Mammalian Physiology Organization of the Endocrine System
... Means of signaling secretion Secretory cells Target organ – capable of responding to signal Mechanism for shutting off secretion ...
... Means of signaling secretion Secretory cells Target organ – capable of responding to signal Mechanism for shutting off secretion ...
Serum total thyroxine and thyroid stimulating hormone
... total thyroxine (TT4) or serum free thyroxine (FT4) and serum thyroid stimulating hormone (thyrotropin) (TSH) for routine screening of dogs for hypothyroidism. Measurement of low TT4 or FT4 together with an increased concentration of TSH has high specificity for diagnosis of hypothyroidism (Peterson ...
... total thyroxine (TT4) or serum free thyroxine (FT4) and serum thyroid stimulating hormone (thyrotropin) (TSH) for routine screening of dogs for hypothyroidism. Measurement of low TT4 or FT4 together with an increased concentration of TSH has high specificity for diagnosis of hypothyroidism (Peterson ...
hormone to prevent neonatal respiratory distress
... TSH reponse to maternal administration of TRH was recently evaluated in utero between 25 and 37 weeks' gestation; this study demonstrated a striking fetal TSH response of up to 100 mU/l within 10-30 minutes from the intravenous TRH injection.38 It is noteworthy that the TSH response of the third tri ...
... TSH reponse to maternal administration of TRH was recently evaluated in utero between 25 and 37 weeks' gestation; this study demonstrated a striking fetal TSH response of up to 100 mU/l within 10-30 minutes from the intravenous TRH injection.38 It is noteworthy that the TSH response of the third tri ...
Hormone Function
... Stimulate vaginal secretion (acid & very stringy – test for ovulation) Skeletal maintenance Effects on brain and behaviour ...
... Stimulate vaginal secretion (acid & very stringy – test for ovulation) Skeletal maintenance Effects on brain and behaviour ...
Ch 5 Cell Signaling and the Hormonal Responses to Exercise
... Influences on Growth Hormone Release 1. Stimulates release of insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) -IGF-1 in muscle responsible for muscle growth 2. Essential growth of all tissues -Amino Acid uptake and protein synthesis ...
... Influences on Growth Hormone Release 1. Stimulates release of insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) -IGF-1 in muscle responsible for muscle growth 2. Essential growth of all tissues -Amino Acid uptake and protein synthesis ...
Hormones-Receptors
... Learning Objectives: (1) Describe the structure of the hypothalamus and pituitary and their vascularization, (2) Explain the functional relationship between the hypothalamus and the posterior pituitary, (3) List the major stimuli for the release of anti-diuretic hormone and oxytocin, (4) Explain the ...
... Learning Objectives: (1) Describe the structure of the hypothalamus and pituitary and their vascularization, (2) Explain the functional relationship between the hypothalamus and the posterior pituitary, (3) List the major stimuli for the release of anti-diuretic hormone and oxytocin, (4) Explain the ...
chemical signals in animals
... through ducts to specific locations inside and outside the body. ...
... through ducts to specific locations inside and outside the body. ...
18-2 Hormones
... • Most are synthesized as prohormones • Inactive molecules converted to active hormones before or after they are secreted ...
... • Most are synthesized as prohormones • Inactive molecules converted to active hormones before or after they are secreted ...
Anti cancer effect of Gingerol and Ginger extract on Ethylene
... The thyroid gland is capable of meeting physiologic demands for T4 and T3 up to a point. However, beyond that point, continuous stimulation of the thyroid may result in changes that could eventually lead to disease, including neoplasia. Persistent elevation of TSH levels stimulates the thyroid gland ...
... The thyroid gland is capable of meeting physiologic demands for T4 and T3 up to a point. However, beyond that point, continuous stimulation of the thyroid may result in changes that could eventually lead to disease, including neoplasia. Persistent elevation of TSH levels stimulates the thyroid gland ...
Chapter 15
... Describe the signs such as an increased blood glucose level and glucose in urine, and the treatment of diabetes mellitus using ...
... Describe the signs such as an increased blood glucose level and glucose in urine, and the treatment of diabetes mellitus using ...
Endocrine Test - The Science of Payne
... 22. Glands that release their secretion into ducts leading to a body surface are called _______________. 23. The central portion of the adrenal gland is the adrenal ____________. 24. A group of lipids called __________ have powerful, regulating effects on a variety of tissues. 25. The hormone that s ...
... 22. Glands that release their secretion into ducts leading to a body surface are called _______________. 23. The central portion of the adrenal gland is the adrenal ____________. 24. A group of lipids called __________ have powerful, regulating effects on a variety of tissues. 25. The hormone that s ...
disorders of the thyroid gland in infancy, childhood and adolescence
... activation and inactivation of thyroid hormone. All three are coordinately regulated during gestation and function to closely regulate the supply of T3 to developing tissues while at the same time protecting the fetus against the effects of excess thyroid hormone. The physiological rationale for the ...
... activation and inactivation of thyroid hormone. All three are coordinately regulated during gestation and function to closely regulate the supply of T3 to developing tissues while at the same time protecting the fetus against the effects of excess thyroid hormone. The physiological rationale for the ...
CHAPTER 36
... receptors that recognize the hormone. Those receptors are coupled to cellular mechanisms that produce the physiologic response. The responsiveness of a target tissue to a hormone is expressed in the dose-response relationship in which the magnitude of response is correlated with hormone concentratio ...
... receptors that recognize the hormone. Those receptors are coupled to cellular mechanisms that produce the physiologic response. The responsiveness of a target tissue to a hormone is expressed in the dose-response relationship in which the magnitude of response is correlated with hormone concentratio ...
Clinical practice guidelines for the management of hypothyroidism
... Primary overt hypothyroidism (OH) refers to reduced thyroid hormone production, which causes an increase in TSH levels. Decreased thyroid secretion can also be a result of reduced stimulation of the thyroid gland due to decreased thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) or TSH action. Hypothyroidism can ...
... Primary overt hypothyroidism (OH) refers to reduced thyroid hormone production, which causes an increase in TSH levels. Decreased thyroid secretion can also be a result of reduced stimulation of the thyroid gland due to decreased thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) or TSH action. Hypothyroidism can ...
Endocrine System - HCC Learning Web
... A hormone stimulates another endocrine gland to make its hormones Example: Hypothalamus makes thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH*) Æ TRH stimulates anterior pituitary to make thyrotropin Æ thyrotropin* stimulates thyroid gland to make thyroid hormones * TRH and thyrotropin are called tropic hormones ...
... A hormone stimulates another endocrine gland to make its hormones Example: Hypothalamus makes thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH*) Æ TRH stimulates anterior pituitary to make thyrotropin Æ thyrotropin* stimulates thyroid gland to make thyroid hormones * TRH and thyrotropin are called tropic hormones ...
The Endocrine System - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... Wingerd, In-Class Activities to Accompany Medical Terminology Complete!, 2nd Edition ...
... Wingerd, In-Class Activities to Accompany Medical Terminology Complete!, 2nd Edition ...
Effects of high-altitude hypoxia on the hormonal response to
... explained by this cold influence (16). T3 and T4 were elevated on exposure to simulated hypoxia at ⫹22 to ⫹24°C ambient temperature, demonstrating a thyroid hormonal increase independent of cold exposure (39). The subjects in our study experienced only intermittent and moderate cold exposure, which ...
... explained by this cold influence (16). T3 and T4 were elevated on exposure to simulated hypoxia at ⫹22 to ⫹24°C ambient temperature, demonstrating a thyroid hormonal increase independent of cold exposure (39). The subjects in our study experienced only intermittent and moderate cold exposure, which ...
Ch 13 MT and Ch11 BS Endocrine System
... There are over 11,000 new cases of thyroid cancer each year in the United States. Females are more likely to have thyroid cancer at a ratio of three to one. Thyroid cancer can occur in any age group, although it is most common after age 30 and its aggressiveness increases significantly in older pati ...
... There are over 11,000 new cases of thyroid cancer each year in the United States. Females are more likely to have thyroid cancer at a ratio of three to one. Thyroid cancer can occur in any age group, although it is most common after age 30 and its aggressiveness increases significantly in older pati ...
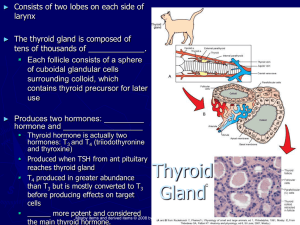
Thyroid Gland
... Produced by C cells (parafollicular cells) located between thyroid follicles Maintains homeostasis of blood _______________ levels Calcium is necessary for muscle contraction, blood clotting, milk secretion, and formation/maintenance of skeleton. Calcium levels must be kept within a narrow range t ...
... Produced by C cells (parafollicular cells) located between thyroid follicles Maintains homeostasis of blood _______________ levels Calcium is necessary for muscle contraction, blood clotting, milk secretion, and formation/maintenance of skeleton. Calcium levels must be kept within a narrow range t ...
Endocrine System
... Anterior pituitary hormones travel to target glands, such as the thyroid gland, to prompt the release of a particular hormone, such as thyroid hormone ...
... Anterior pituitary hormones travel to target glands, such as the thyroid gland, to prompt the release of a particular hormone, such as thyroid hormone ...
Growth Hormone
... (6) AIDS Wasting Syndrome Individual has had more than 10% baseline weight loss that cannot be explained by concurrent illness other than HIV infection Individual will simultaneously be treated with antiviral therapy Other: (7) Other Use(s) (Please submit all supporting documents including labs, pro ...
... (6) AIDS Wasting Syndrome Individual has had more than 10% baseline weight loss that cannot be explained by concurrent illness other than HIV infection Individual will simultaneously be treated with antiviral therapy Other: (7) Other Use(s) (Please submit all supporting documents including labs, pro ...
Endocrine System
... – What stimulates the release of medullary hormones (hormones released from the adrenal medulla). – What causes the release of hormones released from the Adrenal cortex (aldosterone, cortisol and sex hormones). – Whats the function of aldosterone, cortisol and how are the blood concentration regulat ...
... – What stimulates the release of medullary hormones (hormones released from the adrenal medulla). – What causes the release of hormones released from the Adrenal cortex (aldosterone, cortisol and sex hormones). – Whats the function of aldosterone, cortisol and how are the blood concentration regulat ...
Maternal thyroid function during pregnancy Effects on
... maternal thyroid function and antibody status in the Northern Finland Birth Cohort 1986 was analyzed using early pregnancy serum samples. The impact of long-term storage on the stability of thyroid hormones and antibodies was studied and while TSH and thyroid hormone levels were not affected by stor ...
... maternal thyroid function and antibody status in the Northern Finland Birth Cohort 1986 was analyzed using early pregnancy serum samples. The impact of long-term storage on the stability of thyroid hormones and antibodies was studied and while TSH and thyroid hormone levels were not affected by stor ...
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, also known as over active thyroid and hyperthyreosis, is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less in the old and during pregnancy. An uncommon complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature and often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of case of hyperthyroidism in the United States. Other causes include multinodular goiter, toxic adenoma, inflammation of the thyroid, eating too much iodine, and too much synthetic thyroid hormone. A less common cause is a pituitary adenoma. The diagnosis may be suspected based on signs and symptoms and then confirmed with blood tests. Typically blood tests show a low thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and raised T3 or T4. Radioiodine uptake by the thyroid, thyroid scan, and TSI antibodies may help determine the cause.Treatment depends partly on the cause and severity of disease. There are three main treatment options: radioiodine therapy, medications, and thyroid surgery. Radioiodine therapy involves taking iodine-131 by mouth which is then concentrated in and destroys the thyroid over weeks to months. The resulting hypothyroidism is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone. Medications such as beta blockers may control the symptoms and anti-thyroid medications such as methimazole may temporarily help people while other treatments are having effect. Surgery to remove the thyroid is another option. This may be used in those with very large thyroids or when cancer is a concern. In the United States hyperthyroidism affects about 1.2% of the population. It occurs between two and ten times more often in women. Onset is commonly between 20 and 50 years of age. Overall the disease is more common in those over the age of 60 years.