ______________ Begins to disappear at _________ ADRENAL GLANDS Located on to ...
Filled In Endocrine System Notes
... There are two systems that regulate the body. The nervous system relays information to the body using _electrical impulses________ that travel very _quickly______, but the messages are short-lived. The endocrine system uses _hormones____, or _chemical_____ messages that travel through the _blood____ ...
... There are two systems that regulate the body. The nervous system relays information to the body using _electrical impulses________ that travel very _quickly______, but the messages are short-lived. The endocrine system uses _hormones____, or _chemical_____ messages that travel through the _blood____ ...
Name_____________________________________________
... The thymus produces the hormone ____________________________________ Thymosine is responsible for the development of _____________________________. T-cells are essential for the immune system to work properly. The thymus is present at birth, develops during childhood and then gradually disappears du ...
... The thymus produces the hormone ____________________________________ Thymosine is responsible for the development of _____________________________. T-cells are essential for the immune system to work properly. The thymus is present at birth, develops during childhood and then gradually disappears du ...
Conjoint Endocrine Laboratory, Pathology Queensland, Royal
... Conjoint Endocrine Laboratory, Pathology Queensland, Royal Brisbane and Women’s Hospital Research Foundation Clinical Research Centre A post-graduate scholarship is available in the Conjoint Endocrine Laboratory, Pathology Queensland, Royal Brisbane and Women’s Hospital Research Foundation Clinical ...
... Conjoint Endocrine Laboratory, Pathology Queensland, Royal Brisbane and Women’s Hospital Research Foundation Clinical Research Centre A post-graduate scholarship is available in the Conjoint Endocrine Laboratory, Pathology Queensland, Royal Brisbane and Women’s Hospital Research Foundation Clinical ...
The Endocrine and Reproductive System
... The Menstrual Cycle • Before an egg is released, the body prepares to have a baby. • The uterus’s wall thickens with blood in case an egg is fertilized. – If the egg is fertilized, the blood gives nutrients to the egg. – If the egg is not fertilized, the blood and egg are flushed out of the bo ...
... The Menstrual Cycle • Before an egg is released, the body prepares to have a baby. • The uterus’s wall thickens with blood in case an egg is fertilized. – If the egg is fertilized, the blood gives nutrients to the egg. – If the egg is not fertilized, the blood and egg are flushed out of the bo ...
The Endocrine System
... helps control your heart beat and breathing rate. testes: Produces male reproductive hormones like testosterone. ...
... helps control your heart beat and breathing rate. testes: Produces male reproductive hormones like testosterone. ...
Endocrine System
... Endocrine System • The endocrine system is made up of glands that release hormones into the bloodstream to control body functions such as growth, reproduction, and metabolism. ...
... Endocrine System • The endocrine system is made up of glands that release hormones into the bloodstream to control body functions such as growth, reproduction, and metabolism. ...
Intro to Endocrinology
... immediately pull your foot back. Why is it a good thing that the nervous system was in charge of responding to this stimulus rather than the endocrine? ...
... immediately pull your foot back. Why is it a good thing that the nervous system was in charge of responding to this stimulus rather than the endocrine? ...
Objective: You will be able to identify all of the glands of the
... • Read all of p. 591 • How are the functions of LH and FSH different in males and females? ...
... • Read all of p. 591 • How are the functions of LH and FSH different in males and females? ...
Endocrine disruptor

Endocrine disruptors are chemicals that, at certain doses, can interfere with the endocrine (or hormone) system in mammals. These disruptions can cause cancerous tumors, birth defects, and other developmental disorders. Any system in the body controlled by hormones can be derailed by hormone disruptors. Specifically, endocrine disruptors may be associated with the development of learning disabilities, severe attention deficit disorder, cognitive and brain development problems; deformations of the body (including limbs); breast cancer, prostate cancer, thyroid and other cancers; sexual development problems such as feminizing of males or masculinizing effects on females, etc. The critical period of development for most organisms is between the transition from a fertilized egg into a fully formed infant. As the cells begin to grow and differentiate, there are critical balances of hormones and protein changes that must occur. Therefore, a dose of disrupting chemicals may do substantial damage to a developing fetus. The same dose may not significantly affect adult mothers.There has been controversy over endocrine disruptors, with some groups calling for swift action by regulators to remove them from the market, and regulators and other scientists calling for further study. Some endocrine disruptors have been identified and removed from the market (for example, a drug called diethylstilbestrol), but it is uncertain whether some endocrine disruptors on the market actually harm humans and wildlife at the doses to which wildlife and humans are exposed. Additionally, a key scientific paper, published in the journal Science, which helped launch the movement of those opposed to endocrine disruptors, was retracted and its author found to have committed scientific misconduct.Found in many household and industrial products, endocrine disruptors are substances that ""interfere with the synthesis, secretion, transport, binding, action, or elimination of natural hormones in the body that are responsible for development, behavior, fertility, and maintenance of homeostasis (normal cell metabolism)."" They are sometimes also referred to as hormonally active agents, endocrine disrupting chemicals, or endocrine disrupting compounds (EDCs).Studies in cells and laboratory animals have shown that EDs can cause adverse biological effects in animals, and low-level exposures may also cause similar effects in human beings.The term endocrine disruptor is often used as synonym for xenohormone although the latter can mean any naturally occurring or artificially produced compound showing hormone-like properties (usually binding to certain hormonal receptors). EDCs in the environment may also be related to reproductive and infertility problems in wildlife and bans and restrictions on their use has been associated with a reduction in health problems and the recovery of some wildlife populations.